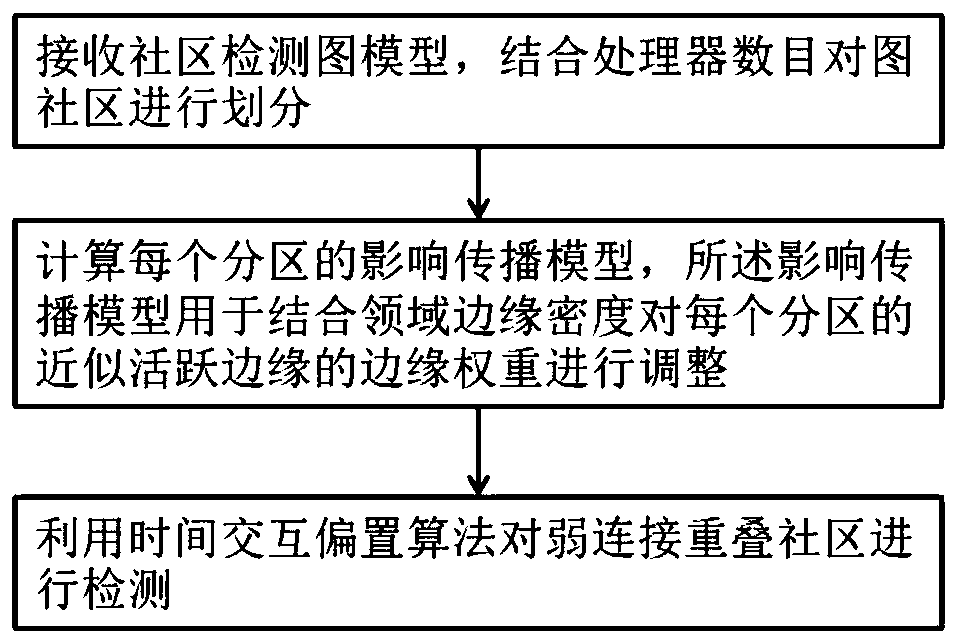
Method for detecting weak connection overlapping communities
A detection method and overlapping community technology, applied in the field of community detection, can solve the problems of not sharing and interacting, and achieve good overlapping community detection performance, strong recognition performance, and improved efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
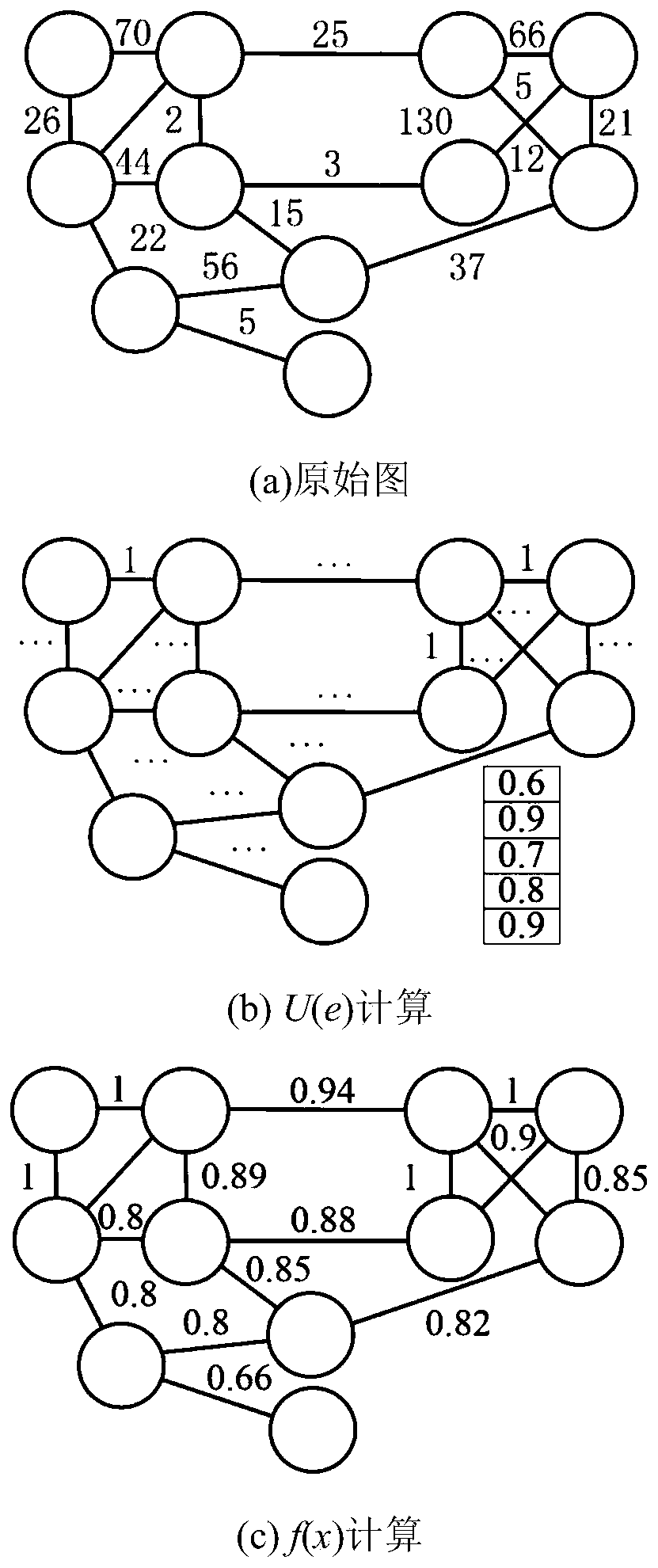
[0086] Example 1: Consider figure 2 A specific example is shown in . exist figure 2 The original weighted graph is given in a. With N(e), the first step redefines the weights from 0 to 1. When executing formula (3) , the result is stored in a hash table, such as figure 2 as shown in b. Some details are omitted here to avoid confusion. Finally, we use a hash table to calculate the final weight of each edge, as in figure 2 As shown in c, it uses f(e) for calculation. In the present invention, considering the basic definition of k-communities can be used to detect overlapping communities.
[0087] Definition 3: (Active Bias Density) The density indicator of an active bias community can be calculated as follows:
[0088] ρ(C)=∑ e∈C f(e) / |C| (4)
[0089] It is the sum of biases within the community divided by the size |C| of the community. The quality of a community can be assessed based on a threshold limiting the community. Therefore, community discovery is perf...
example 2
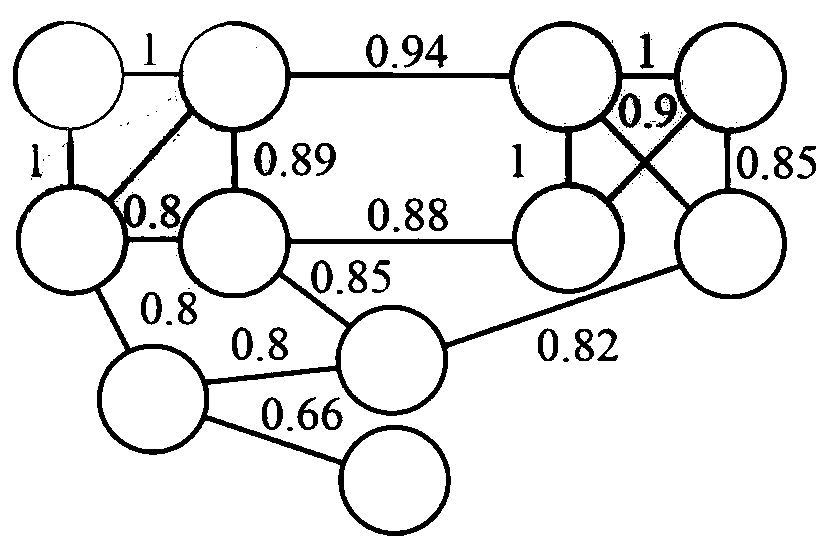
[0090] Example 2: Continue to consider image 3 The example shown, now has a refactored weighted graph. Then, we find all the communities in the graph and use formula (5) to calculate their bias density values, such as image 3 shown. Then, the bias density value of PCs is calculated using formula (4). PCs form a community only if their bias density score is higher than that of each community; otherwise, each cluster is itself a community. figure 2 Two cases are given: the two PCs on the left have smaller density values when combined, while the right part is the contradictory case. The shade of color can represent its density value.
[0091] Question 2. Community-based graph partitioning problem
[0092] The second constraint in the above problem is to balance the partitions on the processors and ensure that each processor has an acceptable amount of data to process. The complexity of solving this problem is NP-hard, and heuristic algorithms can be used to solve the p...
example 3
[0100] Example 3: Consider something like Figure 4 The example shown in a, in order to segment this graph, we first find the communities, and then find the PCs, where the PCs see Figure 4 b is shown by the dotted line. Assuming that the number of processors is P=2, then we need two partitions, one for each processor. The problem is how to divide the three PCs into two partitions as evenly as possible. For this, the objective function J is calculated here. PC first 1 assigned to partition 1, the PC 2 assigned to partition 2, while for PC 3 The distribution of will be designed according to the value of the objective function J.
[0101] The result is that when adding PC 3 to the PC in partition 1 1 When , the calculation result of the objective function J is 54. When adding a PC 3 to the PC in partition 2 2 , the calculation result of the objective function J is 44. Based on calculated results, PC 3 The partition method of will take the latter case and assign it t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com