Method for building non-human primate model with compulsive ritualistic behaviors
A primate and behavioral technology, applied in the field of zoology, can solve the problems of animals lacking language expression ability and difficulty in establishing primate animal models
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
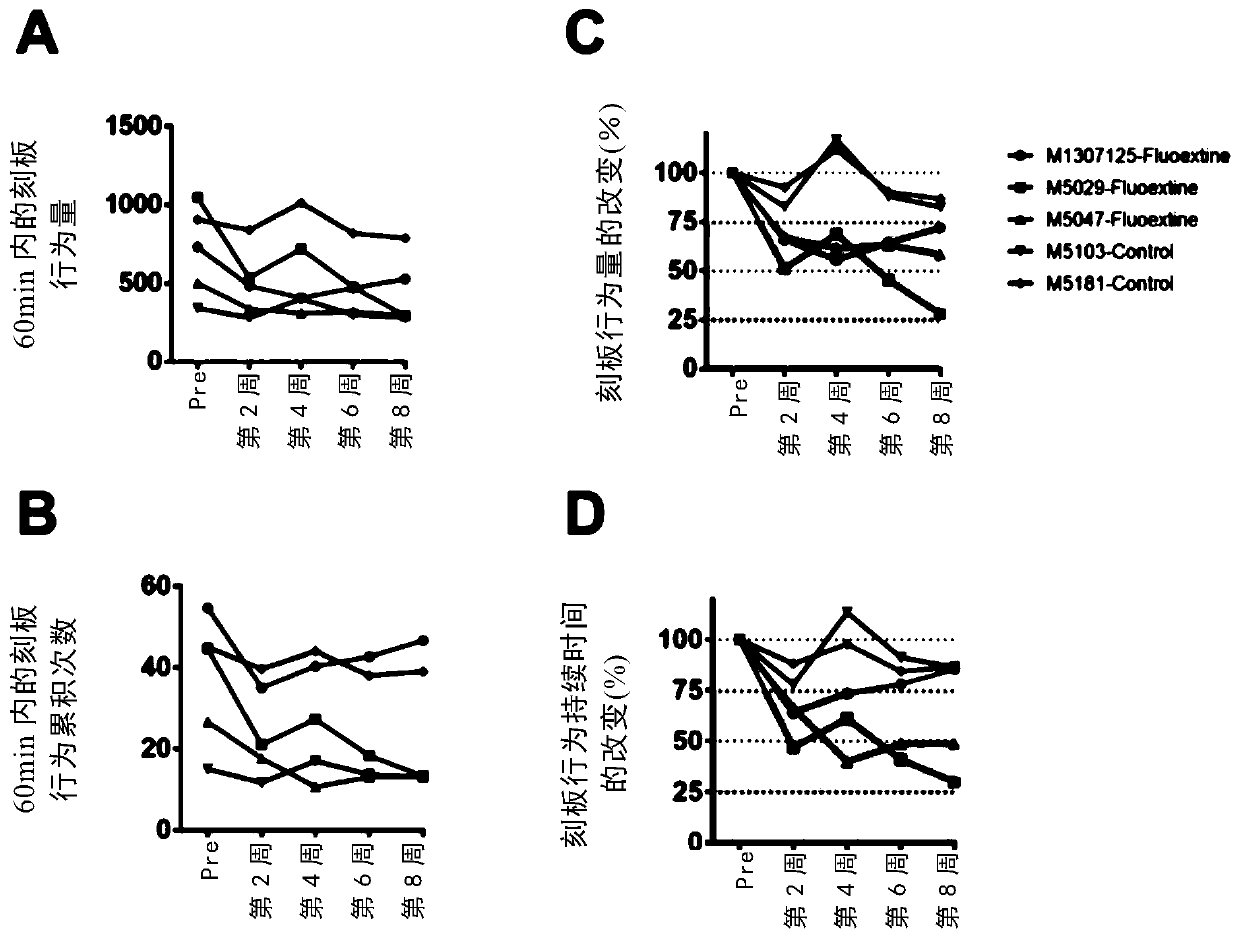
[0069] Embodiment 1. Feasibility observation of stereotyped behavior induced by group or individual behavior
[0070] In this example, the monkeys were bred periodically to induce stereotyped behavior. The "staged" refers to the feeding time is greater than or equal to 4 weeks. The number of experimental monkeys was 100. Install surveillance video equipment and set up surveillance.
[0071] Set up multiple breeding cages, and carry out "single / cage" and "multiple (2-4) / cage" feeding of healthy experimental monkeys. Among them, when the feeding method of "single bird / cage", the cage is 800 × 800 × 800 (length × width × height) mm; when the feeding method of "2 animals / cage", the cage is 1600 × 800 × 800 (length × Width × height) mm; when the feeding method of "3 birds / cage", the cage is 2400×800×800 (length×width×height) mm; when the feeding method of "4 animals / cage", the cage is 1600×1600× 800 (length x width x height) mm.
[0072] Put monkeys weighing 4-7kg into the cag...
Embodiment 2
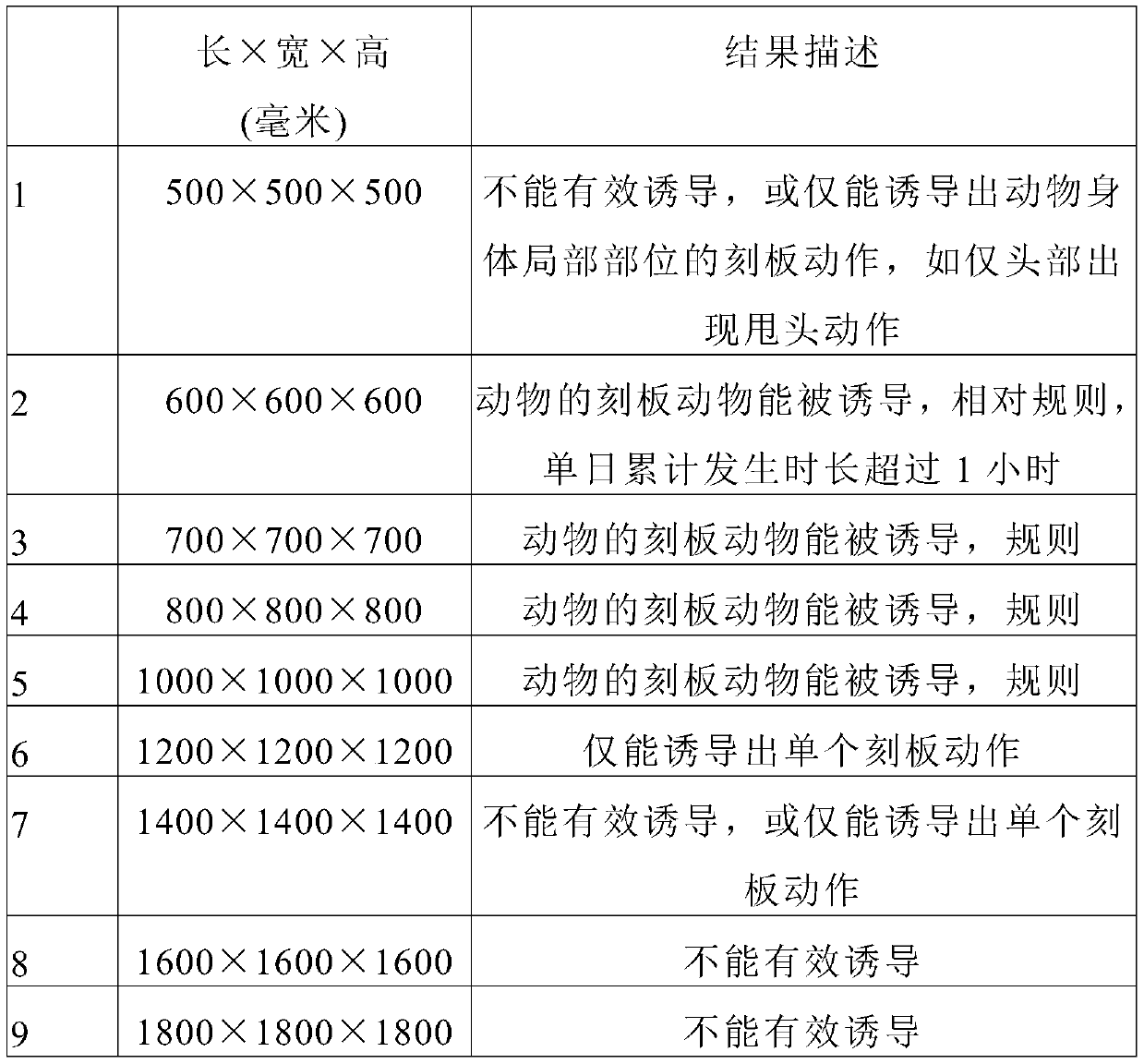
[0075] Embodiment 2, the selection of breeding cage
[0076] In this example, monkeys were bred periodically to induce stereotyped behavior. The "staged" refers to the feeding time is greater than or equal to 4 weeks. The number of experimental monkeys was 100. Install surveillance video equipment and set up surveillance.
[0077] Healthy experimental monkeys were reared in a single cage, and various cages were set up with different sizes, as shown in Table 2, to observe the best cages for inducing stereotyped behaviors or ritual-like actions. Multiple breeding cages can be placed in the same or different rooms, and about 10 cages are placed in each room in this experiment.
[0078] Table 1. Design of breeding cages
[0079]
[0080] Put monkeys weighing 4-7kg into the cages designed in Table 1, and put only one monkey in each cage, and observe the monkeys' stereotyped behavior or ritual-like movements.
[0081] Observation time: Analyze daily 8:00-8:10, 9:00-9:10, 10:...
Embodiment 3
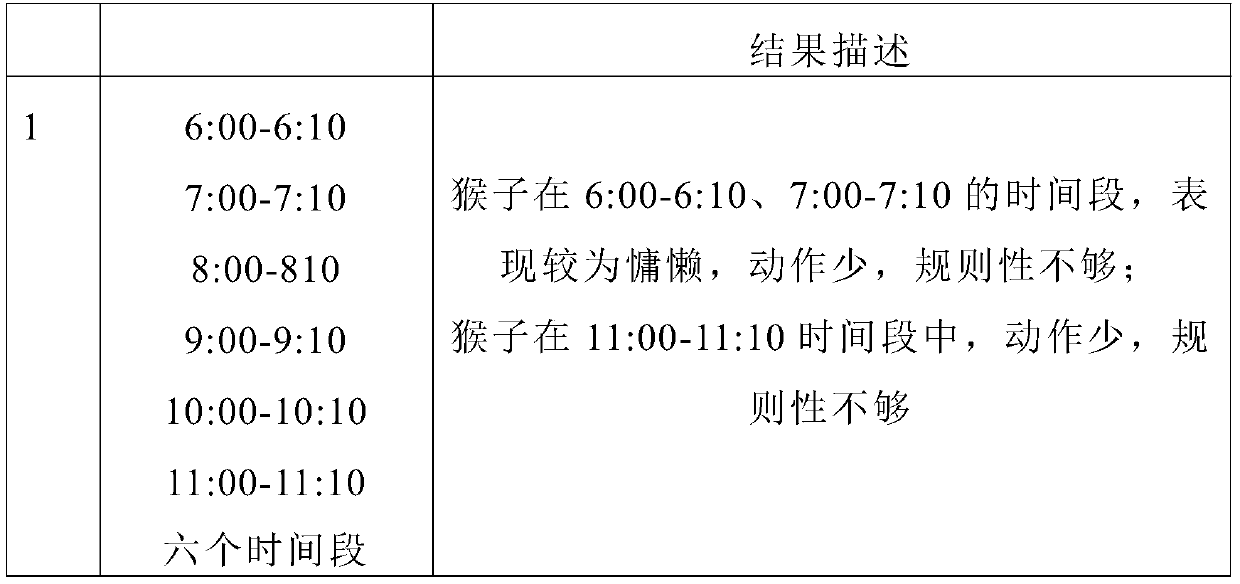
[0084] Embodiment 3, the selection of observation time
[0085] Raise healthy experimental monkeys in a single cage, set up multiple breeding cages, and observe the behavioral habits of the monkeys to determine the best time to observe stereotyped behaviors. Multiple breeding cages can be placed in the same or different rooms, and about 10 cages are placed in each room in this experiment.
[0086]The size of the breeding cage is 800×800×800 mm. Put monkeys with a weight of 4-7kg into the cages designed in Table 1, and put only one monkey in each cage, and observe the behavioral habits of the monkeys.
[0087] Analysis of the first time and last time of daily stereotyped behavior: analysis of 14 consecutive days, the time when each experimental monkey first appeared stereotyped behavior and the time when the last time stereotyped behavior occurred in a single day. Each experimental monkey has three meals a day, and whether there are stereotyped behaviors or ritual-like action...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com