A kind of red fluorescent carbon dot and its preparation method and application
A technology for red fluorescence and fluorescent carbon dots, which is applied in the field of red fluorescent carbon dots and their preparation, can solve the problems of biological tissue damage, weak emission, and limited application of carbon dots, and achieves stable optical properties, good solubility and dispersibility, and good Detect the effect of the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
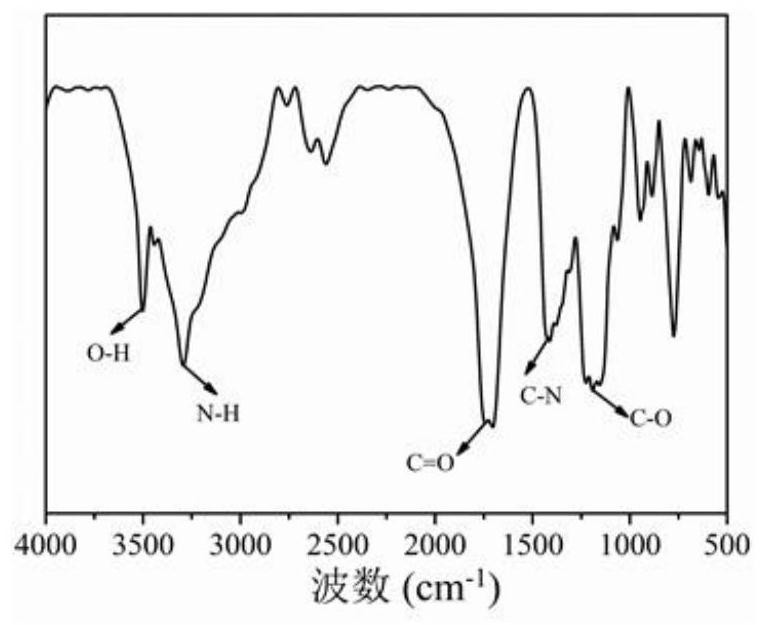
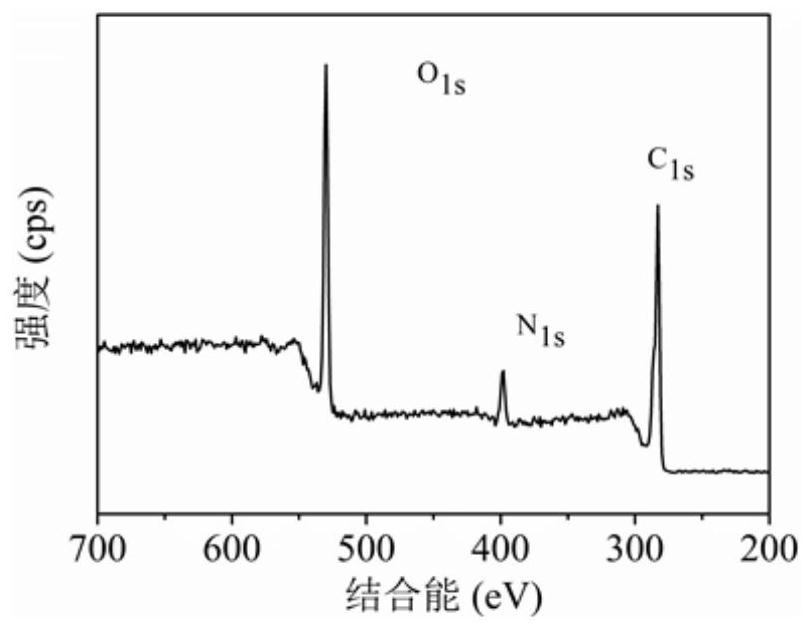
[0031] Step 1: Dissolve 2.5 mg of phenol saffron and 1.5 g of citric acid in 5 mL of deionized water at room temperature, stir well, and sonicate to obtain a clear solution.
[0032] Step 2, transfer the solution to a 25mL hydrothermal reaction kettle.
[0033] Step 3: Put the hydrothermal kettle in an oven and react at 180°C for 6 hours to obtain a red solution.
[0034] Step 4, take out the hydrothermal reaction kettle, cool naturally, and centrifuge the obtained carbon dot solution at 10000rpm for 10min to remove insoluble matter. Further filter with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane.
[0035] In step 5, red fluorescent carbon dots are obtained after freeze-drying the aqueous solution of fluorescent carbon quantum dots. Its fluorescence quantum yield (based on rhodamine B) is 8.3%.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Step 1, at room temperature, dissolve 1.8 mg of phenol saffron red and 1.2 g of citric acid in 2.5 mL of deionized water, stir well, and sonicate to obtain a clear solution.
[0038] Step 2, transfer the solution to a 25mL hydrothermal reaction kettle.
[0039] Step 3: Put the hydrothermal kettle in an oven and react at 160°C for 4 hours to obtain a red solution.
[0040] Step 4, take out the hydrothermal reaction kettle, cool naturally, and centrifuge the obtained carbon dot solution at 10000rpm for 10min to remove insoluble matter. Further filter with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane.
[0041] In step 5, red fluorescent carbon dots are obtained after freeze-drying the aqueous solution of fluorescent carbon quantum dots. Its fluorescence quantum yield (based on rhodamine B) is 3.8%.
Embodiment 3
[0043] Step 1. Dissolve 3.0 mg of phenol saffron and 1.8 g of citric acid in 7.5 mL of deionized water at room temperature, stir well, and sonicate to obtain a clear solution.
[0044] Step 2, transfer the solution to a 25mL hydrothermal reaction kettle.
[0045] Step 3: Put the hydrothermal kettle in an oven and react at 220°C for 8 hours to obtain a red solution.
[0046] Step 4, take out the hydrothermal reaction kettle, cool naturally, and centrifuge the obtained carbon dot solution at 10000rpm for 10min to remove insoluble matter. Further filter with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane.
[0047] In step 5, red fluorescent carbon dots are obtained after freeze-drying the aqueous solution of fluorescent carbon quantum dots. Its fluorescence quantum yield (based on rhodamine B) is 6.7%.
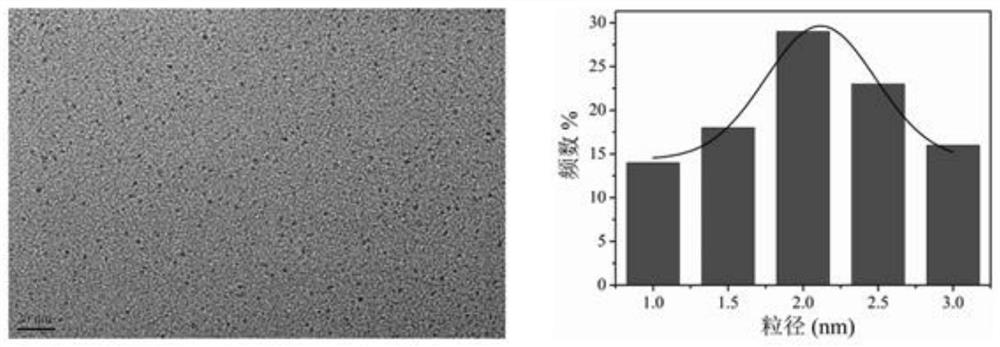
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com