Self-backhaul method of heterogeneous network
A heterogeneous network, self-backhaul technology, used in network planning, advanced technology, wireless communication, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
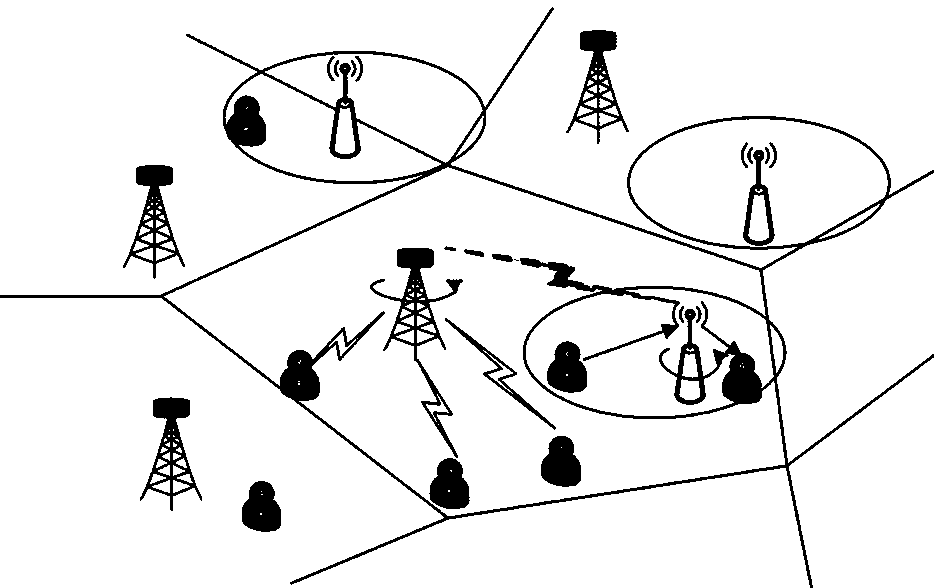
[0054] The present invention proposes a heterogeneous network composed of macro cells and small cells, considering uplink and backhaul transmission, as well as downlink, such as figure 1 shown.
[0055] Same-frequency deployment K+1 layer heterogeneous network, the first layer is the macro cell, and the rest K Layers are small cells. Densely deployed small base stations are connected to the core network through the backhaul provided by the macro base station. Both macro base stations and small base stations use full-duplex technology. When a link is established between a small base station and a macro base station, it is a small cell backhaul link. When a link is established between a user equipment and a small base station, it is a small cell access link. When a link is established between a macro base station and a user equipment, it is a small cell access link. is the access link of the macro cell.
[0056] Full-duplex technology is used for macro base stations using m...
Embodiment 2
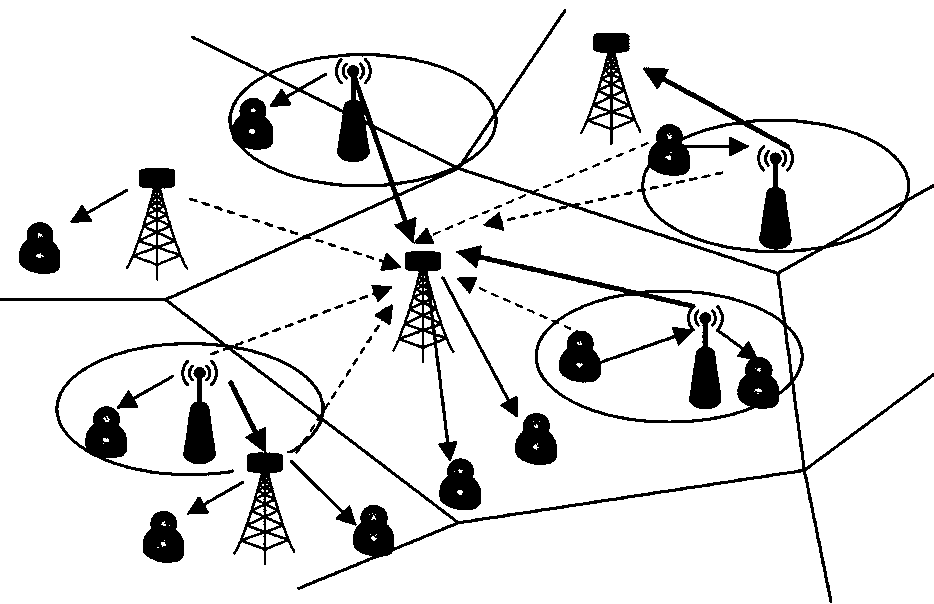
[0066] Based on Example 1, such as figure 1 As shown, this method is based on a K+1 layers of heterogeneous networks. It can be seen from the figure that the macro base station, the small base station and the user simultaneously receive and transmit information, and both the macro base station and the small base station use massive MIMO technology. like Image 6 As shown, the signal power and link reliability are improved by coherently processing the signal at multiple transceiver ports to achieve diversity gain. Using massive MIMO technology, separate links can be created to transmit independent data streams, providing more degrees of freedom for propagation channels and enabling multiplexing.
[0067] In addition, if Figure 7 As shown, in the heterogeneous network of this method, the small base station applies NOMA in the power domain. For users with poor channel conditions, larger power is allocated when sending information, and vice versa for users with better channel...
Embodiment 3
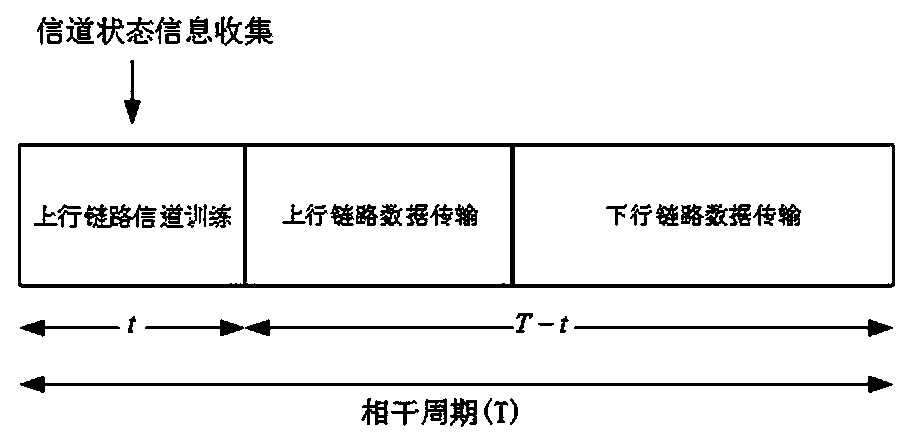
[0069] like Figure 8 As shown, the uplink transmission in two cells has The massive MIMO network representation from the first k The available channel gain from a user to its serving massive MIMO base station. Assuming i.i.d. Rayleigh fading channel model, the base station in the lth cell and the first k The complex propagation coefficient among users can be calculated as:
[0070]
[0071] is the complex fast fading factor, representing the first channel matrix of all users k List , is the magnitude factor affecting collective attenuation and shadow fading, assumed to be constant over frequency and the exponential of the base station antenna because geometric attenuation and shadow fading vary very slowly with respect to the spatial dimension, and gives:
[0072] ,
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com