Method for evaluating microbial powder promoting degradation of garden waste
A technology of garden waste and microbial bacteria, which is applied in the field of application evaluation of microbial powder to promote the degradation of landscaping waste, can solve the problems that the key role is not clear, and the biological effectiveness of liquid bacteria has not been studied.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
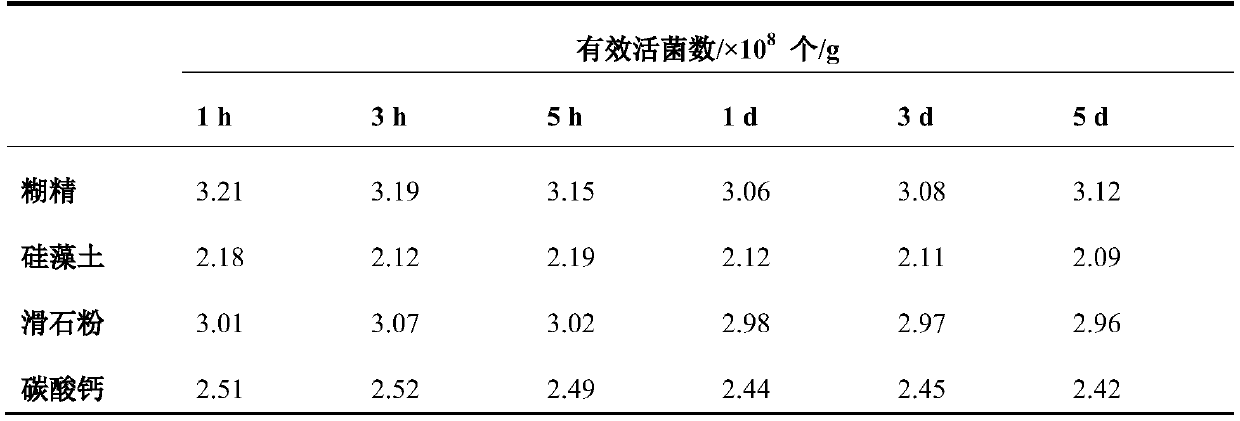
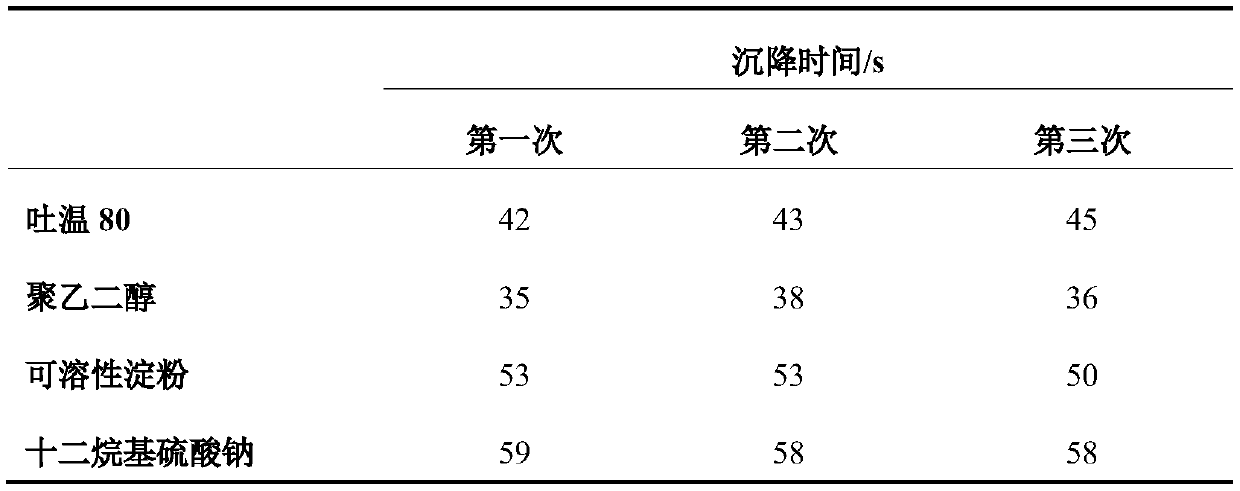
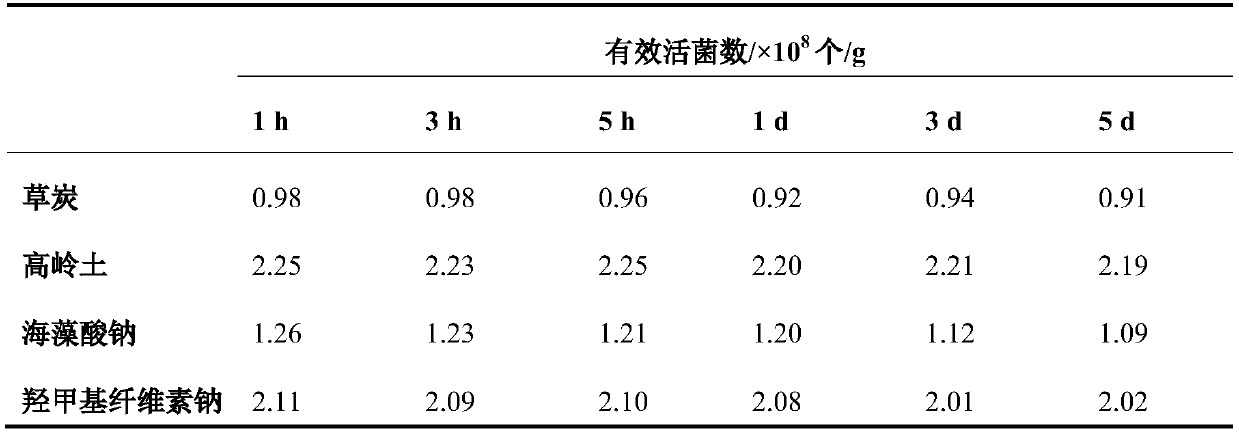
[0025] This embodiment provides a microbial powder capable of degrading garden cellulose, the effective viable bacteria of which are Cellulomonas flavigena which has a strong ability to degrade cellulose. The Cellulomonas lutea used in this example is a model strain of the genus Cellulomonas, which was purchased from the General Microbiology Center of China Committee for the Collection of Microbial Cultures. In order to prepare a solid microbial powder that is durable and convenient to use, in this example, the liquid fermented cells of Cellulomonas lutea were mixed with a specific ratio of suitable adsorptive carrier, wetting agent and protective agent. Specifically, the adsorptive carrier is selected from one or more of dextrin, diatomaceous earth, talcum powder or calcium carbonate, and in terms of mass ratio, the ratio of the flavin-producing cellulomonas to the adsorptive carrier is 1: (0.5-1.5); Wetting agent selects one or more in Tween 80, polyethylene glycol, soluble ...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This embodiment provides a preparation method of microbial bacterial powder that can degrade garden cellulose, including steps: 1) bacterial liquid fermentation, liquid fermentation of Cellulomonas xanthogenes, and production of Cellulomonas xanthomonas in the fermentation liquid when the fermentation is stopped The number of viable bacteria is not less than 2.0×10 8 pcs / mL; 2) Separation of cells, removal of water in the fermentation liquid to obtain Cellulomonas flavinogenes cells; 3) Preparation of bacteria powder, adding adsorption carrier, wetting agent and protective agent according to the mass ratio, stirring Mix evenly and dry in vacuum to obtain the microbial powder.
[0047] 1) Bacterial liquid fermentation
[0048] The number of effective viable bacteria reaches 2.0×10 8 Cellulomonas flavigena (Cellulomonas flavigena) culture fermentation broth of more than individual / mL is used as seed liquid, inoculates in the fermenter that liquid fermentation is used wi...
Embodiment 3
[0065] This embodiment provides the evaluation method of the microbial bacterium powder that embodiment 1 and 2 prepare. This embodiment uses the degradation weight loss rate method to evaluate the degradation efficiency of microbial bacterial powder to landscaping waste, and the microbial bacterial powder of different storage periods (30d, 90d, 150d, 210d, 270d, 330d, 390d and 450d) are respectively configured into 5 For ‰ bacterial powder suspension, calculate its degradation rate of landscaping waste on the 5th day, 10th day and 15th day of incubation at a constant temperature (30±1°C), and the greater the weight loss rate, the higher the degradation efficiency.
[0066] The landscaping waste described in this embodiment refers to one or more withered stems of reed (Phragmites australis), tulip (Tulipa gesneriana), silvergrass (Chloranthus japonicus), and iris (Iris tectorum). In order to avoid the pollution and interference of other bacteria on the selected materials, the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com