Construction of a protein tag vector and its expression and detection method
A construction method and protein technology, applied in the field of biomarkers, can solve problems such as difficulty, non-expression, and uncertainty of the length of the target gene promoter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] It should be noted that the following biotechnology terms are involved in the embodiments of the present invention:
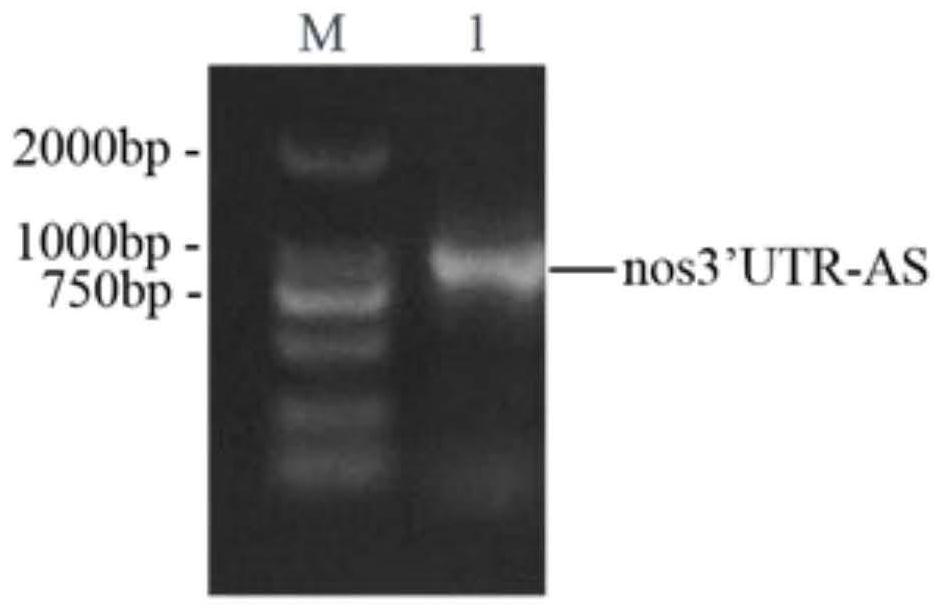
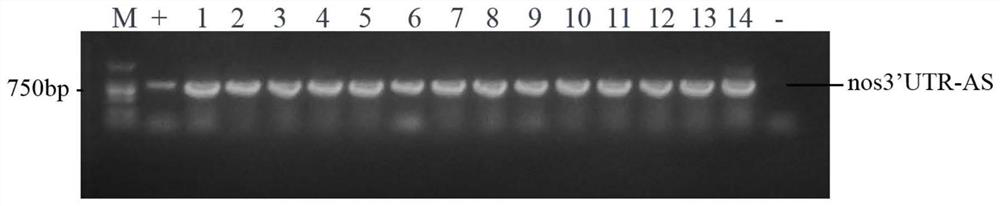
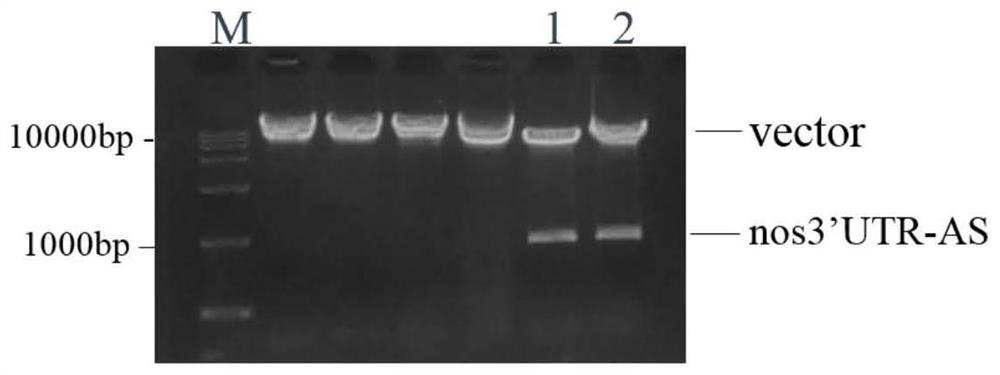
[0039] (1) Marking of the last exon: firstly, the penultimate exon of a gene in the genome (here, the nanos gene, called the target gene) (here, the third exon of the nanos gene, Exon 3) downstream partial sequence", "the last intron (here is the 3rd intron of the nanos gene, Intron 3)", "the last exon (here is the 4th exon of the nanos gene , Exon 4) and its downstream 100bp sequence" were amplified and cloned, called the target sequence. Then, a tag sequence (such as GFP) is inserted in front of the stop codon (such as TAG) after the internal coding sequence of the exon at the end of the target sequence to obtain the transformed target sequence. Finally, the modified target sequence is integrated into the genome through the carrier of the transgene, and the sequence can participate in the RNA splicing and protein translation of the target gene in the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com