Method for extraction of ultra-low molecular weight heparin sodium by nadroparin calcium waste
A technology of nadroparin calcium and heparin sodium, which is applied in the field of producing ultra-low molecular weight heparin, can solve the problems of low raw material utilization rate of heparin sodium, increase of production cost, loss of heparin sodium, etc., and achieve high synthesis difficulty, high cost and high yield low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
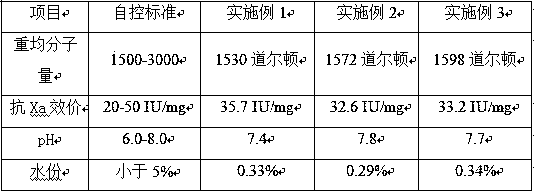
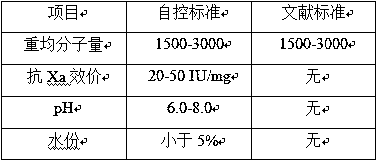
[0026] Cleavage: Weigh 1 kg of heparin sodium, dissolve it with purified water, adjust the pH to 1.5, add 20 g of sodium nitrite, stir and react for 0.5 hours, during which the pH is maintained at 1.5, and the starch-KI reagent is used to judge the cleavage at the end of the reaction. When the starch-KI reagent is negative, the cleavage reaction ends. get lysate
[0027] Reduction: Adjust the pH of the lysing liquid to neutral, add 10 g of sodium borohydride, and stir and react at 20°C for 20 hours; adjust the pH of the liquid to 2.5, and stir for 2 hours. Get the recovery solution.
[0028] 1st classification: Add 3 times the amount of ethanol to the reducing drug solution, add ethanol and stir evenly, a precipitate will be obtained, separate the supernatant from the precipitate, and discard the separated supernatant.
[0029] Secondary fractionation: dissolve the precipitate with purified water, adjust the pH to 5.0, add 300 g of sodium chloride and dissolve. Add 1 times ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Cleavage: Weigh 1 kg of heparin sodium, dissolve it with purified water, adjust the pH to 3.0, add 30 g of sodium nitrite, stir and react for 0.7 hours, during which the pH is maintained at 3.0, and the starch-KI reagent is used to judge the cleavage at the end of the reaction. When the starch-KI reagent is negative, the cleavage reaction ends. get lysate
[0036] Reduction: adjust the pH of the lysing liquid to neutral, add 20 g of sodium borohydride, stir and react at 30°C for 22 hours; adjust the pH of the liquid to 2.8, and stir for 2 hours. Get the recovery solution.
[0037] 1st classification: Add 3 times the amount of ethanol to the reducing drug solution, add ethanol and stir evenly, a precipitate will be obtained, separate the supernatant from the precipitate, and discard the separated supernatant.
[0038] Secondary fractionation: dissolve the precipitate with purified water, adjust the pH to 5.5, add 400g of sodium chloride and dissolve. Add 1 times the a...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Cleavage: Weigh 1 kg of heparin sodium, dissolve it with purified water, adjust the pH to 4.0, add 40 g of sodium nitrite, stir and react for 1.0 hour, during which the pH is maintained at 4.0, and the starch-KI reagent is used to judge the cleavage at the end of the reaction. When the starch-KI reagent is negative, the cleavage reaction ends. get lysate
[0045] Reduction: Adjust the pH of the lysing liquid to neutral, add 30 g of sodium borohydride, and stir and react at 40°C for 24 hours; adjust the pH of the liquid to 3.0, and stir for 2 hours. Get the recovery solution.
[0046] 1st classification: Add 3 times the amount of ethanol to the reducing drug solution, add ethanol and stir evenly, a precipitate will be obtained, separate the supernatant from the precipitate, and discard the separated supernatant.
[0047] Secondary fractionation: dissolve the precipitate with purified water, adjust the pH to 6.0, add 500 g of sodium chloride and dissolve. Add 1 times t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com