LED chiplet and LED chip invisible cutting method
A technology of LED chip and stealth cutting, which is applied in the manufacturing of electrical components, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of low chip cutting yield, increased electrical failure rate of LED chips, and reduced cutting yield. , to reduce the phenomenon of substrate skew cracking, reduce the line width of the cutting track, and improve the cutting yield.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
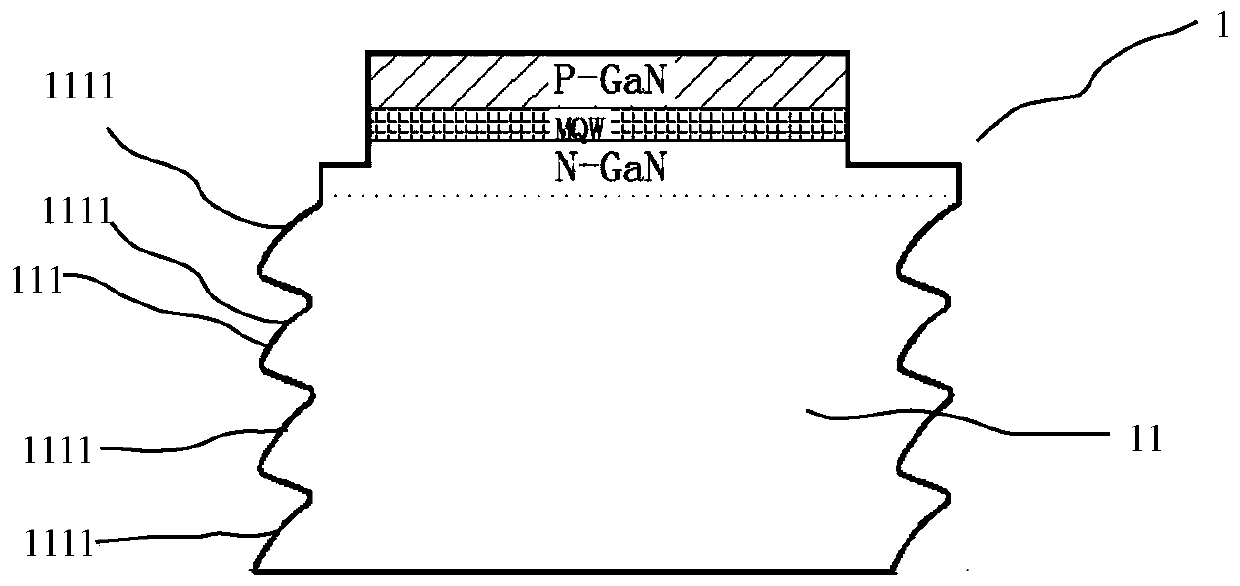
[0054] Such as figure 2 As shown, a LED chip 1, the side surface of the substrate 11 of the LED chip 1 (in this specific embodiment, the substrate 11 is a sapphire substrate, and the c-plane surface of the sapphire substrate grows an epitaxial layer) 111 has a plurality of spaced laser scratches 1111 along the thickness direction of the substrate 11. In this specific embodiment, the number of laser scratches 1111 is four, but it is not limited thereto. In other embodiments, the number of laser scratches 1111 The number can be set according to the thickness of the substrate 11, such as 3, 5 or more than 5 and so on.
[0055] The side surface 111 of the substrate 11 is arranged up and down sequentially along the thickness direction of the substrate 11 (approximately wavy), and the multiple laser scratches 1111 on the same side surface 111 of the substrate 11 are located on the same side of the substrate 11. In a plane parallel to the thickness direction, that is, in the same v...
Embodiment 3
[0064] This embodiment provides a stealth cutting method for LED chips, including:
[0065] In step S0, a full-structure LED chip 3 is produced according to the LED chip process, including forming an epitaxial layer 32 and a dicing line 33 on the c-plane surface of the sapphire substrate 31; and then grinding and thinning the LED chip 3 to a predetermined thickness , this example is 200μm, such as Figure 7 and 8 shown.
[0066] Step S11, first adopt invisible cutting on the back side, move the laser focusing point to the distance a1 from the back side of the LED chip 3 along the Y direction, a1 is 10 μm-30 μm, adjust the laser energy to 0.01W-0.5W, and adjust the laser frequency to 1KHz-100KHz , adjust the moving speed of the stage to 1mm / s-800mm / s, so that it forms a row of holes 34 with a distance D of 3μm-20μm and a diameter d of 1μm-4μm, forming the first laser scratch 341, as Figure 9 shown.
[0067] Step S12, then move the focus of the laser to the distance a1+a2 f...
Embodiment 5
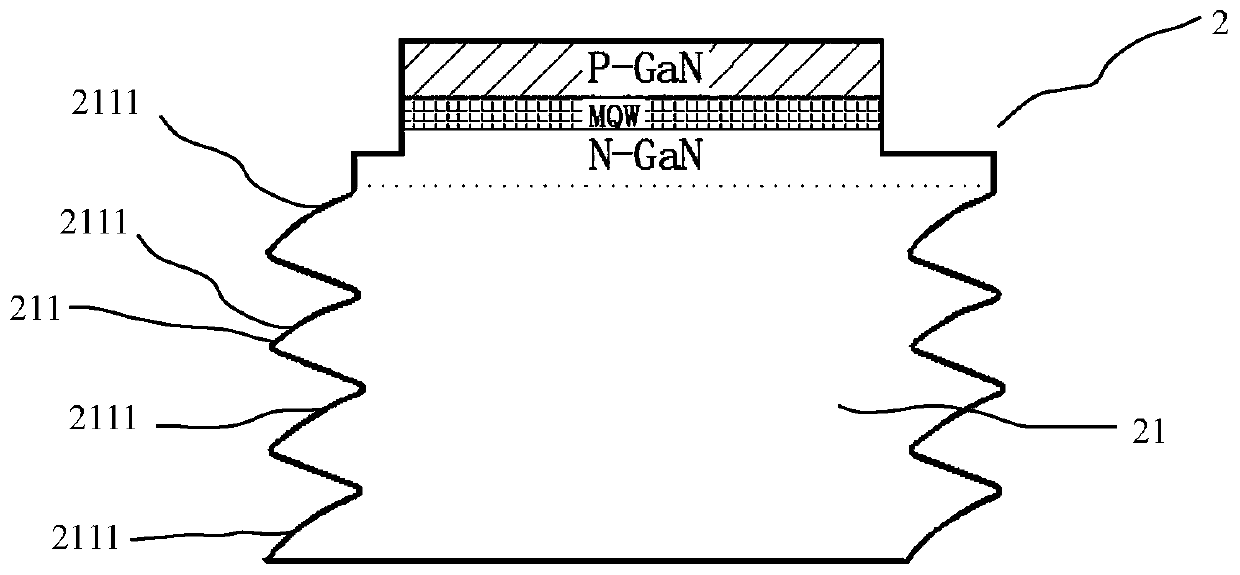
[0085] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: this embodiment adopts a stealth cutting machine with four laser heads, and the four laser beams of the four laser heads respectively form the first laser scratch to the fourth laser scratch at the same time ,Such as Figure 13 As shown, four laser scratches are completed at one time, which increases the output of the machine.
[0086] Of course, in other embodiments, the number of laser heads can be determined according to the number of laser scratches.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com