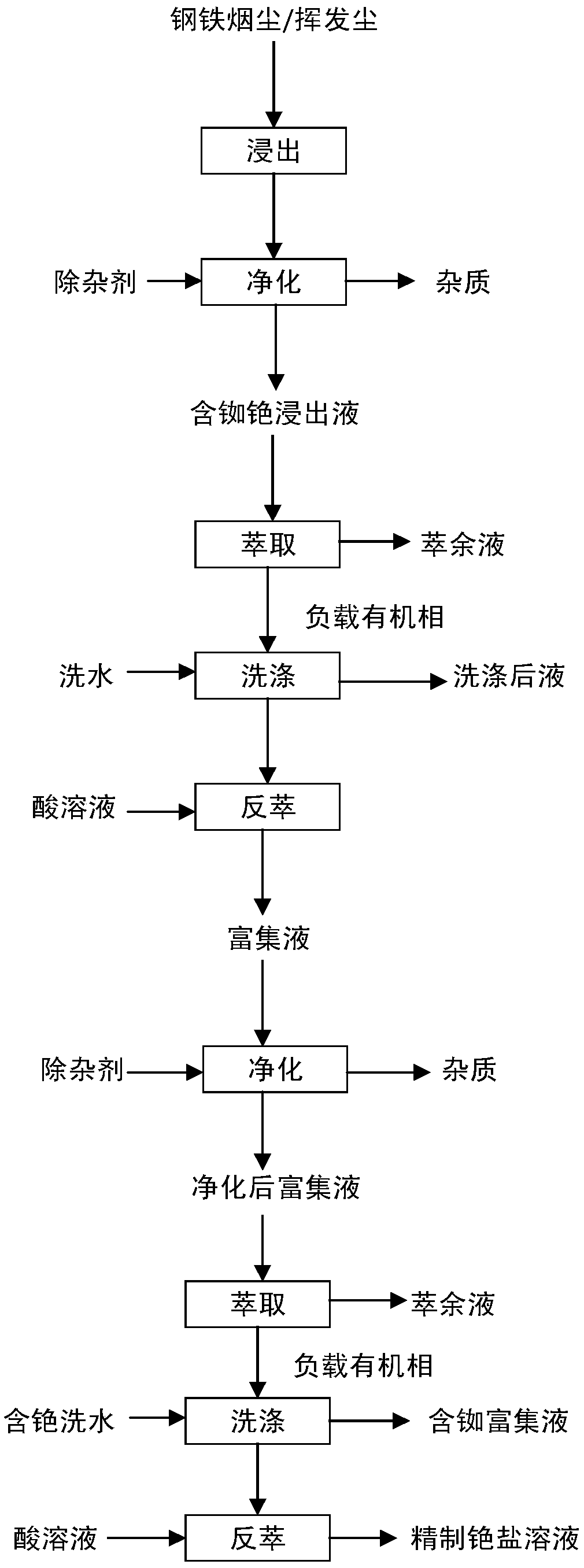
Method for extracting rubidium and cesium from steel soot and/or volatile dust
A soot and steel technology, applied in the field of rubidium and cesium extraction, can solve the problems of high cost, high toxicity of iodine chloride, complex process, etc., achieve efficient recovery and high efficiency, increase the amount of rubidium and cesium resources, and avoid the effect of impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0070] The method that the present invention extracts rubidium and cesium is as follows:
[0071] (1) Add water to the iron and steel dust containing 0.05% rubidium and 0.02% cesium and stir to leach, filter after 10 minutes to obtain a filtrate, continue to add new iron and steel dust to the filtrate and stir to leach. Repeat the above operation (countercurrent leaching) until the cesium content in the leaching solution is not less than 0.2g / L. Add sodium bicarbonate solution to the leaching solution until no precipitation occurs, filter to remove the precipitation, then adjust the pH of the leaching solution to 14 with sodium hydroxide solution, and filter again to make heavy metals and calcium and magnesium impurities form carbonates and hydroxides. The solid was separated to obtain a leach solution containing rubidium and cesium. After analysis, the content of rubidium in the leach solution containing rubidium and cesium was 0.48g / L, and the content of cesium was 0.2g / L. ...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The method that the present invention extracts rubidium and cesium is as follows:
[0080] (1) After the iron and steel dust is volatilized by the rotary kiln, the secondary zinc oxide powder is obtained. After leaching with aqueous sodium carbonate solution, an aqueous solution containing 0.98g / L of rubidium and 0.55g / L of cesium is obtained, in which the content of lead is 4.5mg / L and the content of cadmium is 7.6 mg / L, thallium content 1.8mg / L, zinc content 205mg / L, calcium content 20mg / L, magnesium content 34mg / L. Sodium sulfide solution was added to this solution to precipitate the heavy metals. After the precipitation is separated, a leaching solution containing rubidium and cesium is obtained. After analysis, the content of rubidium in the leach solution containing rubidium and cesium was 0.92g / L, and the content of cesium was 0.52g / L.
[0081] (2) Adjust the pH of the leaching solution containing rubidium and cesium to 12, and extract with BAMBP as the extract...
Embodiment 3
[0088] The method that the present invention extracts rubidium and cesium is as follows:
[0089] (1) The raw material is the soluble salt enrichment obtained by evaporating to dryness after washing water of subzinc oxide (volatile dust) with calcium chloride to remove sulfate radicals and fluoride ions. After analysis, it contains 0.8% rubidium and 0.13% cesium. Add 1% sodium carbonate aqueous solution to the soluble salt enrichment, stir and leach, and filter after 30 minutes to obtain the filtrate. After analysis, the content of rubidium in the leachate containing rubidium and cesium is 3.1g / L, and the content of cesium is 0.51g / L. Among them, the sodium carbonate aqueous solution has both leaching and impurity removal functions.
[0090] (2) Adjust the pH of the leachate containing rubidium and cesium to 14, extract with t-BAMBP as the extractant and kerosene as the diluent, and obtain the raffinate and the loaded organic phase. After the loaded organic phase was washed w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com