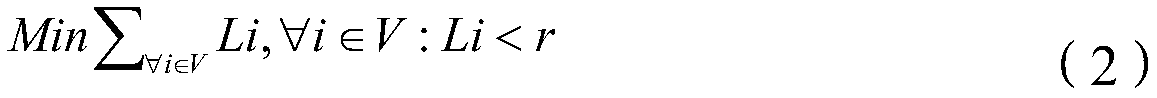Wireless sensor network fault recovery system based on minimum spanning tree
A technology for wireless sensors and network faults, applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, wireless communications, etc., can solve problems such as network connectivity damage and failure to comprehensively consider node performance indicators, and achieve simplified complexity, fast recovery of connectivity, and The effect of shortening the average distance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
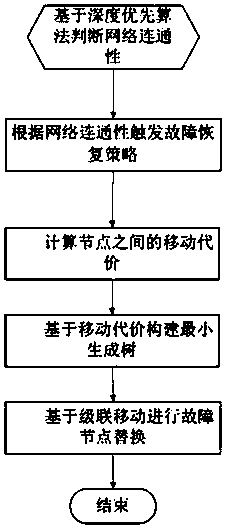
[0071] This embodiment provides a minimum spanning tree-based wireless sensor network fault recovery method, which includes:
[0072] (1) Based on the depth-first network connectivity judgment, according to this step, it can be judged whether the current network is connected, so as to determine whether a recovery strategy needs to be adopted;
[0073] (2) Based on the minimum spanning tree to implement the fault recovery strategy, this step can select the best neighbor node that meets the constraints according to the moving cost of the node, and construct the minimum spanning tree based on the moving cost; at the same time, by using the minimum spanning tree, the fast Select the next mobile node, and move the neighbor node to the faulty node for replacement in cascade movement, so as to achieve the purpose of restoring connectivity, and effectively reduce the moving distance of the node and save the energy of the node.
[0074] Wherein, the step (1) implements the judging proc...
Embodiment 2
[0077] In order to solve the problem of network connectivity recovery in real time in the case of a node transmission failure, this embodiment uses a depth-first method to determine whether the entire network is connected. The tree algorithm selects neighbor nodes, and finally moves the neighbor nodes to the faulty node through cascading to replace the faulty node. After the above steps, the network returns to the normal working mode. On this basis, this embodiment carries out the minimum spanning tree reconstruction process based on the node cost, recalculates the node cost of the node after the failure recovery, and updates the minimum spanning tree. Tree. The content of this embodiment will be further described below.
[0078] 1. Trigger failure recovery strategy based on network connectivity
[0079] (1) Judging network connectivity based on depth-first algorithm
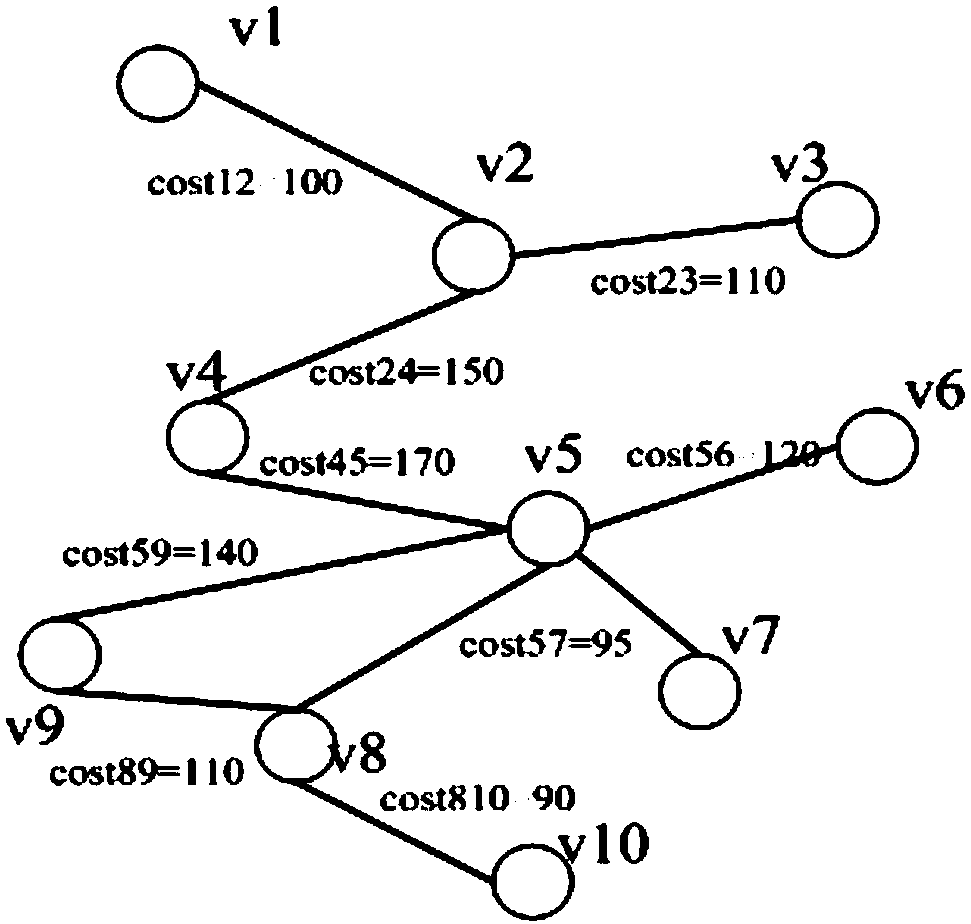
[0080] Suppose a certain network G=(V,E), V represents a set of nodes, and E represents a set of connectio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com