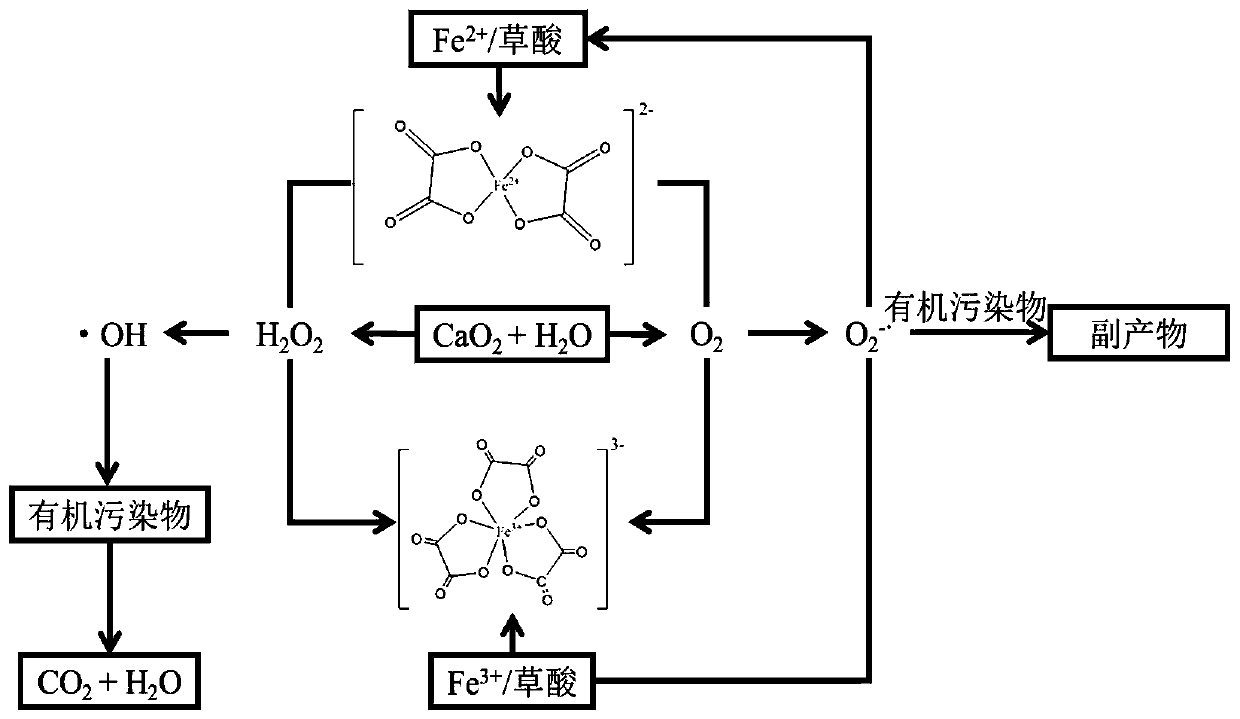
Method for treating organic waste water by iron complexing Fenton reaction
A technology of organic wastewater and Fenton reaction, applied in chemical instruments and methods, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problem of low degradation efficiency of organic wastewater and low production of active free radicals problems, to achieve the effect of promoting stable production, reducing precipitation, and avoiding disproportionation and decomposition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
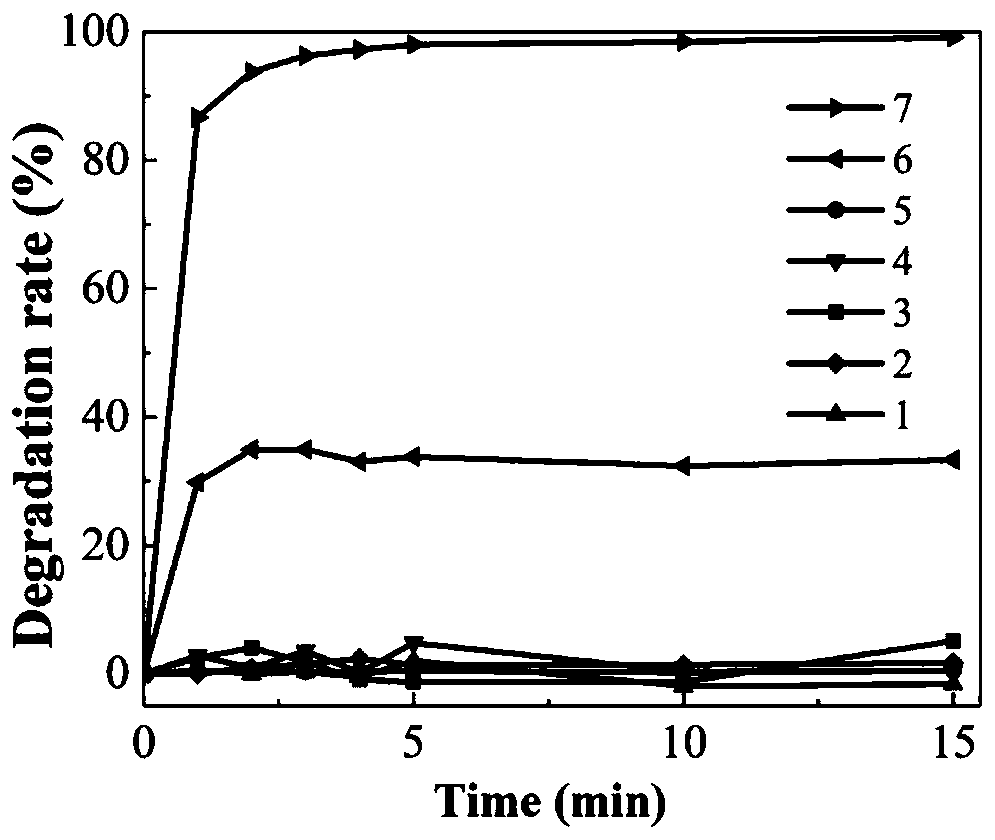
[0031] At room temperature, the FeSO 4 ·7H 2 The three reagents of O, oxalic acid and calcium peroxide, single system, two-two system and three systems were respectively added to the methyl orange solution with a concentration of 50mg / L and a volume of 100mL for reaction, and the FeSO in the obtained reaction solution 4 ·7H 2 The molar concentrations of O, oxalic acid and calcium peroxide were 1.5 mM, 3 mM and 3 mM, respectively. see results figure 2 .
[0032] Result analysis: After 15 minutes of reaction, in "oxalic acid", "FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O" "calcium peroxide", "oxalic acid + FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O" and "oxalic acid + calcium peroxide", almost no methyl orange degradation; secondly, in the "FeSO 4 ·7H 2 Under the action of "O+Calcium peroxide", the degradation rate of methyl orange was only 34%; while under the action of "FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O+oxalic acid+calcium peroxide" (that is, iron-complexed Fenton-like system), the degradation rate of methyl orange reaches 99.1%. figure ...
Embodiment 2
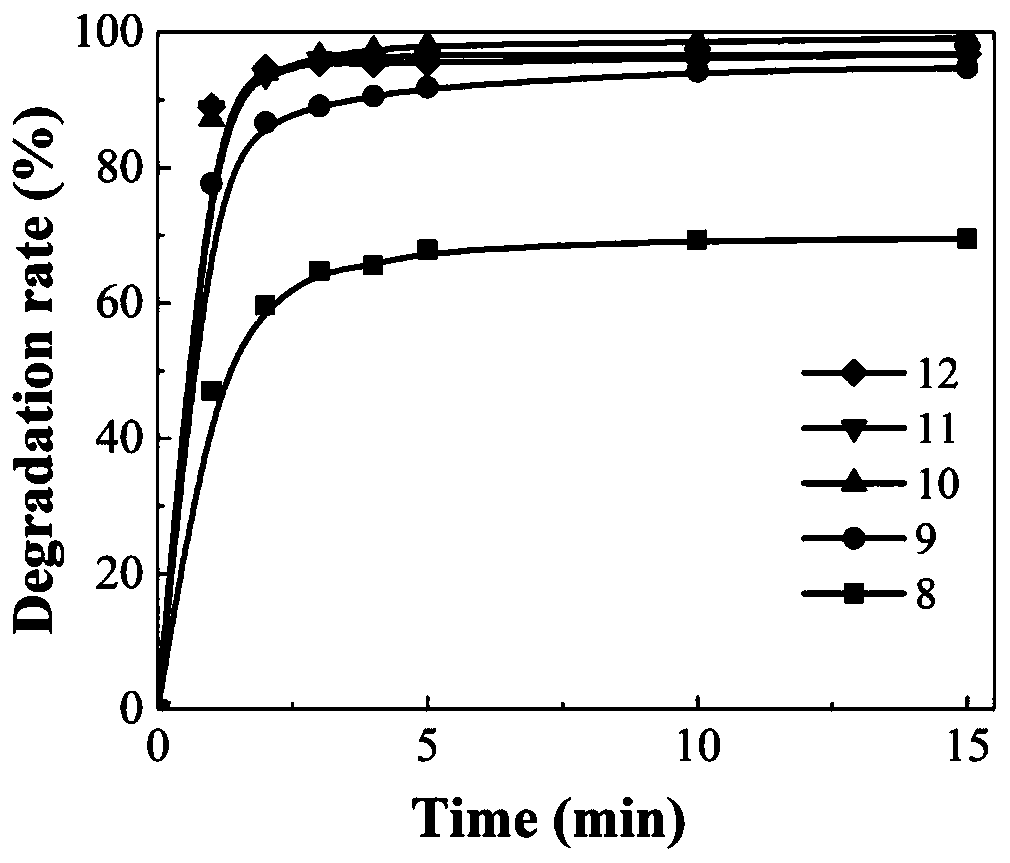
[0034] At room temperature, when adding FeSO 4 ·7H 2 In the case of O and oxalic acid, different volumes of calcium peroxide are added to a methyl orange solution with a concentration of 50 mg / L and a volume of 100 mL for reaction to obtain FeSO in the reaction solution. 4 ·7H 2 The molar concentrations of O and oxalic acid were 1.5mM and 3mM respectively, and the concentrations of calcium peroxide were 0.75mM, 1.5mM, 3mM, 4.5mM and 6mM respectively. see results image 3 .
[0035]Result analysis: When the molar concentration of calcium peroxide is 0.75mM, 1.5mM, 3mM, 4.5mM, 6mM, corresponding to curves 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12, the degradation rates of methyl orange after 15 minutes of reaction are respectively 69.4%, 94%, 99.1%, 96.8%, 96.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0037] At room temperature, in FeSO 4 ·7H 2 Under the premise that the molar ratio of O and oxalic acid is 1:2, 0.75mM, 0.3mM, 1.5mM, 3mM FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and proportional oxalic acid and calcium peroxide were added to the methyl orange solution with a concentration of 50 mg / L and a volume of 100 mL for reaction, and the molar concentration of calcium peroxide in the resulting reaction solution was 3 mM. see results Figure 4 .
[0038] Analysis of the results, when FeSO 4 ·7H 2 When the dosage of O is 0.3mM, 0.75mM, 1.5mM and 3mM respectively, it corresponds to curves 13, 14, 15 and 16 in turn. After 15 minutes of reaction, the degradation rates of methyl orange were 31.7%, 85.5%, 99.1%, and 97.4%, respectively.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com