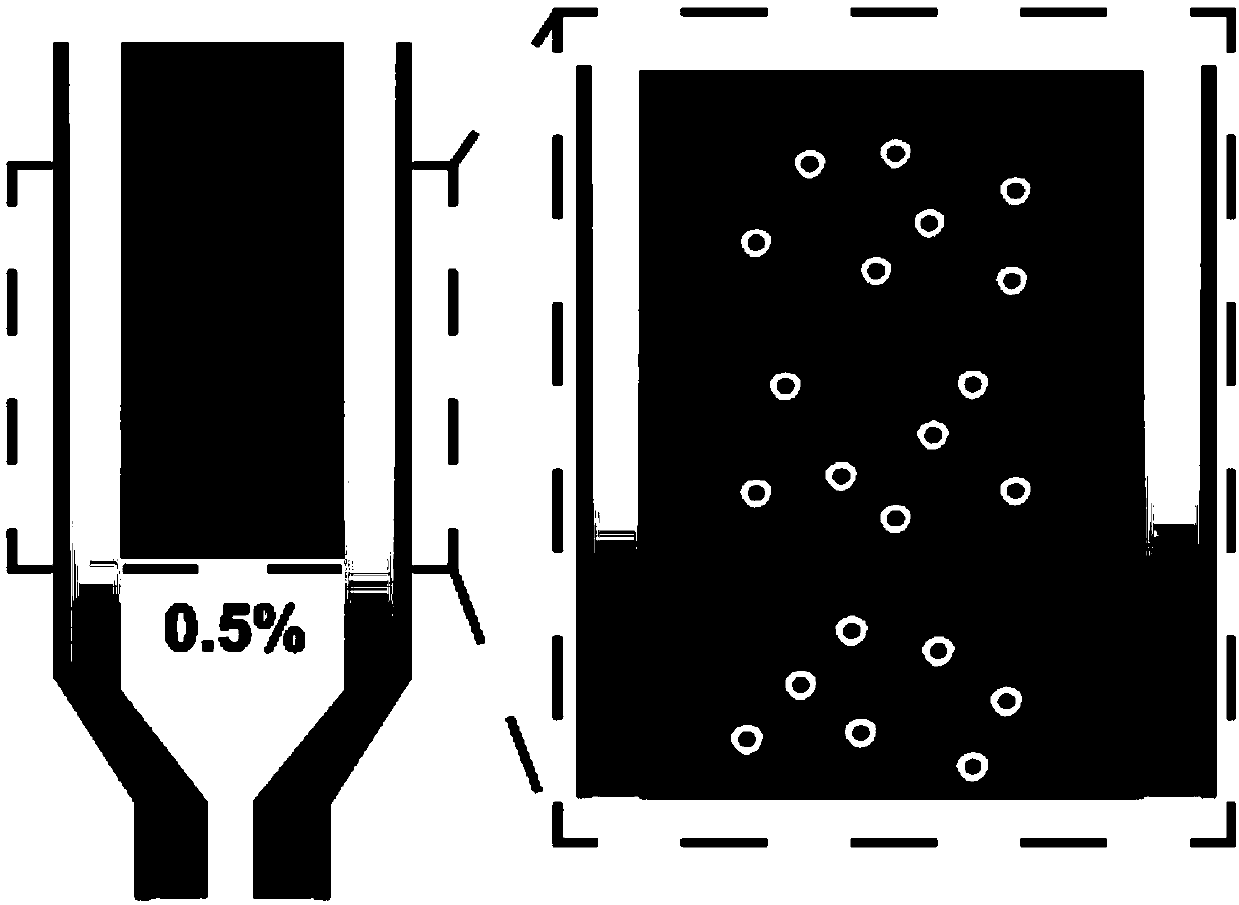
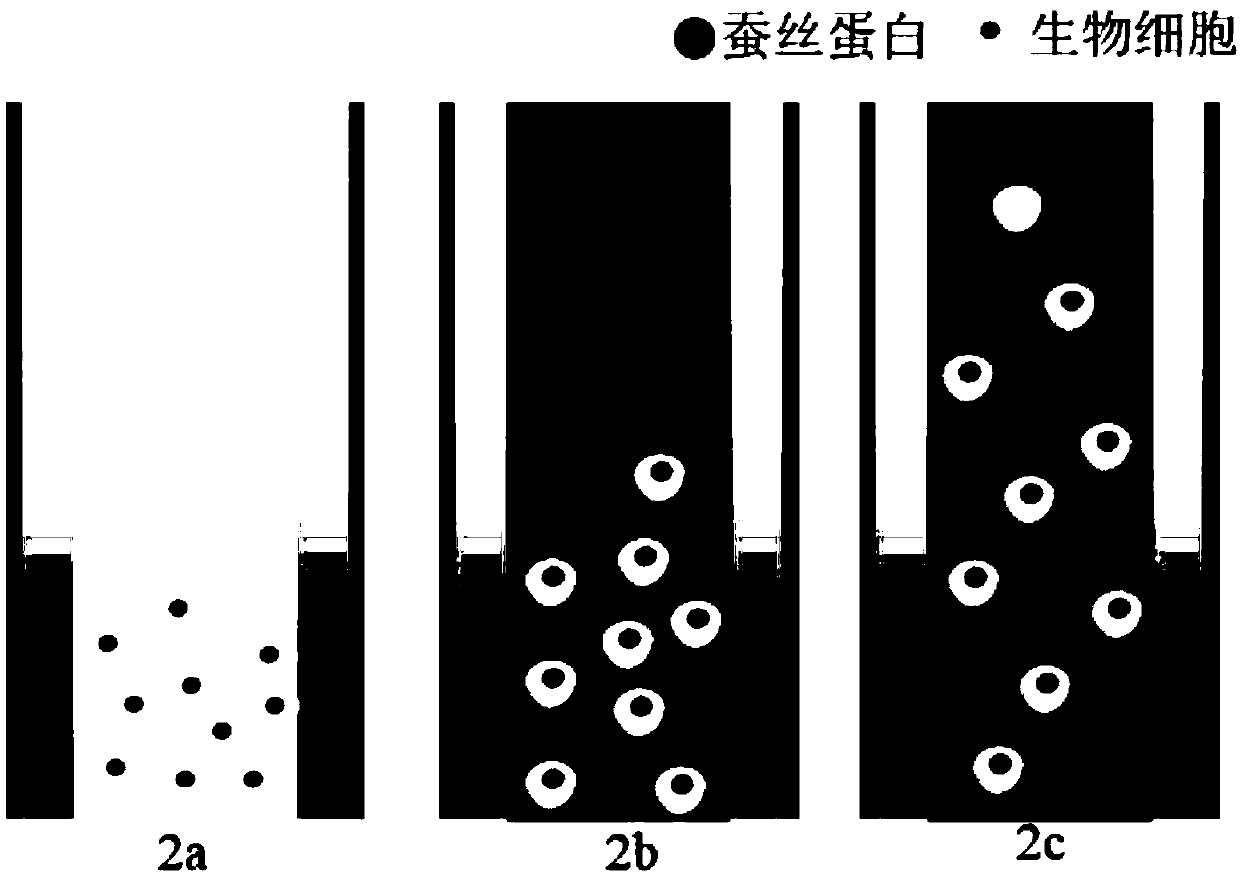
Biologic ink with uniformity-distribution cells based on 3D printing and assembly method thereof
A bio-ink and 3D printing technology, applied in medical science, prosthesis, additive processing, etc., can solve the problem of uneven cell distribution, achieve the effects of slowing down cell deposition, good application prospects, and maintaining biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The bioink body A of the embodiment of the present invention is made up of the following mass fraction components:
[0049]
[0050]The preparation method of the bio-ink body A of the embodiment of the present invention is as follows: dissolve the methacrylic anhydride gelatin in the HEPES equilibrium buffer solution according to the above ratio, add photoinitiator 2959, and stir at 50°C to obtain a uniformly mixed solution. Filter and sterilize with PES membrane filter, then cool down to 37°C, finally add silk protein and fetal bovine serum, and mix evenly by ultrasonic.
[0051] Will 1╳10 6 A bioactive cell was added to the prepared bio-ink body A and mixed evenly to obtain bio-ink A.
Embodiment 2
[0053] The bioink body B of the embodiment of the present invention is made up of the following mass fraction components:
[0054]
[0055] The preparation method of the bio-ink body B of the embodiment of the present invention is the same as that of embodiment 1.
[0056] Will 1╳10 6 A bioactive cell was added to the prepared bio-ink body B and mixed evenly to obtain bio-ink B.
Embodiment 3
[0058] The bioink body C of the embodiment of the present invention is made up of the following mass fraction components:
[0059]
[0060] The preparation method of the bio-ink body C of the embodiment of the present invention is the same as that of the embodiment 1.
[0061] Will 1╳10 6 A bioactive cell is added to the prepared bio-ink body C and mixed evenly to obtain bio-ink C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com