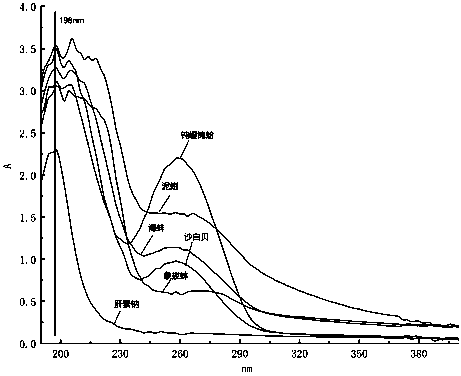
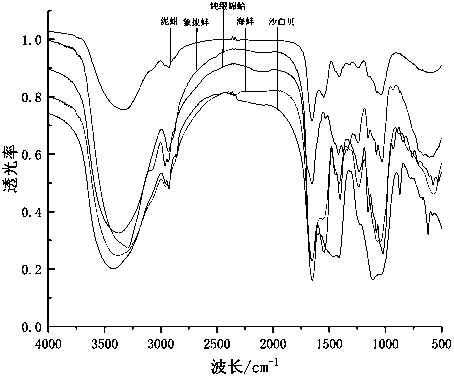
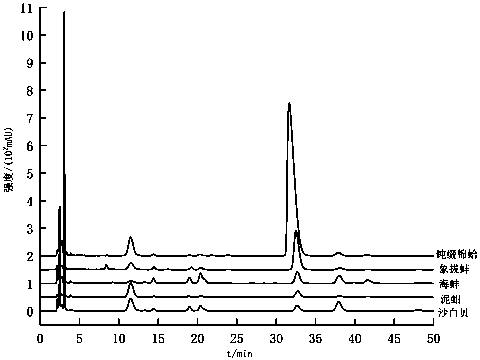
Shellfish heparin with mild anti-coagulation effect as well as preparation method and application thereof
A shellfish and heparin technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of large loss of product activity, high energy consumption, extraction of heparin, etc., and achieve the effects of simple preparation method, stable product quality, and broadening sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] The preparation of embodiment 1 shellfish heparin
[0052] 1. A method for preparing shellfish heparin, comprising the following steps:
[0053] S1. Raw material treatment: wash shellfish raw materials, after shelling, put shellfish meat in acetone at 2°C and soak for 20 hours, remove acetone by suction filtration at room temperature, rinse with distilled water for 3 to 5 times, then add distilled water (solid-liquid ratio =1:3) for homogenization to obtain a homogenate solution; wherein, the shellfish is selected from any one of sea mussels, geoducks, mud clams, clams or clams.
[0054] S2. Autolysis: autolyze the homogenate in a water bath at 50°C for 5 hours;
[0055] S3. Enzymolysis: add NaOH to adjust the pH to 8.0, first add 0.5% trypsin, and enzymolyze at 37°C for 5 hours, then add HCl to adjust the pH to 7.0, then add 0.5% papain, and enzymolyze at 65°C 5h, to obtain the enzymatic solution;
[0056] S4. Enzyme inactivation and centrifugation: put the enzymati...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The preparation of embodiment 2 shellfish heparin
[0062] 1. A method for preparing shellfish heparin, comprising the following steps:
[0063] S1. Raw material processing: wash the shellfish raw material, remove the shell, add distilled water (material-to-liquid ratio=1:1.5) for homogenization, and obtain a homogenate;
[0064] S2. Autolysis: autolyze the homogenate in a water bath at 38°C for 7 hours;
[0065] S3. Enzymolysis: add NaOH to adjust the pH to 7.8, first add 0.3% trypsin, and enzymatically hydrolyze at 32°C for 6.5h, then add HCl to adjust the pH to 6.8, then add 0.3% papain, and enzymatically digest at 62°C Decompose for 5.5h to obtain the enzymatic solution;
[0066] S4. Enzyme inactivation and centrifugation: put the enzymatic solution in boiling water to inactivate the enzyme for 5 minutes, and centrifuge at 8000 rpm for 10 minutes;
[0067] S5. Concentration and alcohol precipitation: After concentrating the supernatant, add 0.3 times the volume o...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The preparation of embodiment 3 shellfish heparin
[0072] 1. A method for preparing shellfish heparin, comprising the following steps:
[0073] S1. Raw material treatment: wash shellfish raw materials, after shelling, put shellfish meat in acetone at 6°C and soak for 28 hours, remove acetone by suction filtration at room temperature, rinse with distilled water for 3 to 5 times, then add distilled water (ratio of solid to liquid) =1:4.5) for homogenization to obtain a homogenate;
[0074] S2. Autolysis: autolyze the homogenate in a water bath at 62°C for 3 hours;
[0075] S3. Enzymolysis: add NaOH to adjust the pH to 8.2, first add 0.7% trypsin, enzymatically hydrolyze at 42°C for 3.5h, then add HCl to adjust the pH to 7.2, then add 0.7% papain, enzymatically at 68°C Decompose for 4.5h to obtain the enzymatic solution;
[0076] S4. Enzyme inactivation and centrifugation: put the enzymatic solution in boiling water to inactivate the enzyme for 15 minutes, and centrifu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com