Method for preparing porous material of slow-release degradable film wrapped medicine fertilizer
A technology of porous materials and degradable films, applied in inorganic fertilizers, fertilizer mixtures, potash fertilizers, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory long-term effect of fertilizers, variation and other biological pollution, complex processes, etc., to achieve large-scale production promotion, prolonged effective The effect of release period and simple process steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
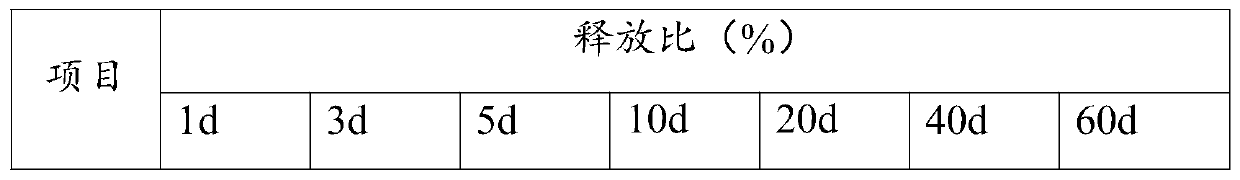
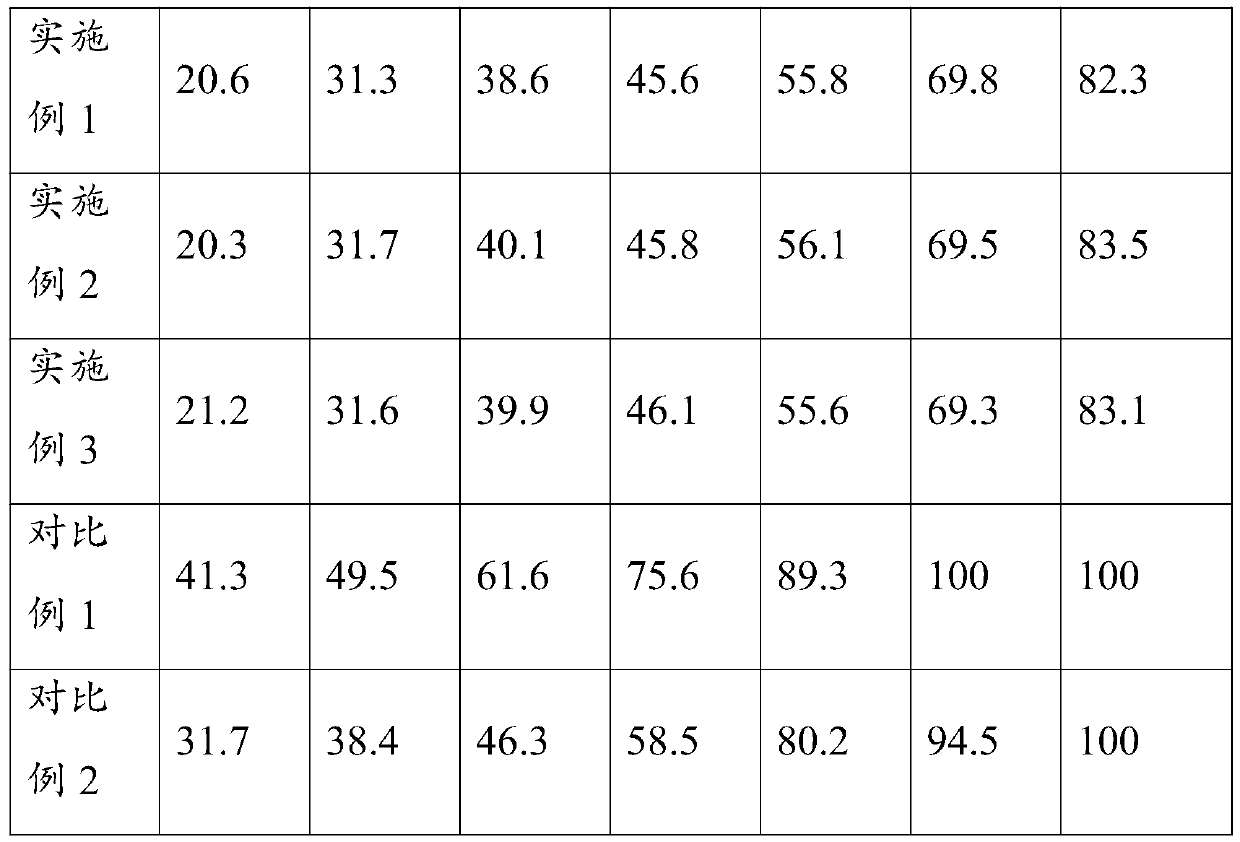
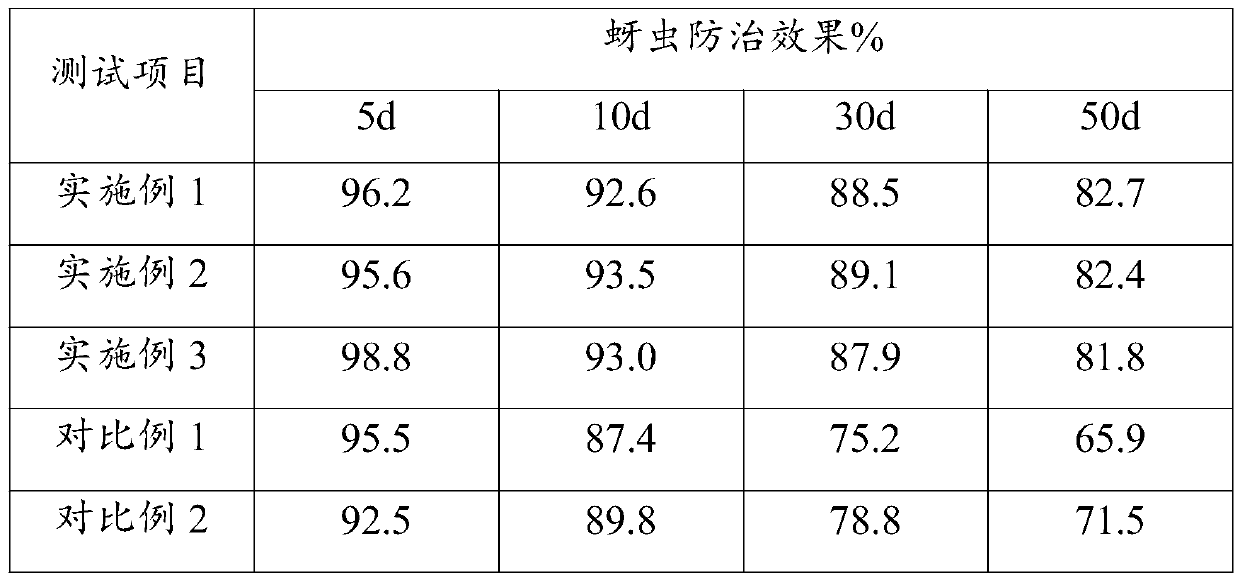
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] 1. Preparation of porous carbonized material:
[0042] 1) Weigh plant ash as raw material, dry at 70°C for 2 hours, mechanically pulverize, pass through a 10-mesh sieve, and superfinely pulverize through a 250-mesh sieve for later use;
[0043] 2) Weighing 45wt% of plant ash powder in proportion, 35wt% of a configured mass fraction of 8% potassium hydroxide alkali solution, and 20wt% of pore-enhancing agent 15% polyvinylpyrrolidone;
[0044] 3) Soak the pulverized plant ash in the mixed solution for 5 hours, put it into the drier for ammoniation and dispersion treatment with ammonia gas for 1 hour;
[0045] 4) Put the plant ash powder into the tube furnace for low-temperature carbonization, set the temperature to rise from 100°C / h to 300°C for 3 hours, during which the protective gas nitrogen is introduced, cooled to room temperature and taken out for later use.
[0046] 2. Pesticide loading of porous materials:
[0047] 1) Weigh 1500ml of 20% sodium pentachlorophenat...
Embodiment 2
[0059] 1. Preparation of porous carbonized material:
[0060] 1) Weigh plant ash as raw material, dry at 70°C for 2.5 hours, mechanically pulverize, pass through a 10-mesh sieve, and superfinely pulverize through a 250-mesh sieve for later use;
[0061] 2) Weigh 60wt% of plant ash powder in proportion, 30wt% of the configured mass fraction 8% potassium hydroxide alkali solution, and 10wt% of pore-enhancing agent 3% urea solution;
[0062] 3) Soak the pulverized plant ash in the mixed solution for 5 hours, put it into the drier for 1.5 hours for ammonification and dispersion treatment with ammonia gas;
[0063] 4) Put the plant ash powder into the tube furnace for low-temperature carbonization, set the temperature to rise from 100°C / h to 300°C for 3 hours, during which the protective gas nitrogen is introduced, cooled to room temperature and taken out for later use.
[0064] 2. Pesticide loading of porous materials:
[0065] 1) Weigh 1500ml of 20% sodium pentachlorophenate aq...
Embodiment 3
[0077] 1. Preparation of porous carbonized material:
[0078] 1) Weigh plant ash as raw material, dry at 73°C for 2 hours, mechanically pulverize, pass through a 10-mesh sieve, and superfinely pulverize through a 250-mesh sieve for later use;
[0079] 2) Weighing 55wt% of the plant ash powder in proportion, 30wt% of the configured mass fraction 8% potassium hydroxide alkali solution, and 15wt% of the pore-enhancing agent 3% urea solution;
[0080] 3) Soak the pulverized plant ash powder in the mixed solution for 5.5 hours, wash it with a large amount of distilled water until the pH value is 7-9, and put it into the dryer for 1.5 hours of ammonification and dispersion treatment with ammonia gas;
[0081] 4) Put the plant ash powder into the tube furnace for low-temperature carbonization, set the temperature to rise from 100°C / h to 300°C for 3 hours, during which the protective gas nitrogen is introduced, cooled to room temperature and taken out for later use.
[0082] 2. Pesti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com