FPGA online fault injection method based on code mutation
A technology of fault injection and coding, which is applied in the direction of faulty hardware testing methods, faulty computer hardware, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that users cannot freely choose faults, etc., and achieve the effect of improving efficiency and reducing collection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
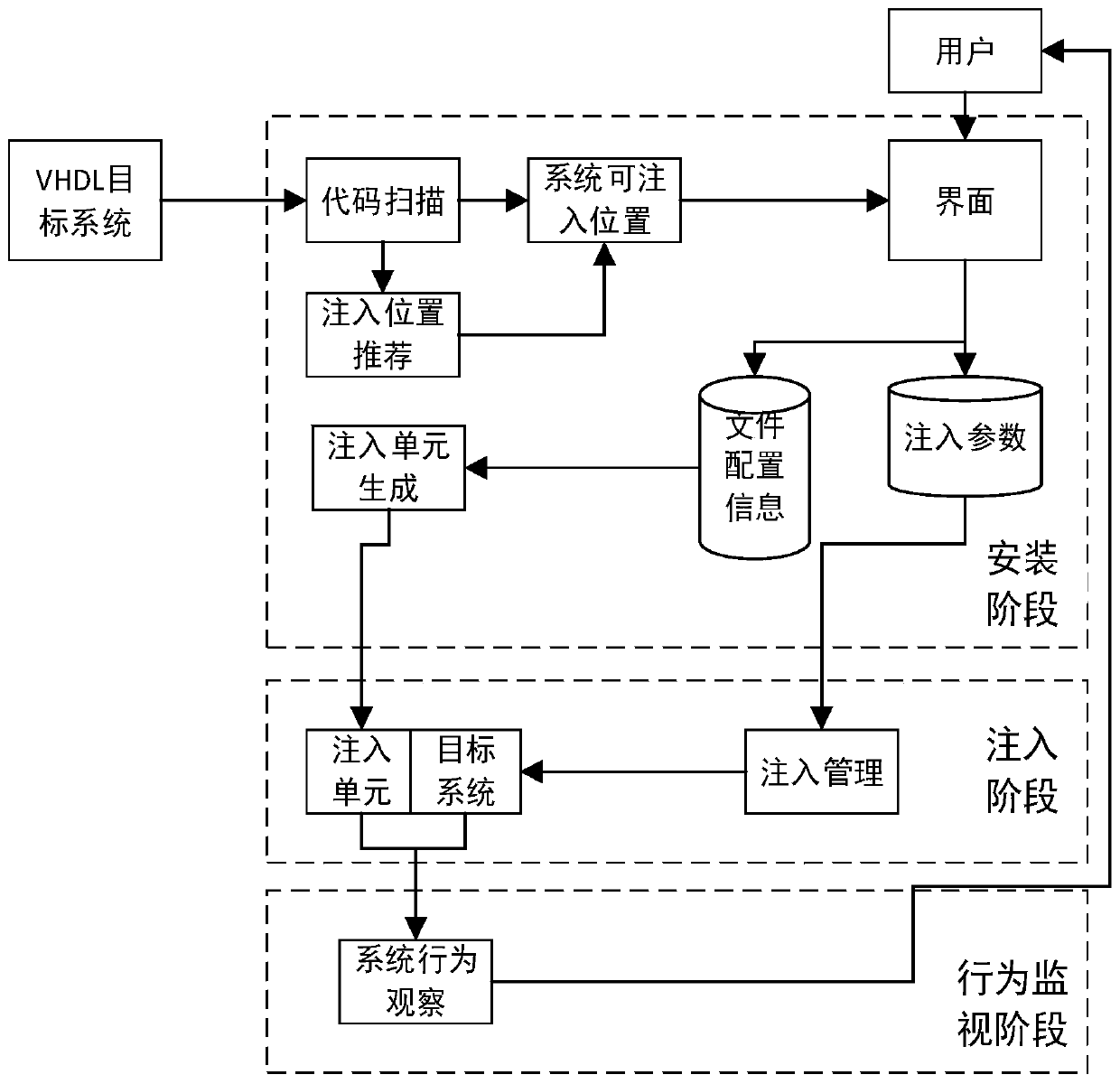
[0030] Specific implementation mode one: refer to figure 1 Specifically illustrate this embodiment, the FPGA online fault injection method based on code mutation described in this embodiment, comprises the following steps:
[0031] Step 1: First scan the code and perform mathematical modeling on the VHDL system;
[0032] Step 2: According to the fault injection location selected by the user, inject file configuration, modify the signal, and generate an injection unit;
[0033] Step 3: Generate fault injection parameters according to the user's selection;
[0034] Step 4: Analyze the fault injection parameters generated in Step 3 and write them into the parameter register;
[0035] Step five: through the control of the host computer, the activation of the fault injection unit is completed when the FPGA target system is running.
[0036] The first step in the installation phase is to conduct code analysis, and conduct mathematical modeling of the VHDL system by scanning the c...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 1. The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the fault injection location in Step 2 is realized through the syntax tree of the target system.
specific Embodiment approach 3
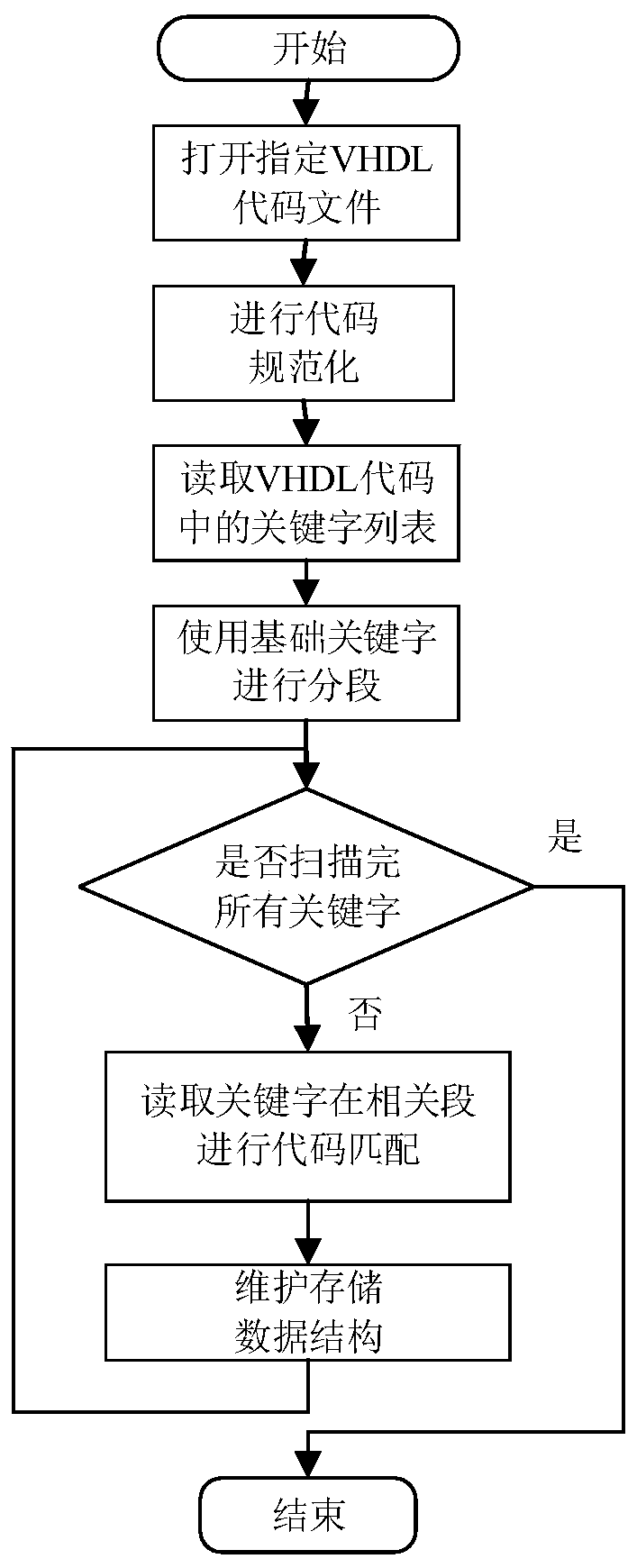
[0041] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is a further description of Embodiment 2. The difference between this Embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that the detailed steps of step 1 are:
[0042] Step 11: Code specification of the VHDL code file;
[0043] Step 1 and 2: Read the keyword list in the VHDL code, and use the basic keywords to segment the code;
[0044] Step 13: Determine whether all keywords have been scanned, if so, end, if not, then perform step 14;
[0045]Step 14: Read keywords to perform code matching in relevant segments, then write the information and matching positions into the data structure, and perform steps 1 and 3.
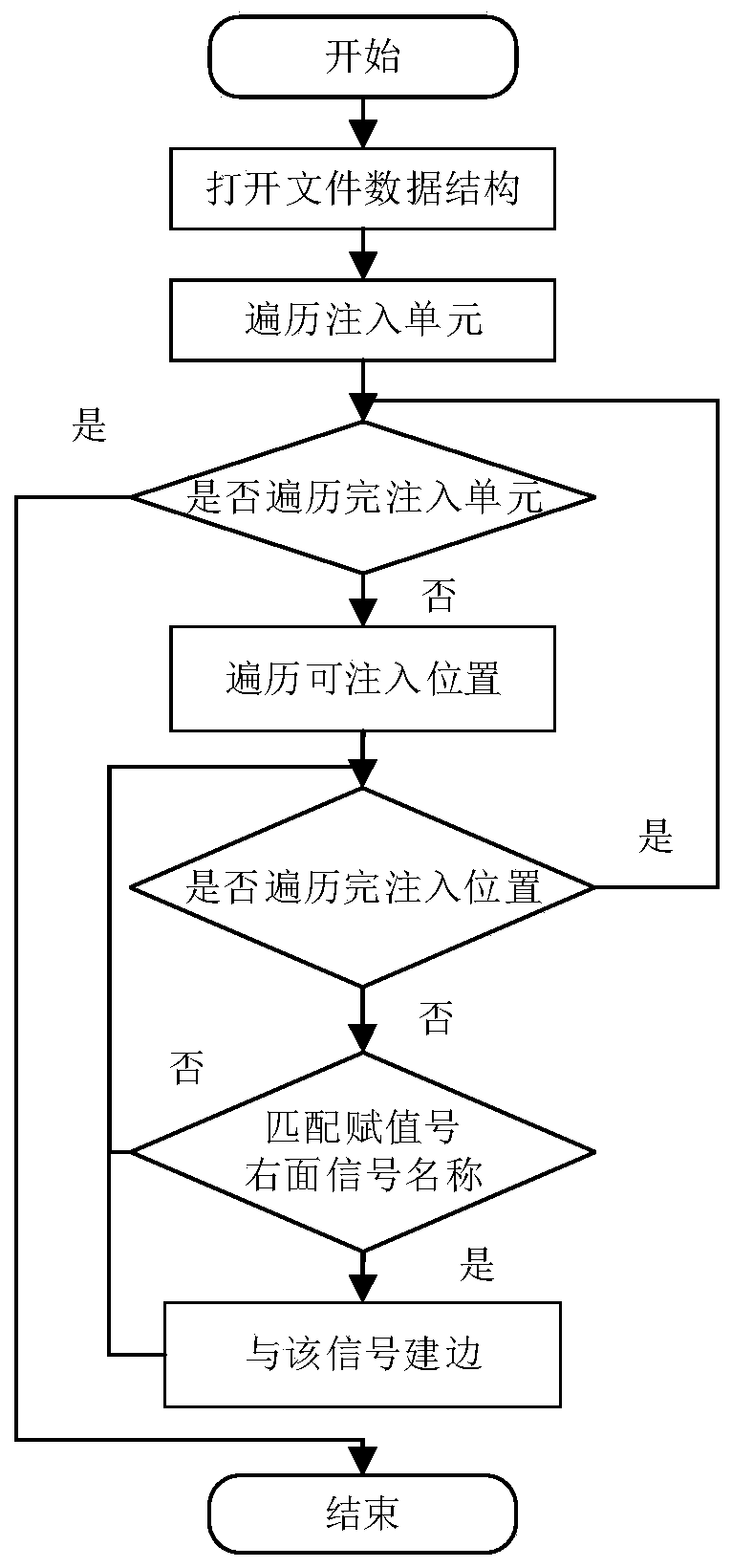
[0046] The recommended function of fault injection analyzes the reliability bottleneck of the system in the fault propagation network by constructing the fault propagation network of the system. The construction of the fault propagation network is divided into signal connections within a single file and signal connections between multiple files. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com