Four kinds of single nucleotide polymorphism-based molecular markers of muskmelon blight resistance and their application
A single nucleotide polymorphism, molecular marker technology, applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of molecular markers and disease resistance genes. High-throughput screening and identification of vine blight, etc., to achieve the effect of improving vine blight resistance, efficiency and effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090]Example 1 Example 1, Flower Peel Telting Piga and Snow Red Cit Characters Defense
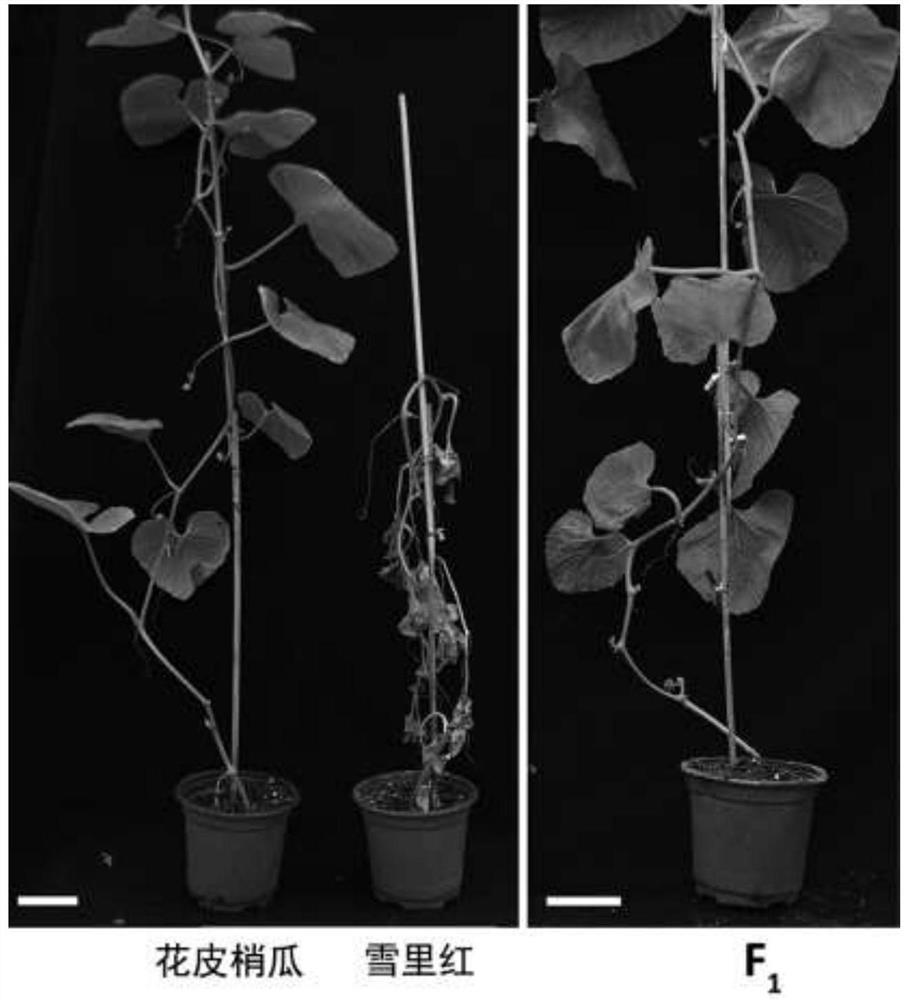
[0091]Choose a melon material from the laboratory germplasm --- Flower tip tap, snow red and flower peeling melons and snow red hybrids F1 progeny, melon sarametic bacteria vaccination, using plant pattern symptoms to determine resistance . Such asfigure 1 .
[0092]First, melon valence sick pathogen inoculation:
[0093]1), cultivation of citroen diseases
[0094]Configuration of PDA medium: Take 6.0 g of potato powder, 20.0 g of glucose, 20.0 g of agar powder, 2.0 g of dihydrogen phosphate 2.0 g, chloramphenicol 0.1 g. The above components were dissolved with distilled water to 1 L, and pH was transferred to 6, high temperature and high pressure sterilization for 20 min with NaOH or HCl.
[0095]Activation of the citroening bacteria: The strain preserved in glycerin from the ultra-low temperature refrigerator is taken out, and the strain is inoculated into the PDA medium on the ultra-net working table, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0111]Example 2, melon spande disease resistance genetic analysis and genetically positioning:
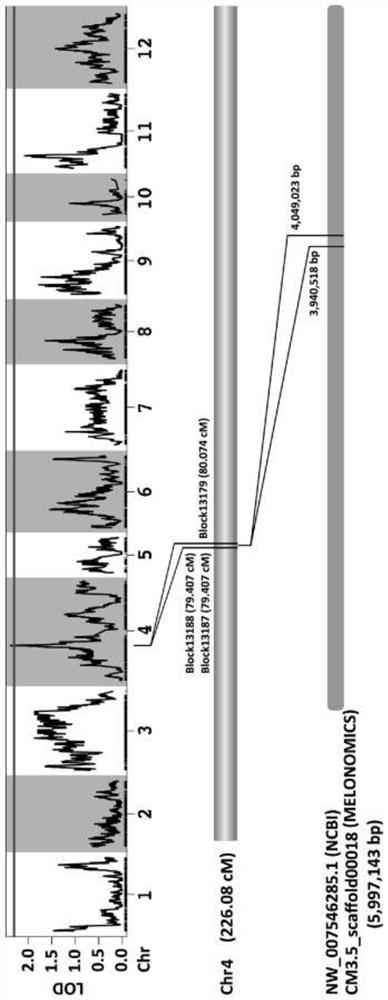
[0112]Choose a melon material from the laboratory germplasm - trumberry, snow red, flower peel tap melon and snow red hybrid F1 progeny and F1 self-employed F2 group, melon sarametic pathogen inoculation, The resistance of disease resistance is performed using the plants of phenotypic symptoms. The disease is then performed based on high-throughput relegation sequencing method, such asfigure 2 .
[0113]Resistant Genetic Analysis: Taking 219 monographs of the F2 population in Example 1, inoculation of the F2 population, according to the phenotype decision resistance, the F2 population has a separation of the disease of melon vine sickness. 165 strains of anti-illnesses, 54 susceptible plants, number of anti-illnesses: melon sensation plant = 3: 1, indicating that the anti-valence traits of the melon were controlled by dominant monologically.
[0114]Resistant gene positioning:
[0115]First, extract...
Embodiment 3
[0125]Example 3, development and verification with KASP tags
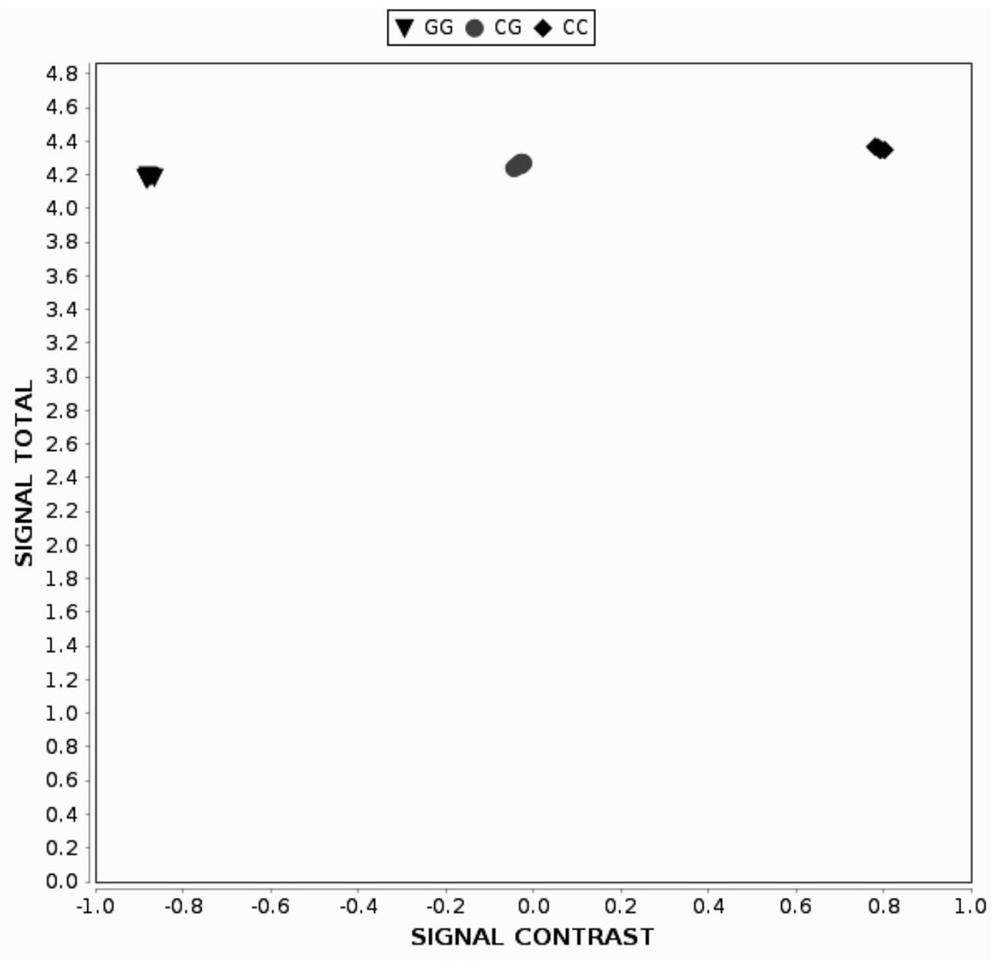
[0126]The specific approach is to select a melon material from the laboratory germplasm - trumberry, snow red, flower skin tip and snow red hybrid F1 generation and F1 self-employed F2 group, first put SNP Transformed into KASP tags, using primer KASP tags CMGSBRS1, CMGSBRS2, CMGSBRS3, CMGSBRS4 amplification to identify its genotype and genetic separation law.
[0127]1, KASP mark CMGSBRS1, CMGSBRS2, CMGSBRS3, CMGSBRS4 development:
[0128]First, SNP information extraction:
[0129]The SNP information is extracted with the resistance gene closely chain according to the second embodiment.
[0130]Second, extract DNA
[0131]Extract the tip of tap melon, snow red, flower peel tap melon and snow red hybrid F1 possession genomic DNA, and the method is in Example 2.
[0132]Third, PCR amplification
[0133]1), the reaction system
[0134]The primer sequence is as follows:
[0135]CMGSBRS1: Aliquot 1: Gaatctaccaaaagtatcagtagaaagag
[0136]Aliquot 2: Gaatc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com