Passive type permanent magnet repulsion type magnetic bearing structure
A passive, magnetic bearing technology, applied in the direction of bearings, shafts, bearings, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems of high control precision, large system power consumption, complex structure, etc., and achieve stable rotor rotation, reduce loss, and small volume Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
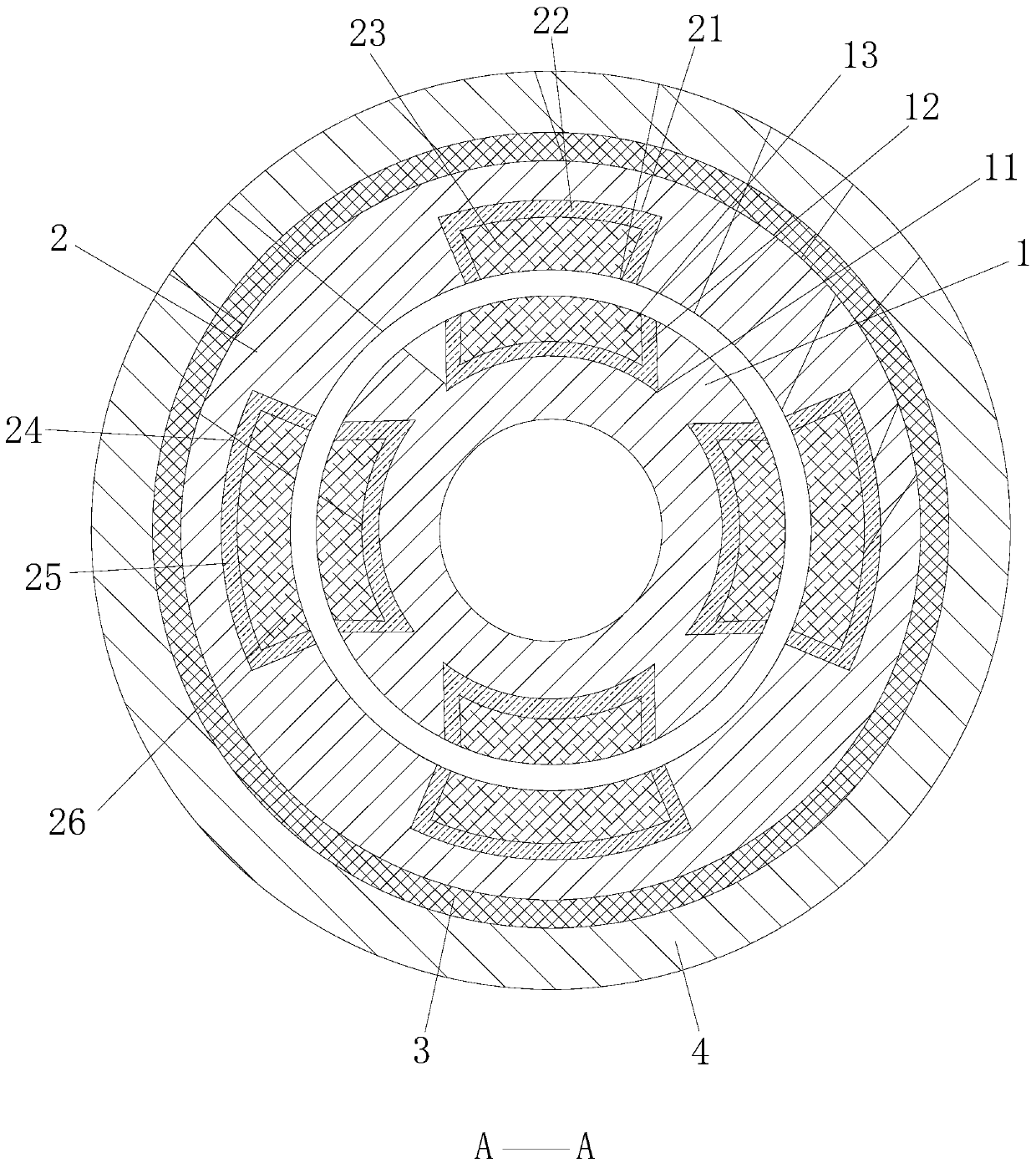
[0074] The above-mentioned magnetic bearing structure, the magnetic bearing composed of the stator 2 and the rotor 1, is mainly used to provide radial bearing capacity.
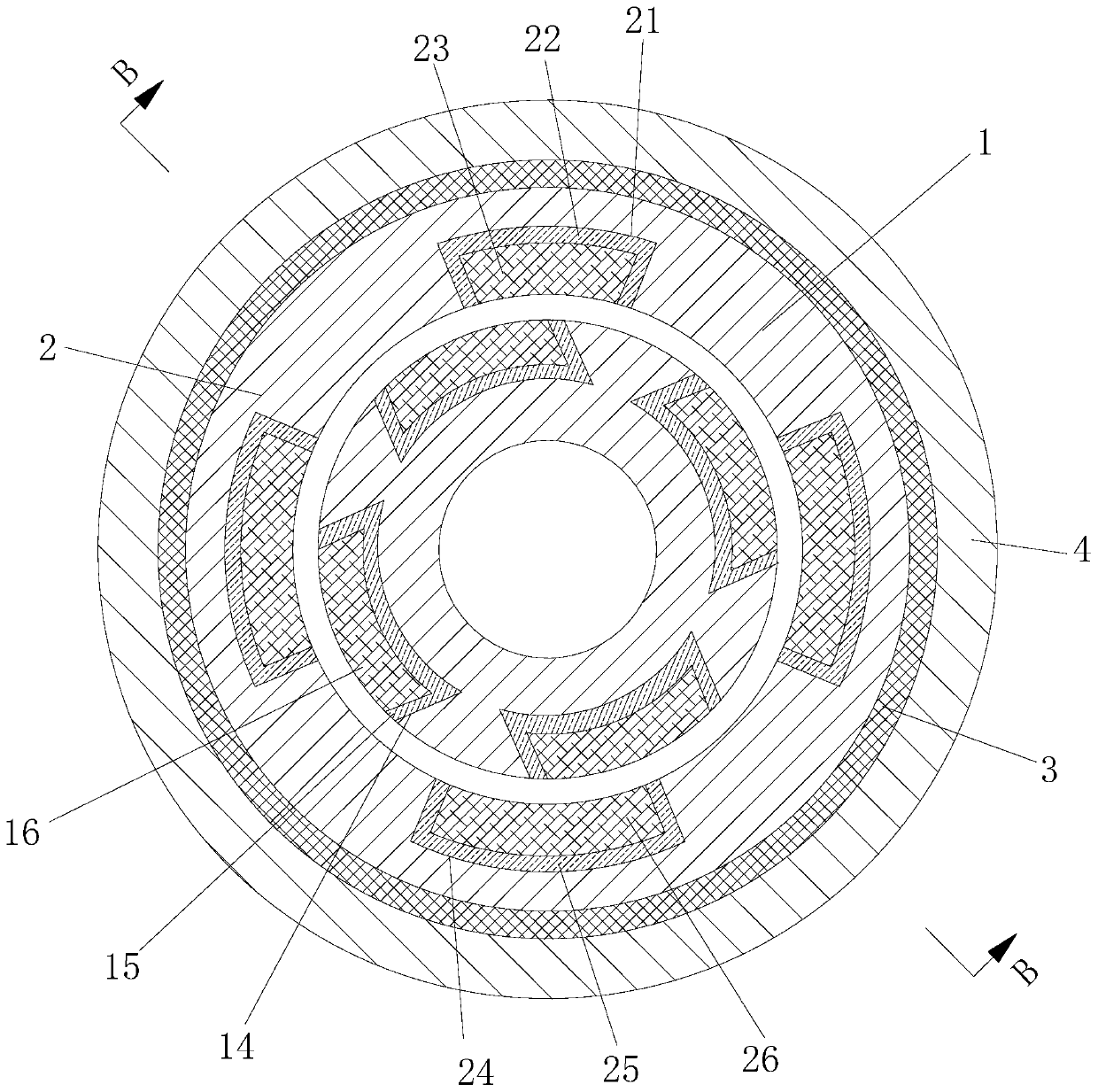
[0075] The force between the stator 2 and the rotor 1 is the repulsive force generated between the first rotor permanent magnet 13 , the second rotor permanent magnet 16 , the first stator permanent magnet 23 and the second stator permanent magnet 26 .
[0076] Its magnetic field lines are as Figure 7 and Figure 8 shown. Wherein the first stator permanent magnet 23 is positioned at the upper side in the stator 2, the second stator permanent magnet 26 is compared with the first stator permanent magnet 23, and the magnet area corresponding to the second stator permanent magnet 26 and the rotor permanent magnet is large, Therefore, the generated repulsive force is relatively large, which can offset the gravity of the rotating shaft itself, so that the air gap between the rotor 1 and the stator 2 is evenly di...
Embodiment 2
[0078] The radial force of the magnetic bearing varies with the size of the air gap. When the axial air gap of the two magnets decreases, the force at the place where the air gap decreases becomes larger, otherwise the radial force decreases.
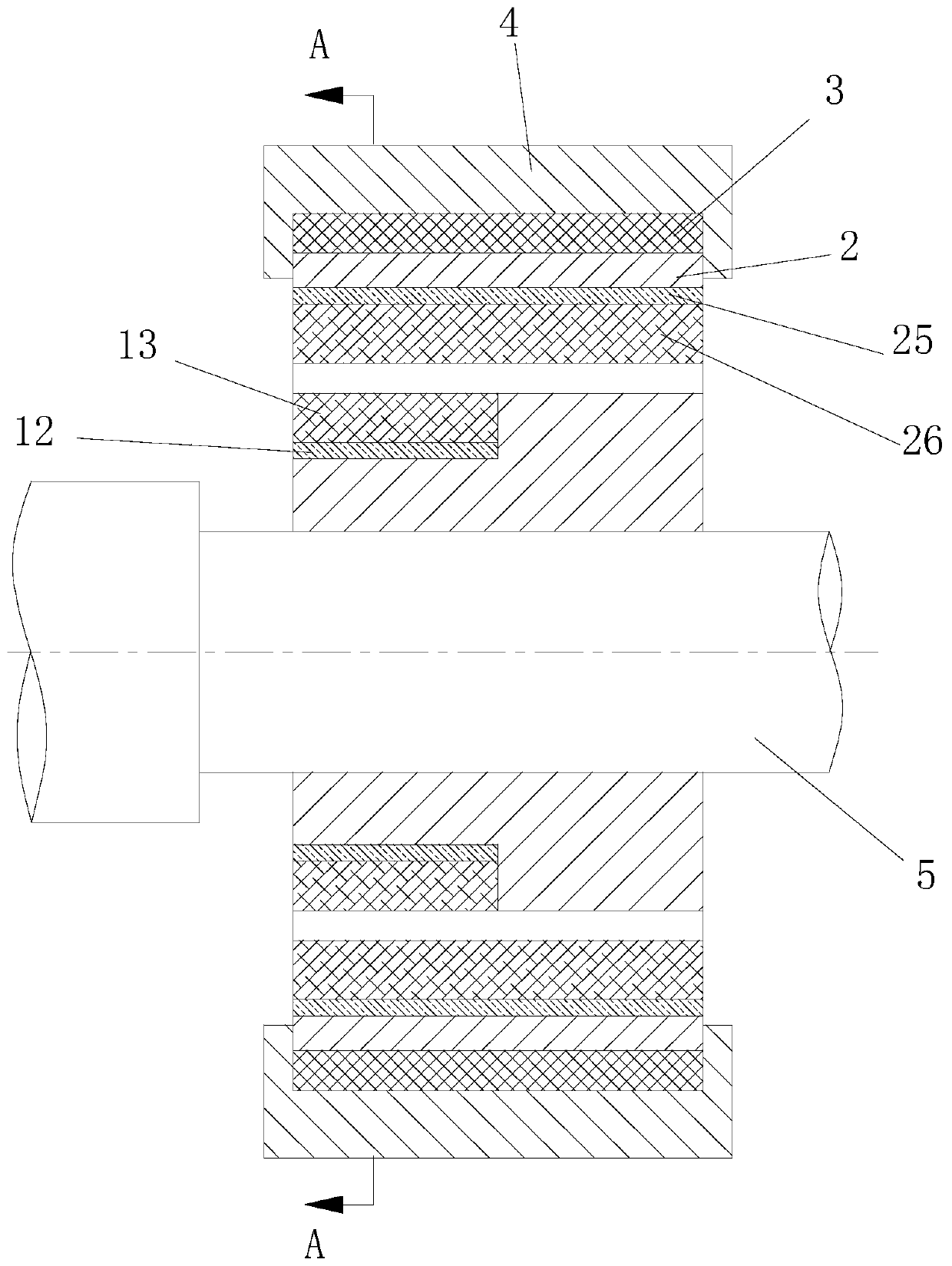
[0079] Power is provided by an external motor to drive the rotating shaft and the rotor part of the bearing to rotate. During the rotation of the bearing rotor, when the stator on the left side of the bearing and the permanent magnet of the rotor are completely opposite, the stator on the right side of the bearing and the permanent magnet of the rotor are completely staggered, as figure 1 and image 3 As shown, the radial force required by the bearing at this time is completely the repulsion force generated by the left permanent magnet;
[0080] When the bearing rotor rotates at a certain angle, the permanent magnets on the left and right sides of the bearing are partially distributed, and the sum of the relative areas of the permanent ...
Embodiment 3
[0084] The principle of the present invention is: the magnetic force lines of the permanent magnet pass through the air gap and the magnetic isolation sheet to form a circuit to provide a magnetic field for the magnetic bearing and bear the radial force on the magnetic bearing;
[0085] Wherein the first stator permanent magnet of the stator is located on the upper side in the middle of the stator, and the second stator permanent magnet of the stator is compared with the first permanent magnet, and the magnet area corresponding to the second permanent magnet and the rotor permanent magnet is larger, and the repulsive force generated Relatively large, so it can offset the gravity of the shaft itself.
[0086] When there is external interference, the distance between the bearing rotor and the bearing stator will change, the size of the air gap will decrease or increase accordingly, and the corresponding repulsion force will also increase or decrease accordingly, and the force on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com