Doubly-fed induction generator fault detection method based on sliding mode observer
A doubly-fed induction motor and sliding mode observer technology, which is applied in the direction of motor generator testing, control generator, motor generator control, etc., can solve problems affecting system reliability, etc., and achieve simple structure and strong anti-interference ability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
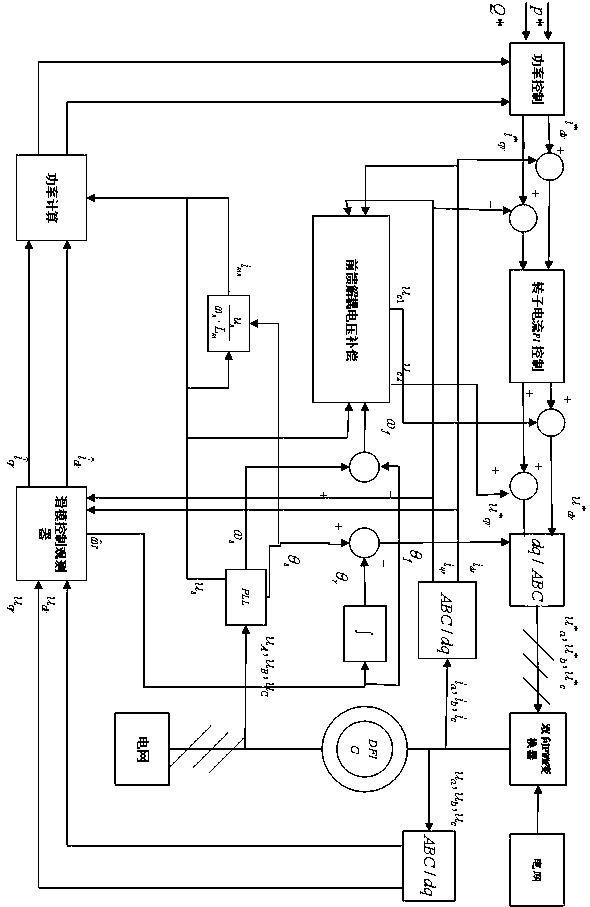
[0024] Specific embodiment one: the doubly-fed induction generator fault detection method based on sliding mode observer described in this implementation method, it comprises the following steps:
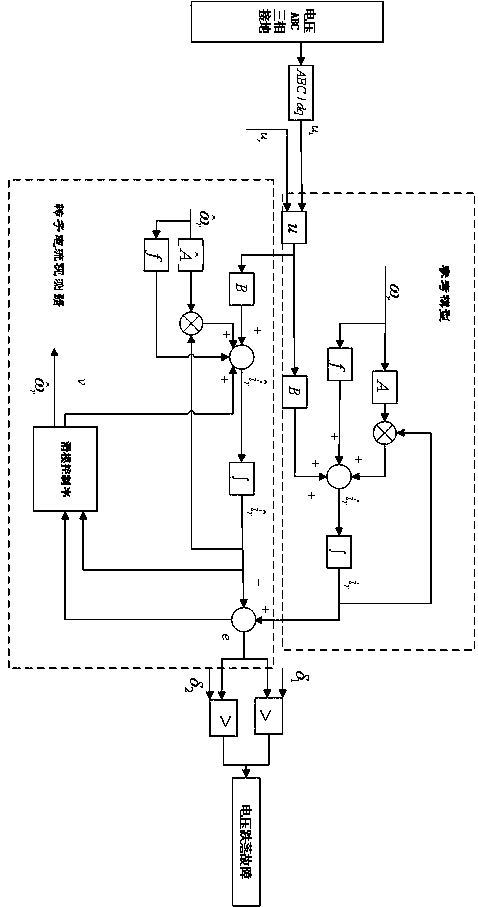
[0025] Step 1. The stator side of the doubly-fed induction motor is connected to the grid terminal, and the stator voltage signal can be obtained through the voltage sensor , the stator current signal can be obtained through the current sensor , the rotor side of the doubly-fed induction motor is connected to the back-to-back power converter and the rotor voltage signal can be obtained through the voltage sensor , the rotor current signal can be obtained through the current sensor ;
[0026] Step 2: Transform the stator and rotor voltage signals through clark and park to obtain synchronous rotation Stator and rotor voltage signal in the coordinate system , at the same time, the stator and rotor current signals are transformed by clark and park to obtain synchronous rotatio...
specific Embodiment approach 2
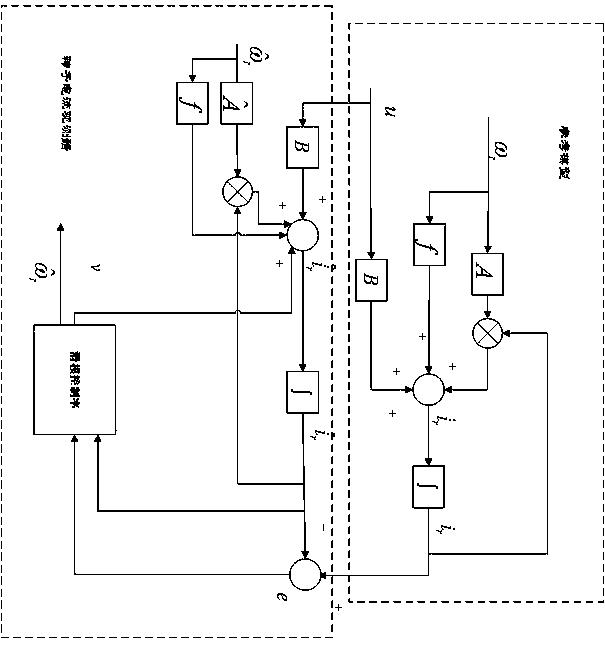
[0034] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is a further limitation of the sliding mode observer-based doubly-fed induction generator fault detection method described in specific embodiment one,
[0035] In step 3, according to the voltage equation and the flux equation of the double-fed motor, the method of establishing the state space equation is as follows:
[0036] The voltage equation is:
[0037] ,
[0038] ,
[0039] The flux linkage equation is:
[0040] ,
[0041] ,
[0042] ,
[0043] In the formula, respectively The stator and rotor voltage vectors of the shaft, respectively The stator and rotor current vectors of the shaft, respectively The flux vectors of the stator and rotor of the shaft, are the rotor and stator resistances, respectively, are the self-inductance of the stator and rotor, respectively, is the mutual inductance between the stator and rotor, are the leakage inductance of the stator and rotor, respectively, are ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0048] Specific embodiment three: this embodiment is a further limitation of the sliding mode observer-based doubly-fed induction generator fault detection method described in specific embodiment one,
[0049] In step 4, when only the rotor current state space model is considered, the stator voltage oriented control method is used to obtain the relationship between the stator current item and the rotor current item, and the method to obtain the state equation without the stator current item is:
[0050] The stated only considers the stator current When the state space model is used, its state space model is:
[0051]
[0052] In the formula, , , , , , , , respectively The stator and rotor voltage vectors of the shaft, respectively The stator and rotor current vectors of the shaft, are the rotor and stator resistances, respectively, are the self-inductance of the stator and rotor, respectively, is the mutual inductance between the stator and roto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com