A face recognition method based on block collaborative representation
A face recognition and collaborative representation technology, applied in the field of face recognition, can solve the problem that the recognition rate needs to be improved, and achieve the effect of improving the robustness and improving the effect of face recognition.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Embodiment 1, experimental research on information loss of pixels.
[0056] The present invention has carried out the experimental research of missing pixel point information, randomly selects 10%, 20%, 30%, 40% of the pixel points of the face image, sets the value of the randomly selected pixel points to 0, and transforms the pixel points Does not carry valid information. According to the above specific program steps, experiments were carried out on three face databases. The experimental results of AR, Extend Yale B and ORL face databases are as follows: Image 6 , Figure 7 and Figure 8 shown. With the increase of the missing percentage of face image pixel information, the recognition rates of both FRAPRC and FRARC decreased. In the case of different pixel information missing percentages, the recognition rate of FRAPRC was higher than that of FRARC. In the case of missing, FRAPRC has a better recognition effect than FRARC; in the case of different pixel informati...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Experimental research on different corrosion blocks.
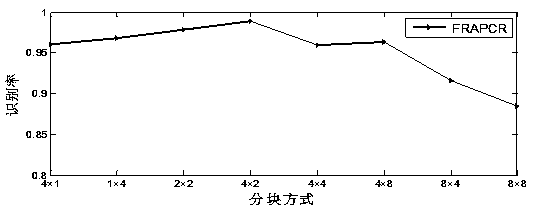
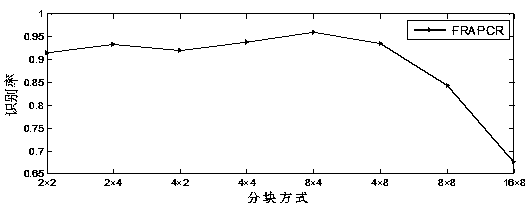
[0058] The present invention has carried out experimental research on the presence of corrupted blocks in face images, randomly selecting 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40% of the continuous blocks of the image, and replacing them with image information that is not related to the face image, 40% of which are corrupted The face image of the block case such as Figure 9 b) as shown. According to the above specific program steps, experiments were carried out on three face databases. The experimental results of AR, Extend YaleB and ORL face databases are as follows: Figure 10 , Figure 11 and Figure 12 shown. As the percentage of corrupted face image blocks in the original face image increases, the recognition rates of both FRAPRC and FRARC decrease. In the case of partial corruption of the face image, the recognition rate of FRAPRC is higher than that of FRARC. When the face image is corrupted, FRAPRC has a bette...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Embodiment 3, experimental research on face occlusion.
[0060] The face images in the AR face database include original face images, face images occluded by glasses, and face images occluded by scarves. Figure 13 shown. When there is an occlusion problem in the image, this paper uses 14 unoccluded face images from the AR database as the training set; 7 glasses and 7 scarf occluded face images are used as the eye and scarf test sets respectively. The personal face database is tested, and the experimental results are as follows: Figure 14 shown. In the case of glasses occlusion and scarf occlusion, the recognition rate of FRAPCR is higher than that of FRACR, and in the case of glasses occlusion.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com