Method for detecting fat coverage of Simmental cattle carcass by dlk1 gene marker
A Simmental, coverage technology, used in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
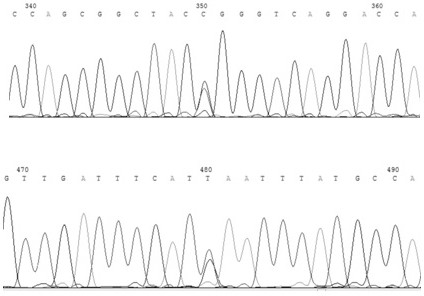
[0022] The acquisition of DLK1 gene fragments in Chinese Simmental cattle and the establishment of polymorphism detection methods in functional regions:
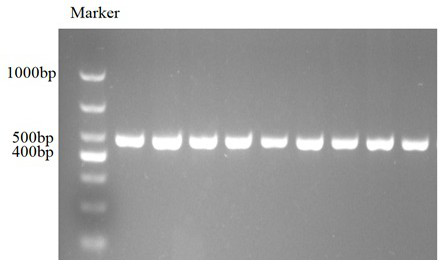
[0023] 1.1 Test materials: 237 28-month-old Chinese Simmental bulls came from Baolongshan beef cattle fattening farm in Tongliao City, Inner Mongolia. Jugular vein blood collection, all blood samples were 10 mL / head, anticoagulated with ACD anticoagulant, and frozen at -20°C. Genomic DNA was extracted from blood samples with a blood genomic DNA extraction kit;
[0024] 1.2 Primer design and PCR amplification: Chinese Simmental cattle were selected as test materials. In order to detect as many SNPs sites as possible, fragments with higher SNP density were selected, and the following primer pairs were designed according to the selected bovine DLK1 gene sequence:
[0025] Forward primer F: 5'-TCCACAGTGGAGGCTACTAAG-3';
[0026] Reverse primer R: 5'-CTTGTCTCCTGACTTCCTAAG-3';
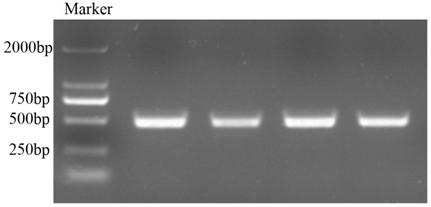
[0027] Carry out PCR amplification in the Chinese ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The DLK1 gene SNPs genetic markers obtained by screening were used to calculate the genotype frequency and gene frequency.
[0037] The C allele frequency of DLK1-478 C / T locus in Chinese Simmental cattle population is 0.865, and CC is the dominant genotype; the T allele frequency of DLK1-609 T / G locus is 0.846, and TT is the dominant genotype .
[0038]Table 1. Genetic diversity of 2 SNPs of DLK1 gene in Chinese Simmental cattle population
[0039] SNP mapping group sample allele frequency genotype frequency I3-478 C>T 237 C (0.865) T (0.135) CC (0.738) CT (0.253) TT (0.008) I3-609 T>G 217 T(0.846) G (0.154) TT (0.719) TG (0.234) GG (0.028)
Embodiment 3
[0041] Association analysis of DLK1 molecular genetic markers with Chinese Simmental beef quality and carcass traits:
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com