Built-in device for individualized branch stent type arch part reconstructed artificial blood vessel
An artificial blood vessel and built-in device technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of inability to accurately control the bleeding in the descending part of the operation field, high operative mortality and complication rates, spinal cord damage, etc. Uniform thickness and precise bleeding control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
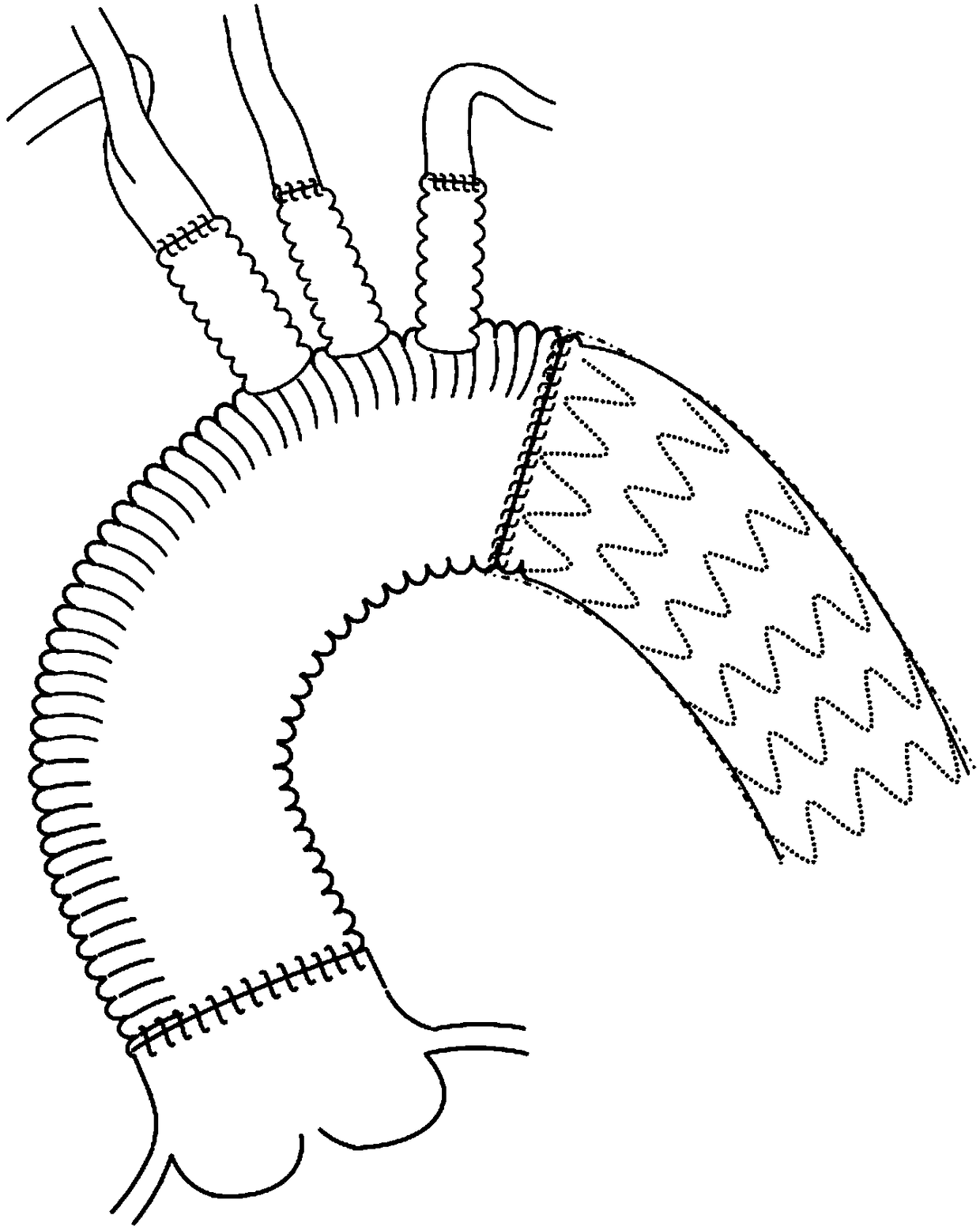
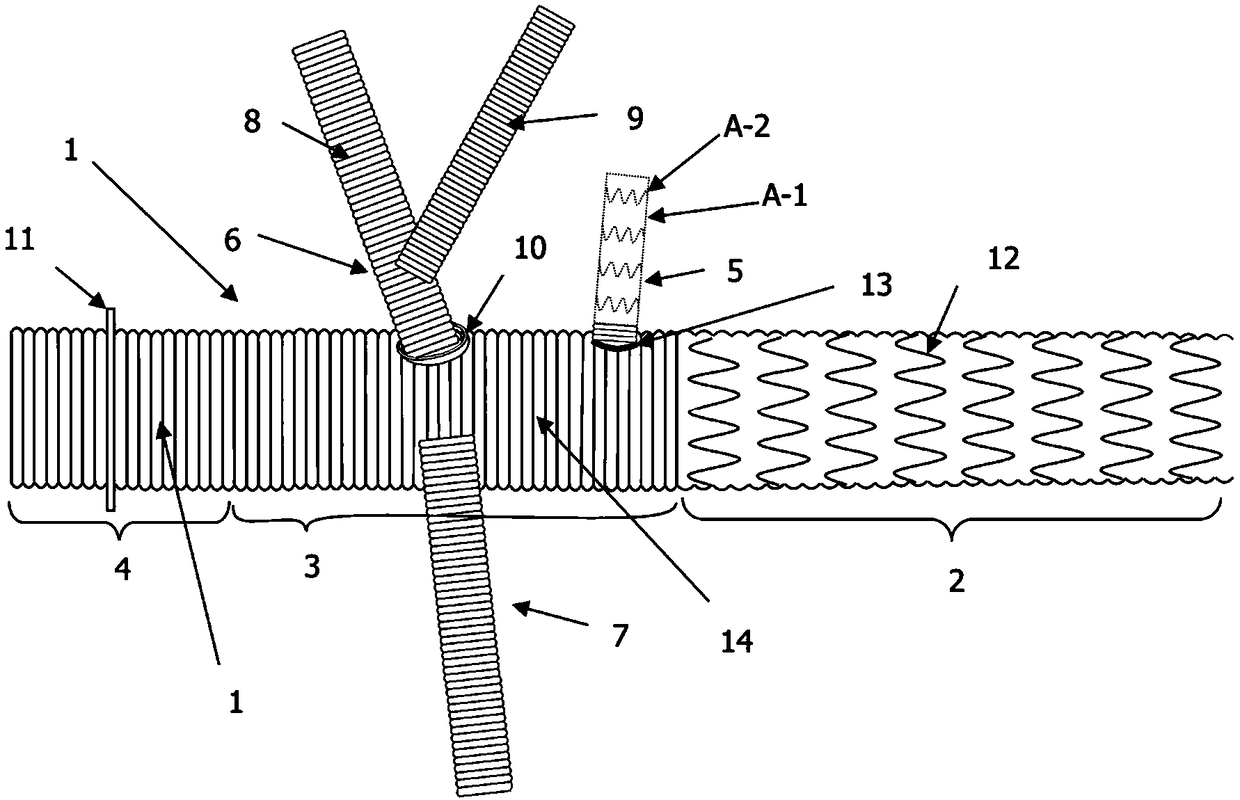
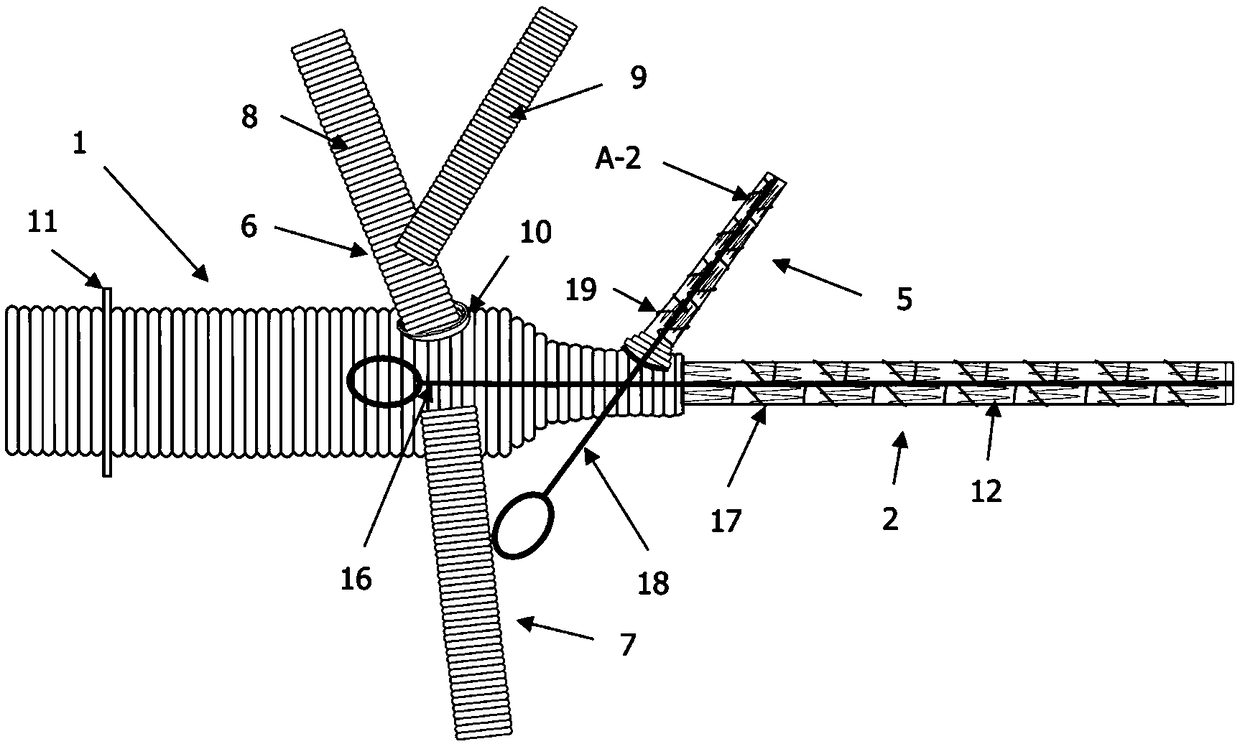
[0022] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 2 to Figure 6 This embodiment is described. This embodiment includes a hard arch 20. The hard arch 20 is an arc-shaped pipe with the same radius of curvature or a radius of curvature that gradually decreases from the proximal end to the distal end. The hard arch 20 is provided with a plurality of branch windows and annular indentations 24, and the rigid arch 20 is installed inside the arch aortic stent vessel 3 of the individualized branch stent-type arch reconstruction artificial blood vessel.
[0023] This embodiment can quickly realize the fast suture-free connection of the ascending aorta.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0024] Specific implementation mode two: combination Figure 2 to Figure 4 Describe this embodiment, the front upper edge of the hard arch 20 of this embodiment is provided with a branch window 1 21, the upper edge of the end section of the hard arch 20 is provided with a branch window 2 22, the hard arch 20 The ventral side of the middle section is provided with a branch window 3 23; so set, the Y-shaped arch branch 6, branch stent blood vessel 5, and arch branch 4 7 of the inventive branch stent type arch reconstruction artificial blood vessel reserve their respective entrances in the aortic arch. The blood port ensures sufficient blood supply to all brachiocephalic arteries; the position of the branch window 22 is designed to match the origin of the left subclavian artery at the top of the arch under normal conditions, ensuring accurate endovascular treatment in situ and avoiding its Displacement and endoleak occurred; the first branch window 21 corresponds to the common ro...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0025] Specific implementation mode three: combination Figure 2 to Figure 4 To illustrate this embodiment, the first branch window 21 and the third branch window 23 of this embodiment are both circular or elliptical openings, and the second branch window 22 is a semicircular hole with an open distal end. In this way, the branch window 1 is consistent with the shape of the root of the branch 6 of the Y-shaped arch, which is the common root of the innominate artery and the left common carotid artery, and the opening is slightly larger than the root of the branch 6 of the Y-shaped arch, so as to ensure sufficient blood supply to the two brachiocephalic arteries; The second branch window 22 is located at the distal end of the hard arch 20, corresponding to the root of the left subclavian artery. Under normal circumstances, the aortic arch will turn backwards after the left subclavian artery is sent out, and the individual variation is large, so the hard arch should not be too lon...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bending angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Bending radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com