Plants with increased photorespiration efficiency
A plant and glycolic acid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, transferase, etc., can solve the problems of no proven effectiveness and no attempt to fully optimize farmers' field photorespiration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0103] Example 1: Materials and methods
[0104] Plant material and growing conditions
[0105] Arabidopsis Columbia (Col-0) was used as wild type reference. Salk_03569C (plgg1-1), CS859747 (bass6-1) and Salk_052903C (bass6-2) were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (abrc.osu.edu). Plants at elevated (2000ppm CO 2 ) or ambient (400ppm CO 2 ) in an 8-hour light / 16-hour dark cycle (22°C / 18°C), at 250 μmol·m -2 ·s -1 Growth was performed in a growth chamber (Conviron, USA) using LC1 Sunshine Mix at PAR and 65% relative humidity (RH).
[0106] Chlorophyll fluorescence measurement
[0107] Arabidopsis plants grown in ambient air conditions and moved to low CO 2 Conditions were kept in sealed transparent plastic containers under constant light for 24 hours, similar to (Badger et al., 2009) followed by chlorophyll fluorescence measurements. Chlorophyll fluorescence measurements were performed as previously described (Oxborough and Baker, Plant, Cell & En...
Embodiment 2
[0132] Example 2: Analysis of Arabidopsis bass6 mutant phenotype
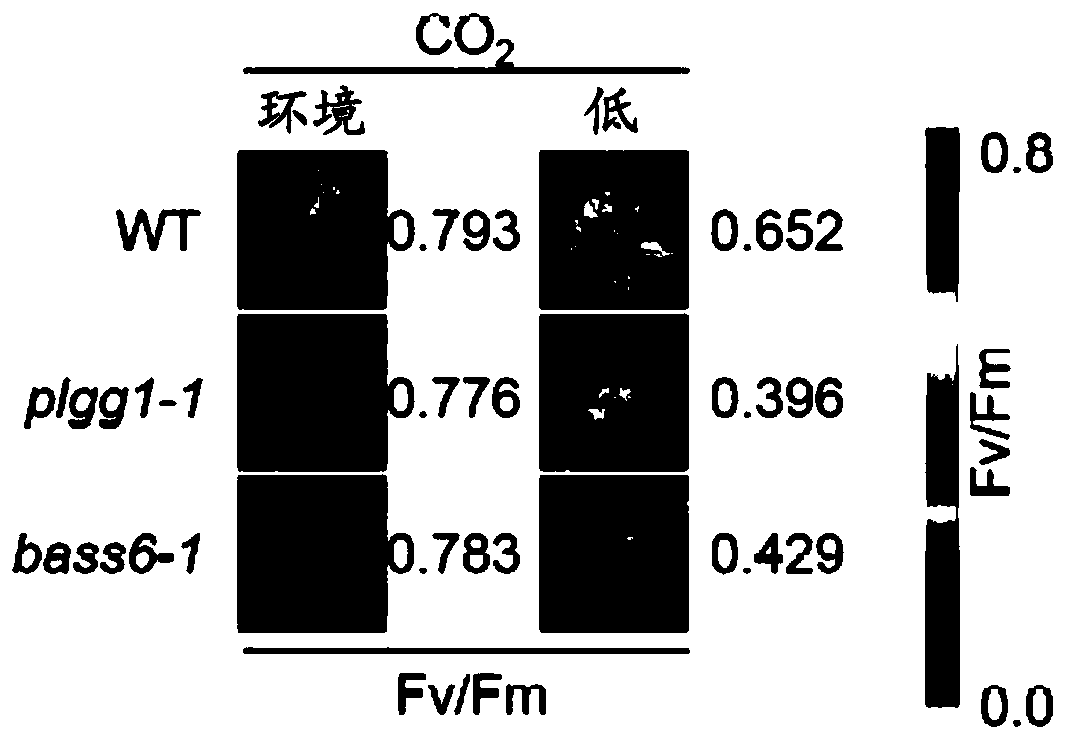
[0133] Two independent T-DNA insertion lines targeting the gene At4g22840 lacking expression of the putative chlorophyll inner membrane protein BASS6 were analyzed. To determine whether BASS6 is involved in photorespiration, in ambient CO 2 Two T-DNA lines (bass6-1 and bass6-2) were grown under (400ppm) conditions. The bass6 mutant line displayed a smaller rosette size compared to the wild-type control, similar to the glycolate / glycerate transporter mutant involved in photorespiration plgg1-1 ( figure 2 - with ambient CO 2 Growth ((in a growth chamber at 250 μmol m -2 ·s -1 The light intensity was 400ppm CO for 8 weeks under 8h light / 16h dark cycle (22℃ / 18℃) 2 ) compared to WT, representative photographs of bass6 and plgg1 mutants). At low concentrations of CO 2 Down-illumination of photorespiratory mutants resulted in decreased dark-adapted Fv / Fm chlorophyll fluorescence, likely due to photodamage to p...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Example 3: BASS6 protein localization in the chloroplast envelope
[0139] Although previous studies have shown that BASS6 protein localizes to the chloroplast envelope, a subcellular localization prediction program more strongly supports a mitochondrial localization of BASS6 (Gigolashvili et al., supra). To determine the localization of the BASS6 protein, transient expression of the BASS6-GFP fusion protein was analyzed in both protoplasts and whole leaf tissues of N. benthamiana. Chlorophyll autofluorescence was used to identify chloroplasts ( Figure 7 Panels B, E, H and K). BASS6-GFP signal surrounds chloroplast autofluorescence ( Figure 7 , panels G to I), similar to the known glycolate / glycerate transporter PLGG1 ( Figure 7 , panels D to F), indicating that BASS6 localizes to the chloroplast envelope. In addition, expression of BASS6-GFP or PLGG1-GFP induces the formation of plastid microtubule structures (stromule) ( Figure 7 , star-shaped arrows in panel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com