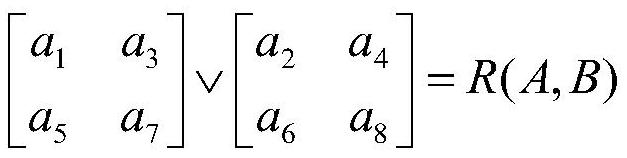Robot Obstacle Avoidance Algorithm Based on Topological Relationship
A topological relationship and robot technology, applied in the field of robots, can solve problems such as inaccurate, incomplete and imprecise spatial relationships, complex processes, etc., and achieve the effects of improving coordinate accuracy, safe and convenient use, and improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
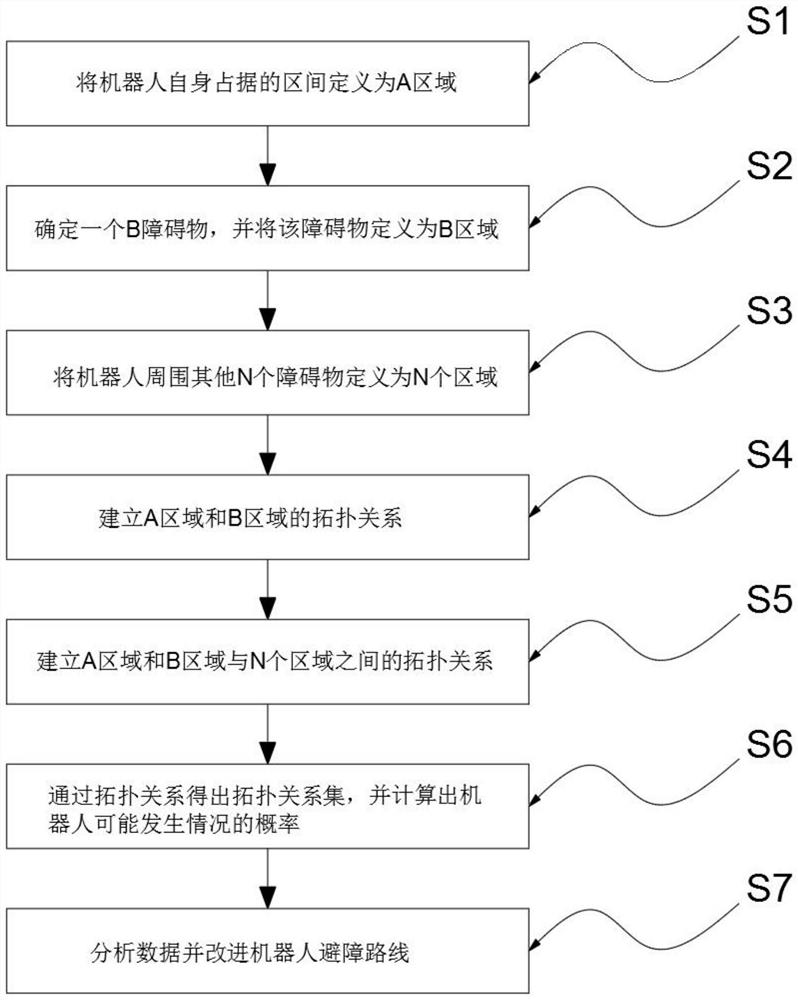
[0035] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-2 As shown, the present invention provides a technical solution, a robot obstacle avoidance algorithm based on topological relationships, including the following specific steps:
[0036] S1. Define the area occupied by the robot itself as area A;
[0037] S2. Determine an obstacle, and define the obstacle as area B;
[0038] S3, defining other N obstacles around the robot as N areas;
[0039] S4. Establish a topological relationship between the A area and the B area;
[0040] S5. Establishing the topological relationship between the A area, the B area and the N areas;
[0041] S6. Obtain the topological relationship set through the topological relationship, and calculate the probability that the robot may happen;
[0042] S7, analyze the data and improve the obstacle avoidance route of the robot;
[0043] When N is equal to 1, there is an area A representing the robot, and areas B and C representing obstacles.
[0044] According to the a...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2: the robot obstacle avoidance algorithm based on topological relationship, comprises following specific steps:
[0066] S1. Define the area occupied by the robot itself as area A;
[0067] S2. Determine an obstacle, and define the obstacle as area B;
[0068] S3, defining other N obstacles around the robot as N areas;
[0069] S4. Establish a topological relationship between the A area and the B area;
[0070] S5. Establishing the topological relationship between the A area, the B area and the N areas;
[0071] S6. Obtain the topological relationship set through the topological relationship, and calculate the probability that the robot may happen;
[0072] S7. Analyze the data and improve the obstacle avoidance route of the robot.
[0073] When N is equal to any value from 1 to infinity, there is area A representing the robot, area B, area C, area D representing obstacles....
[0074] According to the above-mentioned technical solution, in step S1, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com