Spinal support
A spine and magnesium alloy technology, applied in the field of spine stents, can solve problems such as reducing biocompatibility, allergic reaction, dislocation, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing re-collapse, facilitating expansion and maintaining height
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
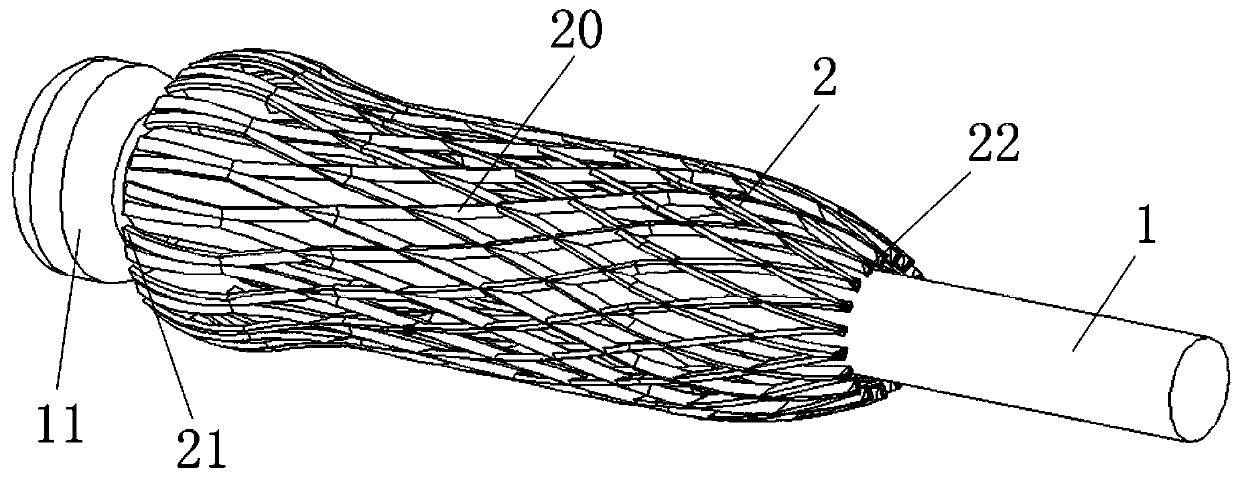
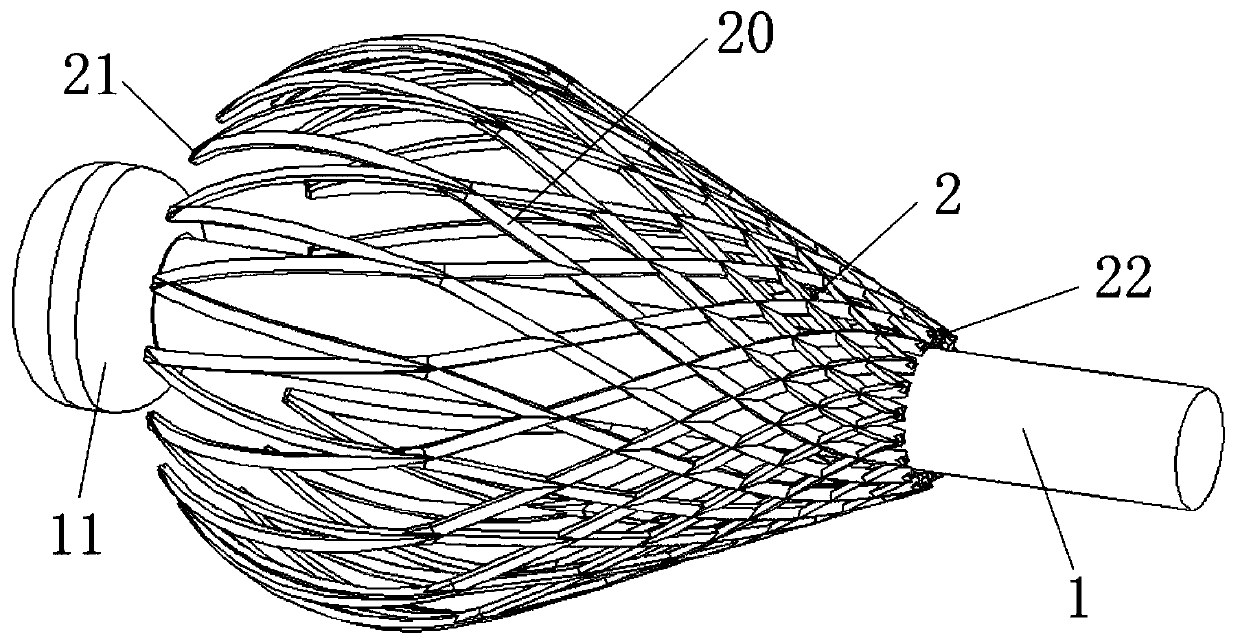
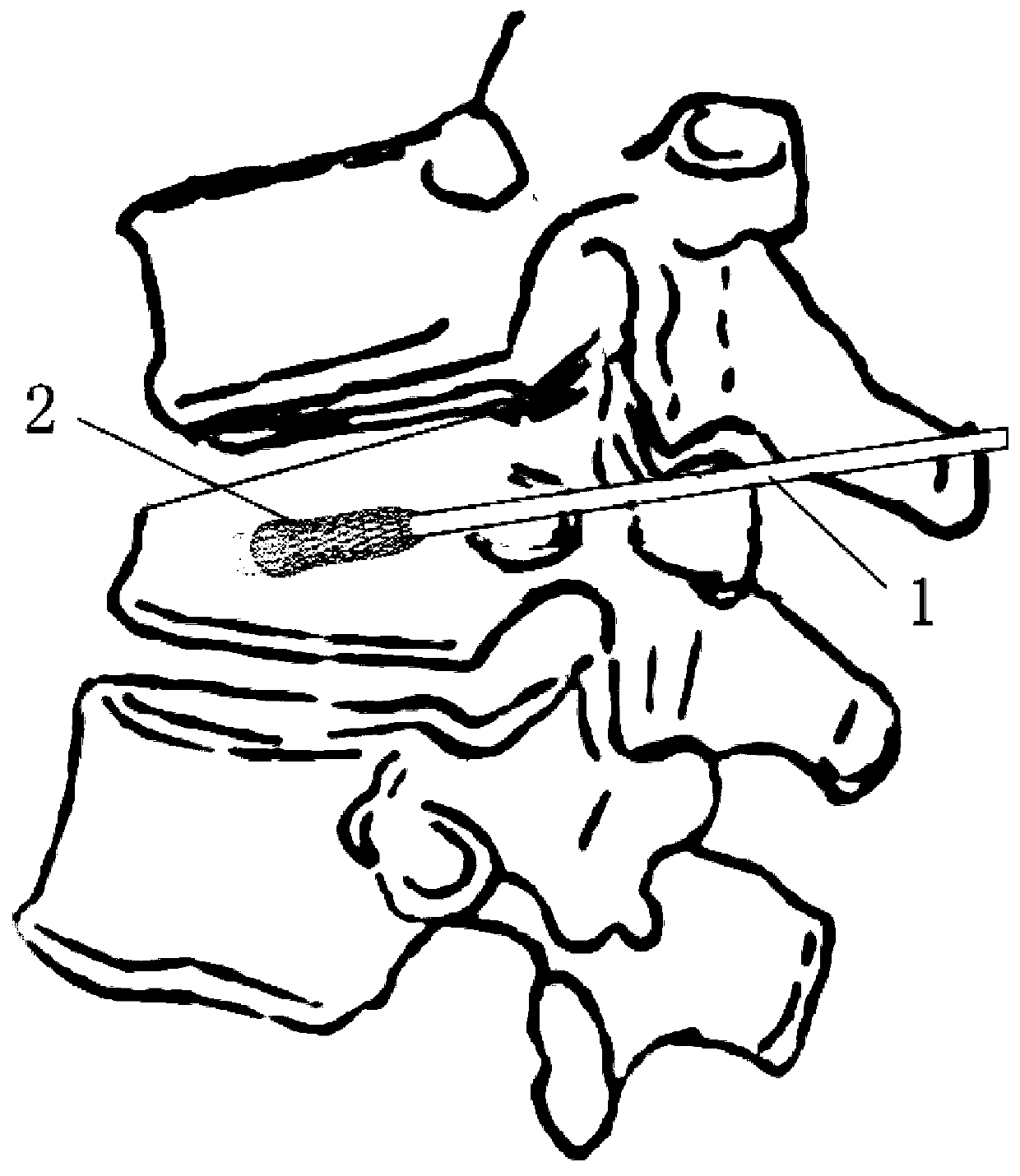
[0042] see figure 1 and figure 2 . figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of the preferred structural contraction state of the spinal column bracket of the present invention. figure 2 It is a structural schematic diagram of the preferred structural expansion state of the spinal column bracket of the present invention. The spinal bracket of the present invention includes a catheter 1 , an air bag and a magnesium alloy telescoping body 2 .
[0043] The airbag is arranged on the catheter 1, and the airbag communicates with the catheter 1; the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 has a front end 21 and a rear end 22, and the front end 21 and the rear end 22 are separated by The telescoping part covers the airbag; in the expanded state, the cross-sectional area of the front end 21 is larger than the cross-sectional area of the rear end 22 .
[0044] Specifically, the front end of the catheter 1 is provided with a position-limiting protrusion 11 for position-limiting. ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The structure of the spinal bracket of this embodiment is substantially the same as that of the first embodiment, except that in the contracted state, the length of the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 along the axial direction of the catheter 1 is 27 mm.
[0063] In the maximum expanded state, the maximum height of the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 along the radial direction of the catheter 1 is 17mm, and its maximum volume is 5.0ml. The magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 of this specification is suitable for patients with medium-sized vertebral bodies.
[0064] The optimum maximum height of the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 in this embodiment along the radial direction of the catheter 1 after expansion is 15 mm.
Embodiment 3
[0066] The structure of the spinal bracket of this embodiment is substantially the same as that of the first embodiment, except that, in the contracted state, the length of the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 along the axial direction of the catheter 1 is 31 mm.
[0067] In the state of maximum expansion, the maximum height of the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 along the radial direction of the catheter 1 is 17mm, and its maximum volume is 5.5ml. The magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 of this specification is suitable for patients with larger vertebral bodies.
[0068] The optimum maximum height of the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 in this embodiment along the radial direction of the catheter 1 after expansion is 16 mm.
[0069] Generally, the specifications of the magnesium alloy telescopic body 2 in Embodiment 1 to Embodiment 3 are the most commonly used.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com