Directed degradation method of waste polyurethane material
A polyurethane material and polyurethane technology, which is applied in the field of directional degradation of waste polyurethane materials, can solve a large number of metal salts, carbon-carbon bond structure side reactions and other problems, and achieve the effects of low price, reduced recycling cost, and low solvent cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The waste polyurethane material to be degraded in this embodiment is poly-1,2-propylene glycol polyether polyurethane, and the specific structure is as follows:
[0038]
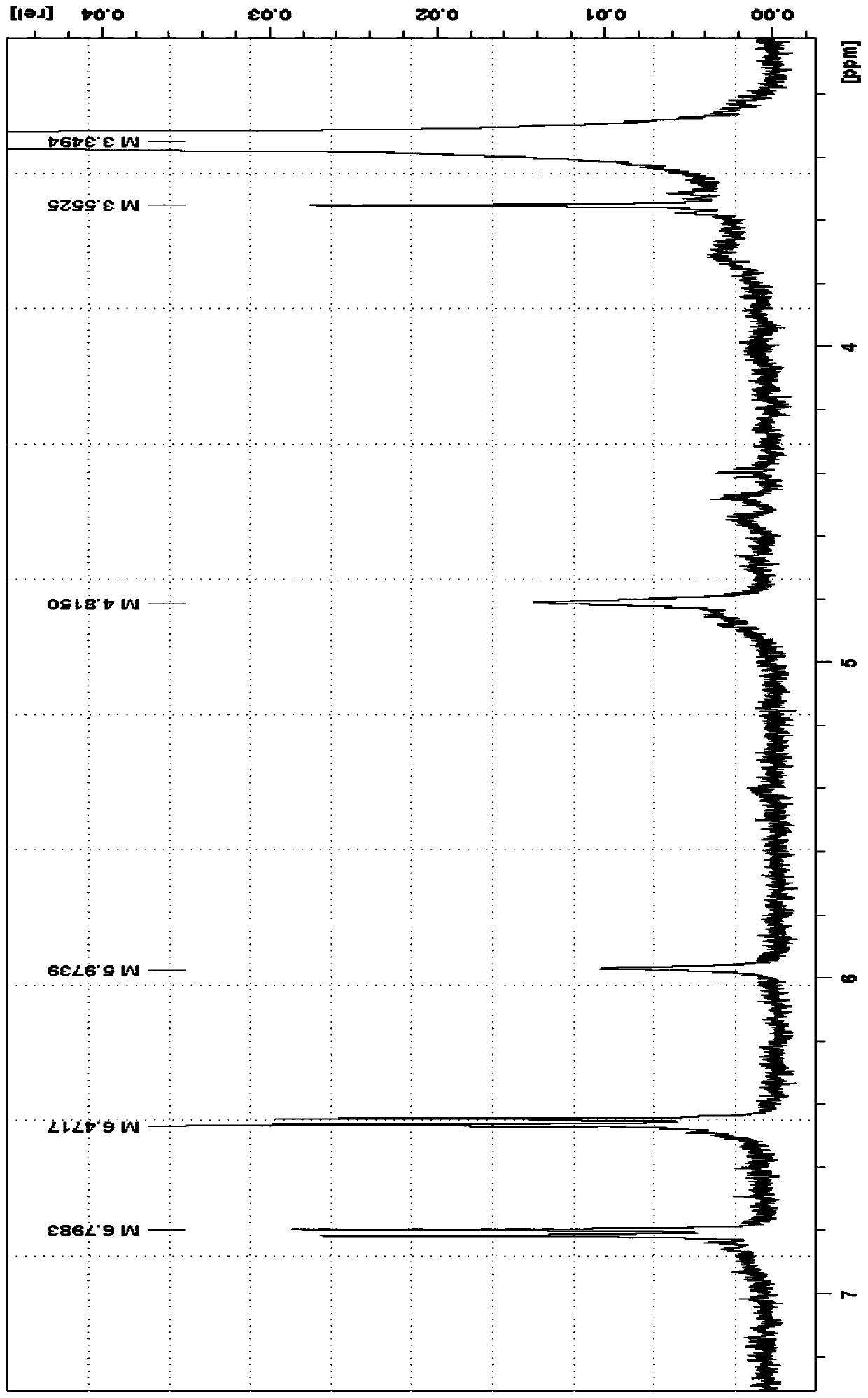
[0039] Mix 0.4g of pulverized waste polyurethane materials with a particle size of 0.01cm, 0.004g of urea, and 0.4g of 100% ethanol to form a 0.804g degradation system, and react in a hydrothermal kettle at 100°C for 12h , after the reaction degradation is completed and cooled, add 8g of water to the reaction system and let it stand. After the precipitation is complete, filter, wash and dry the filter cake to obtain 0.13g of aromatic polyamines; the filtrate is extracted and layered with chloroform, and the layers are obtained The chloroform phase was dried at 80° C. to obtain 0.25 g of long-chain polyether polyols; the aqueous phase obtained by stratification was recovered and reused for the degradation of polyurethane.
Embodiment 2
[0041] The structure of the waste polyurethane material to be degraded in this embodiment is the same as in Example 1
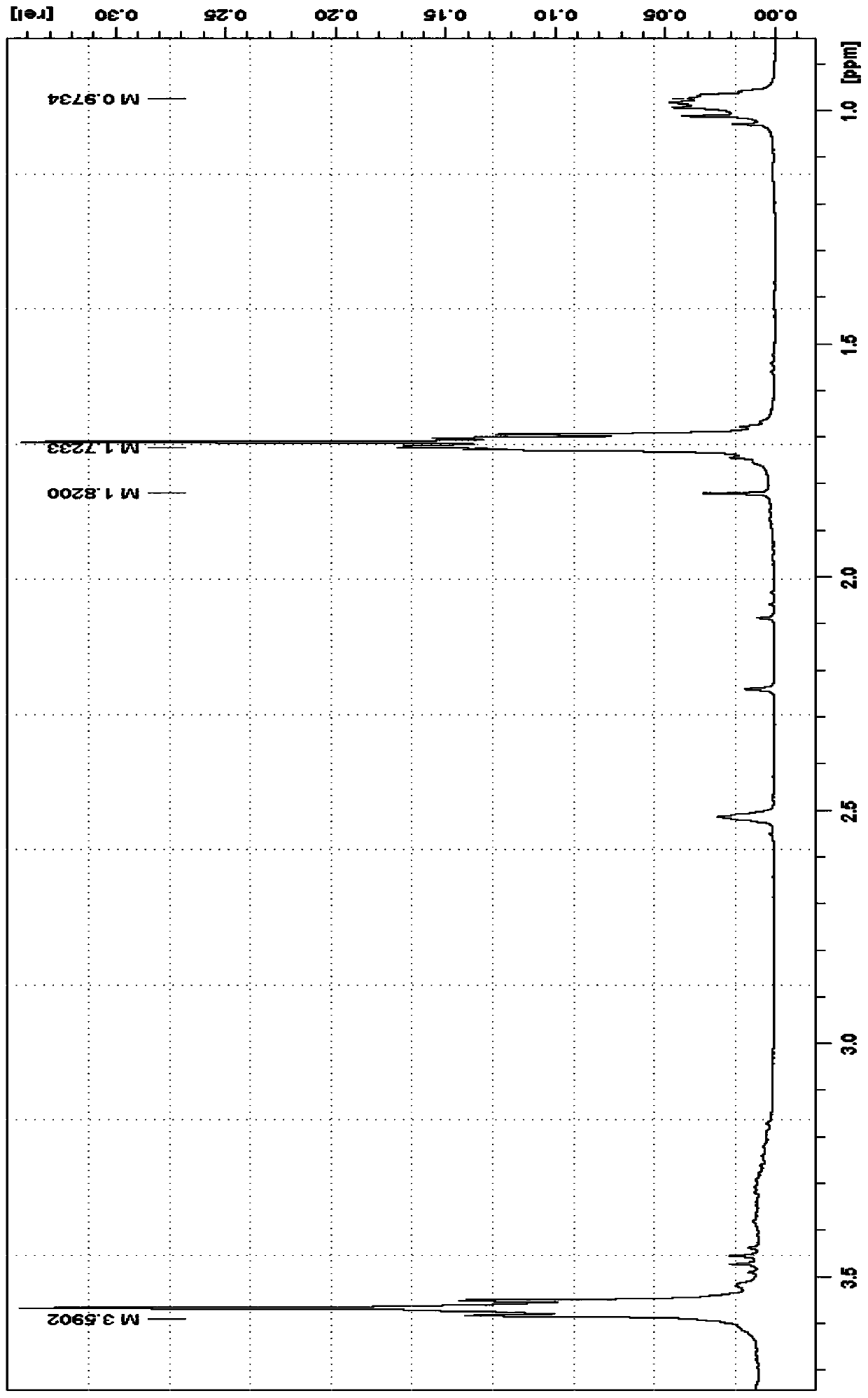
[0042] Mix 0.4g of pulverized waste polyurethane materials with a particle size of 0.05cm, 0.2g of piperazine, and 4g of 60% acetone to form a 4.6g degradation system, and react in a hydrothermal kettle at 140°C for 8 hours After the reaction degradation is completed and cooled, add 20g of water to the reaction system and let it stand. After the precipitation is complete, filter, wash and dry the filter cake to obtain 0.11g of aromatic polyamines; The toluene phase was dried at 100° C. to obtain 0.29 g of long-chain polyether polyols; the water phase obtained by layering was recovered and reused for the degradation of polyurethane.
Embodiment 3
[0044] The structure of the waste polyurethane material to be degraded in this embodiment is the same as in Example 1
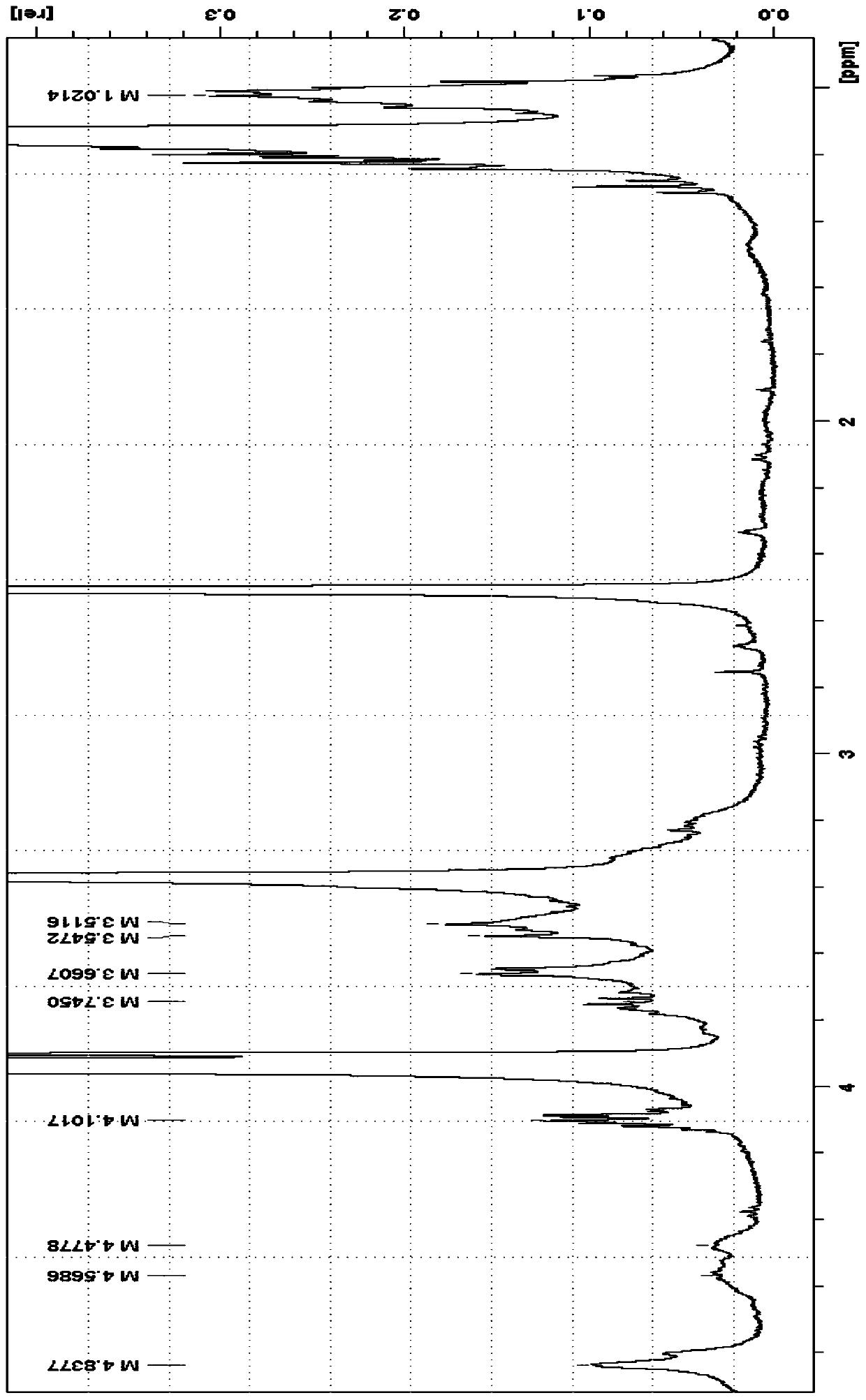
[0045] The 0.4g pulverized waste polyurethane material with a particle size of 1cm and 0.8g 1,4-dimethylpiperazine and 20g mass fraction are mixed with 20% methanol to form a 21.2g degradation system. The reaction was carried out at ℃ for 1 hour. After the reaction degradation was completed and cooled, 42.4 g of water was added to the reaction system and left to stand. After the precipitation was complete, it was filtered, the filter cake was washed and dried to obtain 0.16 g of aromatic polyamines; the filtrate was washed with petroleum Ether extraction and layering, the petroleum ether phase obtained by layering was dried at 85° C. to obtain 0.23 g of long-chain polyether polyols; the aqueous phase obtained by layering was recovered and reused for the degradation of polyurethane.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com