An Algorithm for Transforming Nodal Loads Between Grids of Different Engineering Physics Models
A technology of node load and engineering physics, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, instrumentation, geometric CAD, etc., to achieve the effect of improving adjustability, improving computing efficiency, and improving algorithm accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
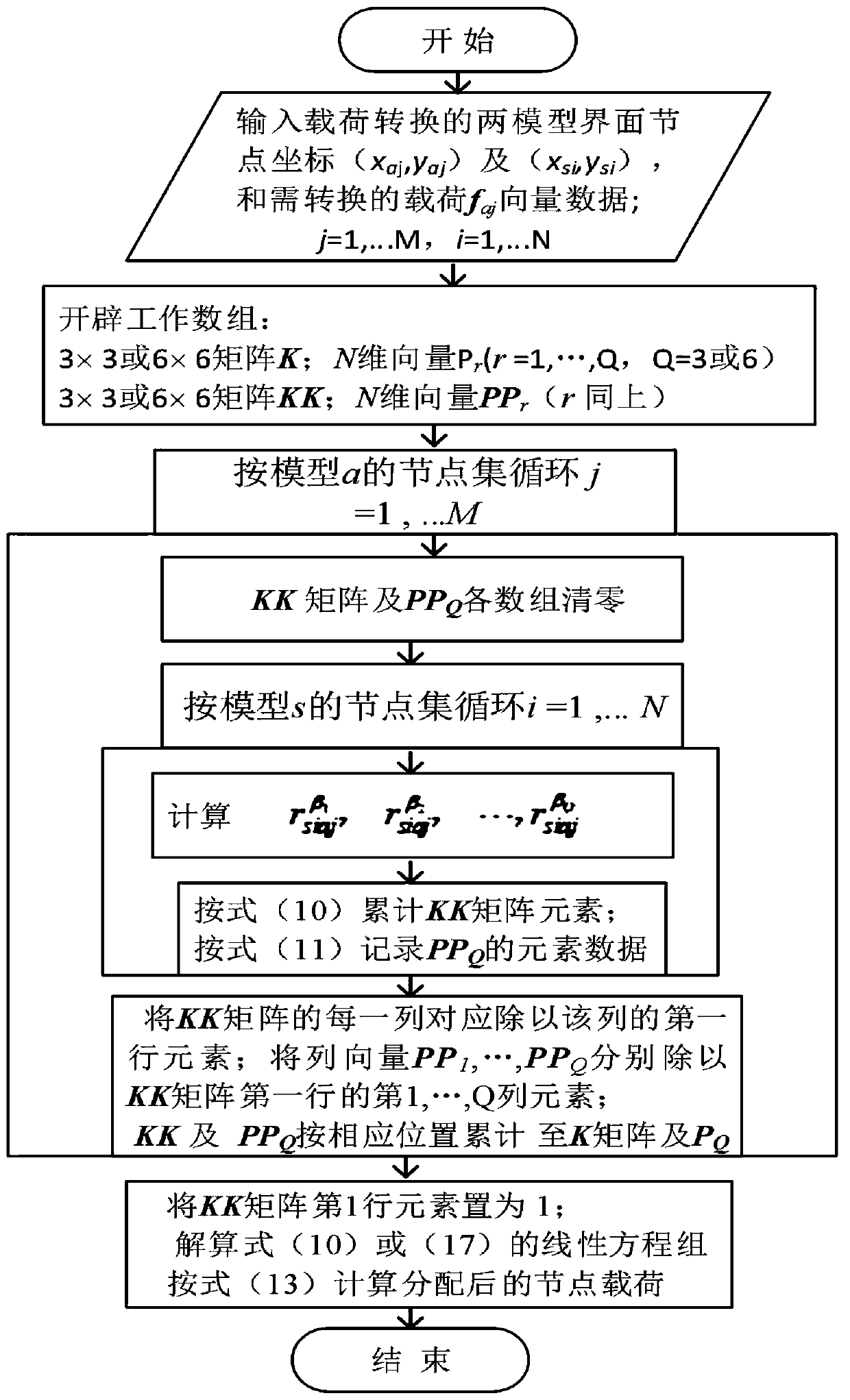
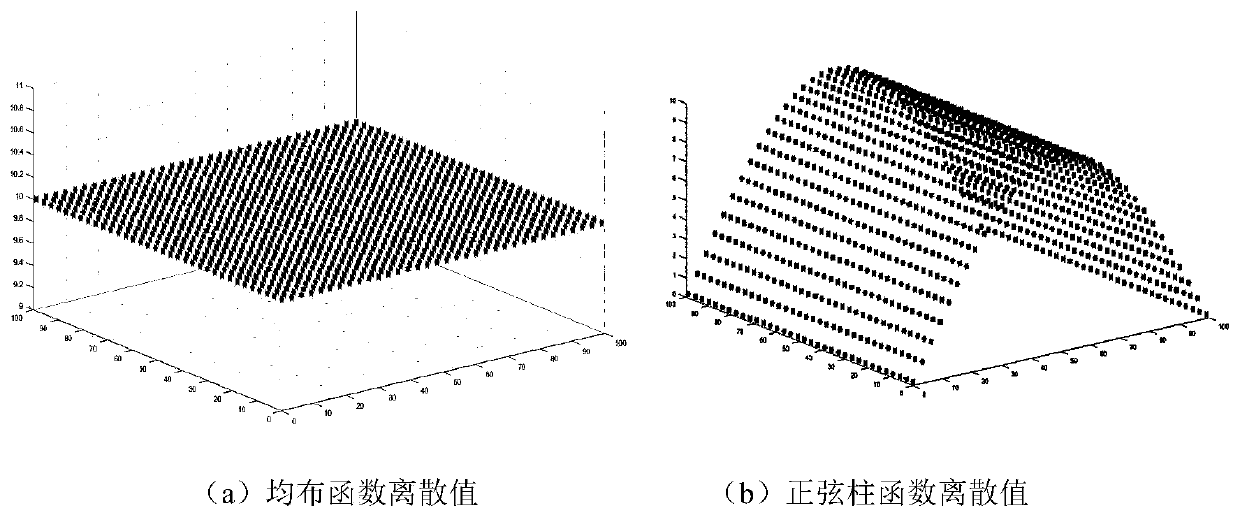
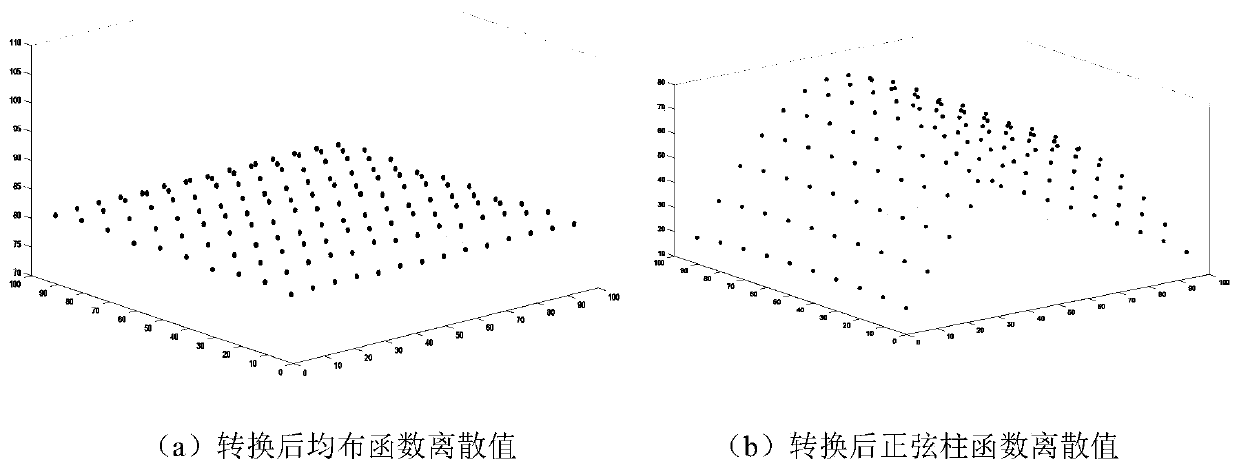
[0128] In this embodiment, there are two forms of node load distribution on regular plane grids, namely, uniform distribution and sinusoidal distribution. The nodes of the fine grid of model a are converted to the centroid points of the coarse grid of model s, and three constraints are adopted. The load-independent transformation algorithm implementation of the equations was performed in order to test the basic capabilities of the algorithm of the present invention. The specific process includes the following steps:
[0129] Step S11, set up two kinds of grid node coordinates on a 100 * 100 plane with Matlab software: one is the node coordinates (x aj ,y aj )j=1,...,34; the other is the 15×11 rectangular grid s node coordinates (x sk ,y sl ), k=1,...,15; l=1,...,11. Make two kinds of function values on the grid a: one is a function with a uniform value equal to 10; the other is to calculate the node function value according to the sinusoidal column function 10×sin(π·x / 10...
Embodiment 2
[0134] The present embodiment is the configuration of the right half wing of an unmanned aerial vehicle, and the plane view of the wing is as Figure 4shown. The analysis task is to convert the nodal load data calculated by computational fluid dynamics CFD on the wing object surface to the grid centroid point of the coarse grid used for structural analysis. The radial basis interpolation function RBF point-by-point quasi-interpolation distribution algorithm in the literature is adopted, and the 3-constraint equation independent load conversion algorithm and the 6-constraint equation independent load conversion algorithm of the present invention are used to implement the load distribution calculation of this example respectively, and adopt the present invention The LAC index given in step 7 evaluates the distribution characteristics of its distributed load.
[0135] Step S21, using Matlab software to design a software program according to the radial basis interpolation functio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com