A method for the production of colaric acid by acid-resistant high-density Escherichia coli
A technology of Escherichia coli and koala acid, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of low efficiency of koala acid, and achieve the effects of high yield, short fermentation time and fast cell growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 Escherichia coli species Escherichia coli S17-3 Acquisition, Identification and Preservation
[0048] Escherichia coli S17-3 A model Escherichia coli used in laboratories around the world Escherichia coli The mutant strain of S17-1, the Escherichia coli has undergone ultraviolet mutagenesis in the inventor's laboratory, and long-term cultivation, both ultraviolet mutagenesis and natural random mutation may cause changes in the properties of microorganisms. The strain's culture performance changes, as well as subsequent genome sequencing and comparison, have confirmed that mutations at multiple gene sites have occurred, and were preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 16, 2018, with the preservation number of CCTCC 2018200.
[0049] Escherichia coli species isolated by the present invention Escherichia coli S17-3, which is a short bacillus with blunt ends, about 0.5 um-3 um in size, has milky white and smooth surface round colo...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Construction method of Escherichia coli S17-3 high-density growth system
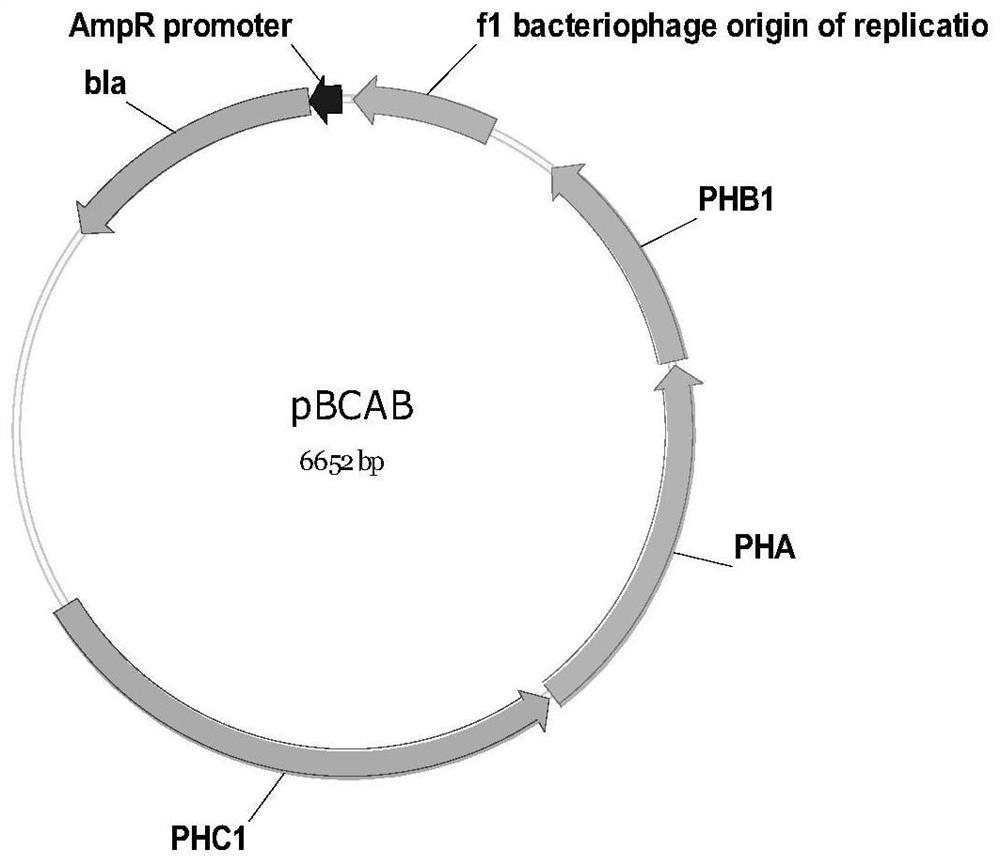
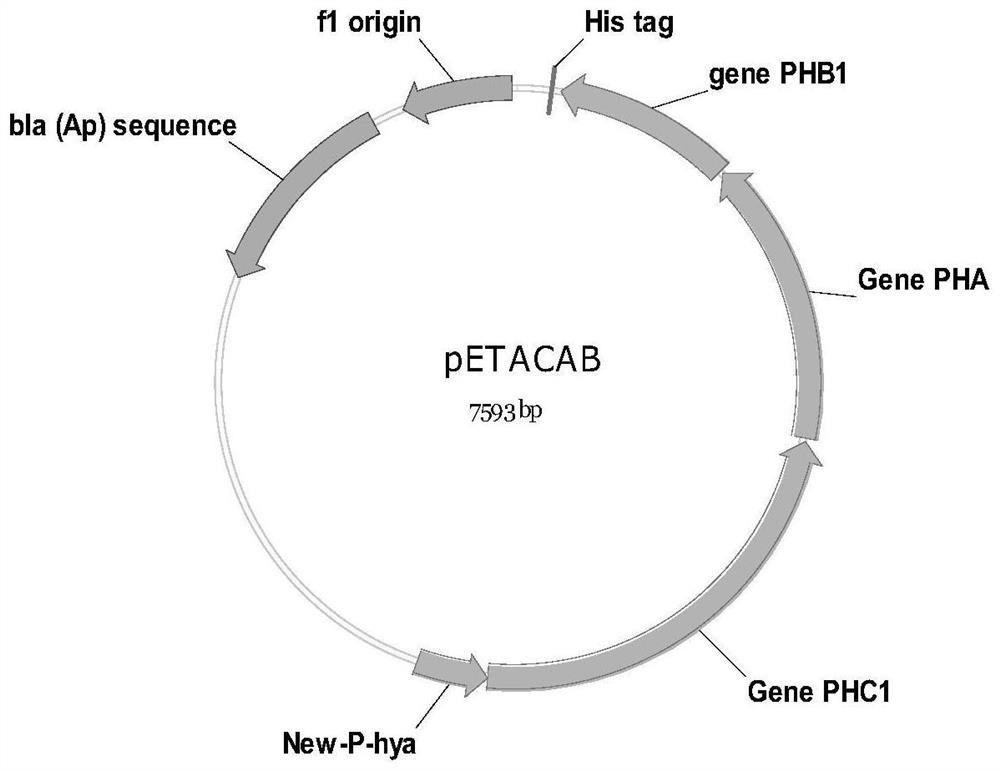
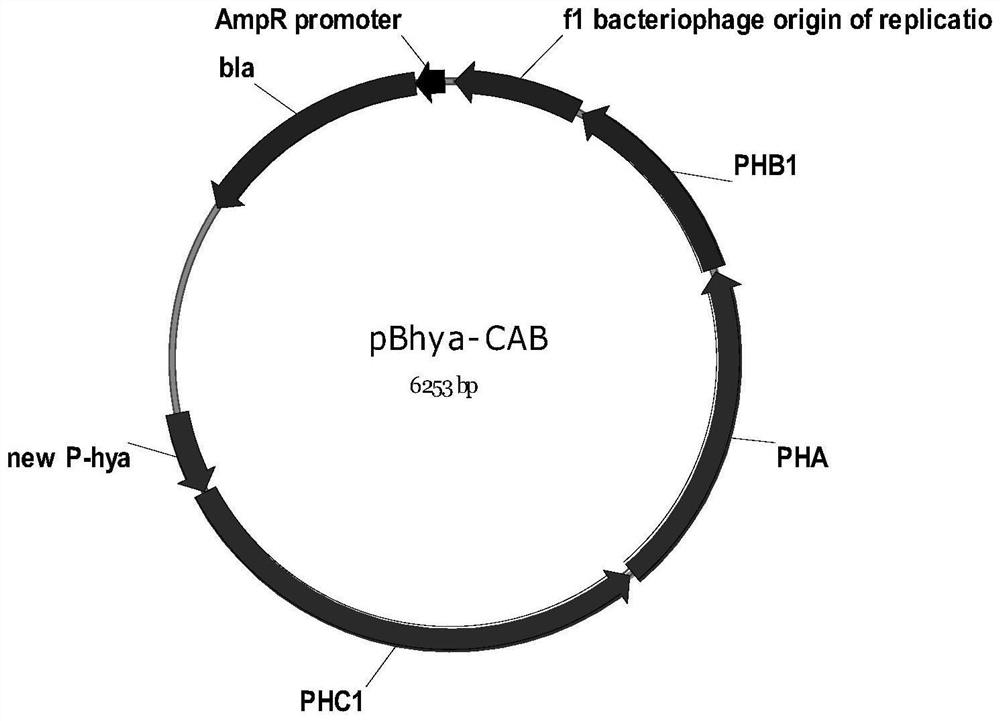
[0056] a. Construction of recombinant plasmids pETACAB and pBhya-CAB
[0057] The map of the constructed recombinant plasmid pETACAB is as follows figure 2 shown. First, a 3870 bp fragment was excised from the plasmid pET-A stored in the laboratory by double enzyme digestion (restriction sites Nde I and Hind III) (the nucleotide sequence of the 3870 bp fragment is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, Specifically:
[0058]tatggcacgtctctcctccttgcgacaccggcaggacaccgggcgcttatggtcggcaagcgacgtccctgtagcaaggcaaaccatcgcttcacgtgagatgctgaaaacgaaagctcatccttctgcactggcgcacgtcgccagaaagtattgttaataaagcgtagtgaaacttttgcacaaaacaatacaaactgtgtggatttatcttttagcgataaaaatggacctatttttcttttggccgggcggtggggatgtttagccggttgctaaacgagtaaaagagaaggaattcggatcctagagggaaaccgttgtggtctccctatagtgagtcgtattaatttcgcgggatcgagatctcgggcagcgttgggtcctggccacgggtgcgcatgatcgtgctcctgtcgttgaggacccggctaggctggcggggttgccttactggttagcagaatgaatcaccgatacgcga...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Example 3 Recombinant Escherichia coli fermented and produced colaric acid at an initial low pH value
[0105] Use recombinant Escherichia coli S17-3 / pBhya-CAB as the production strain for shake flask fermentation: pick Escherichia coli S17-3 / pBhya-CAB with an inoculation loop and inoculate it into a test tube containing 3 ml LB, at 37 °C, 200 r / overnight on a shaker. Inoculate the overnight cultured Escherichia coli into a 500 mL shake flask containing 50 mL of liquid LB medium at an inoculum size of 1%, add 20 g / L of glucose and 50 ul of 100 ug / ml of ampicillin , and also carried out fermentation culture at 37°C, 200 r / min shaker. The initial pH of the medium was controlled at pH 4.5 using 3 M hydrochloric acid. After 24 hours of fermentation, samples were taken to measure the production of coracic acid. The method for determining the production of coracic acid is as follows: firstly prepare a fucose mother liquor of 10 g / L, and dilute the mother liquor to a conce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com