Breeding method for cellulase high-yield bacteria
A cellulase and high-yield technology, applied in the field of cellulase bacteria, can solve the problems of reduced enzyme production capacity and easy degradation of strains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
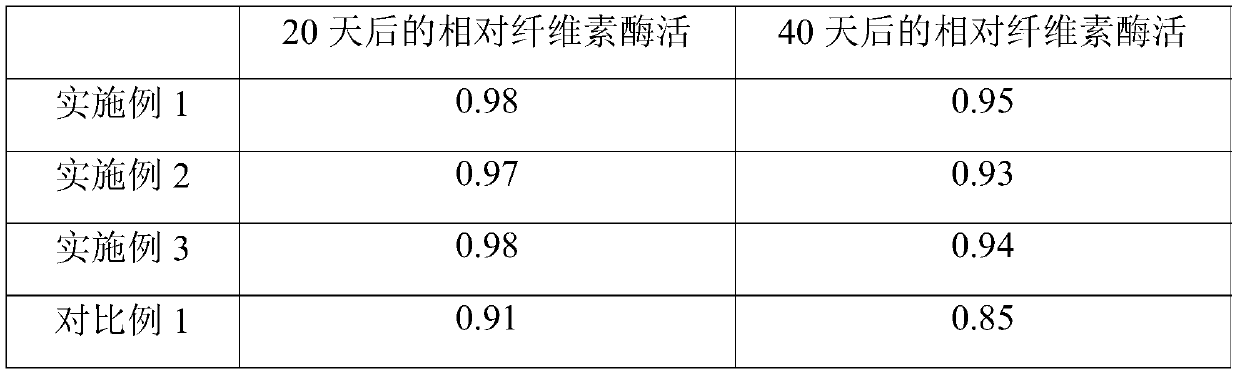
Embodiment 1
[0029] 1) Trichoderma viride and Reesei were cultured in the first culture medium (containing 25mg / L nitrosoguanidine and 42mg / L diethyl sulfate) according to the colony ratio of 1:1.8 for 8h (can be 4- 8h), followed by 60 Co-γ rays (intensity of 60eV) were irradiated for 20 minutes to obtain mutant mixed mold strains;
[0030] 2) Cultivate Clostridium krusei thermocellulolyticus in the second medium (containing 12mg / L ethyl methanesulfonate, 20mg / L diethyl sulfate) for 4h (can be 1.5-4h), and then use Ultraviolet rays (provided by a 500w ultraviolet generator) were irradiated for 25 minutes to obtain mutant strains;
[0031] 3) The above-mentioned mutant mixed mold strains and mutant strains were cultured in MS medium according to the colony ratio of 1:1 to obtain cellulase high-producing bacteria.
Embodiment 2
[0033] 1) Trichoderma viride and Reesei were cultured in the first culture medium (containing 33mg / L nitrosoguanidine and 44mg / L diethyl sulfate) according to the colony ratio of 1:2 for 5h (can be 4- 8h), followed by 60 Co-γ rays (intensity of 80eV) were irradiated for 15 minutes to obtain mutant mixed mold strains;
[0034] 2) Cultivate Clostridium krusei thermocellulolyticus in the second medium (containing 16mg / L ethyl methanesulfonate, 22mg / L diethyl sulfate) for 2h (can be 1.5-4h), and then use Ultraviolet rays (provided by a 55w ultraviolet generator) were irradiated for 20 minutes to obtain mutant strains;
[0035] 3) The above-mentioned mutant mixed mold strains and mutant strains were cultured in MS medium according to the colony ratio of 1:1.3 to obtain cellulase high-producing bacteria.
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1) Trichoderma viride and Reesei were cultured in the first culture medium (containing 37mg / L nitrosoguanidine and 46mg / L diethyl sulfate) according to the colony ratio of 1:2.2 for 4h (can be 4- 8h), followed by 60 Co-γ rays (intensity of 100eV) were irradiated for 10 minutes to obtain mutant mixed mold strains;
[0038] 2) Cultivate Clostridium krusei thermocellulolyticus in the second medium (containing 18mg / L ethyl methanesulfonate, 25mg / L diethyl sulfate) for 1.5h (can be 1.5-4h), then Adopt ultraviolet light (provided by the ultraviolet generator of 600w) to irradiate 18min to obtain mutant strain;
[0039] 3) The above-mentioned mutant mixed mold strains and mutant strains were cultured in MS medium according to the colony ratio of 1:1.5 to obtain cellulase high-producing bacteria.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com