An organic electroluminescent device and a display device
An electroluminescent device and electroluminescent technology, applied in the direction of electro-solid devices, electrical components, luminescent materials, etc., can solve the problems of low luminous efficiency and low lifespan of devices, and achieve the goal of improving luminous efficiency, reducing energy level barrier, improving Effect of Luminous Efficiency and Lifespan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-7
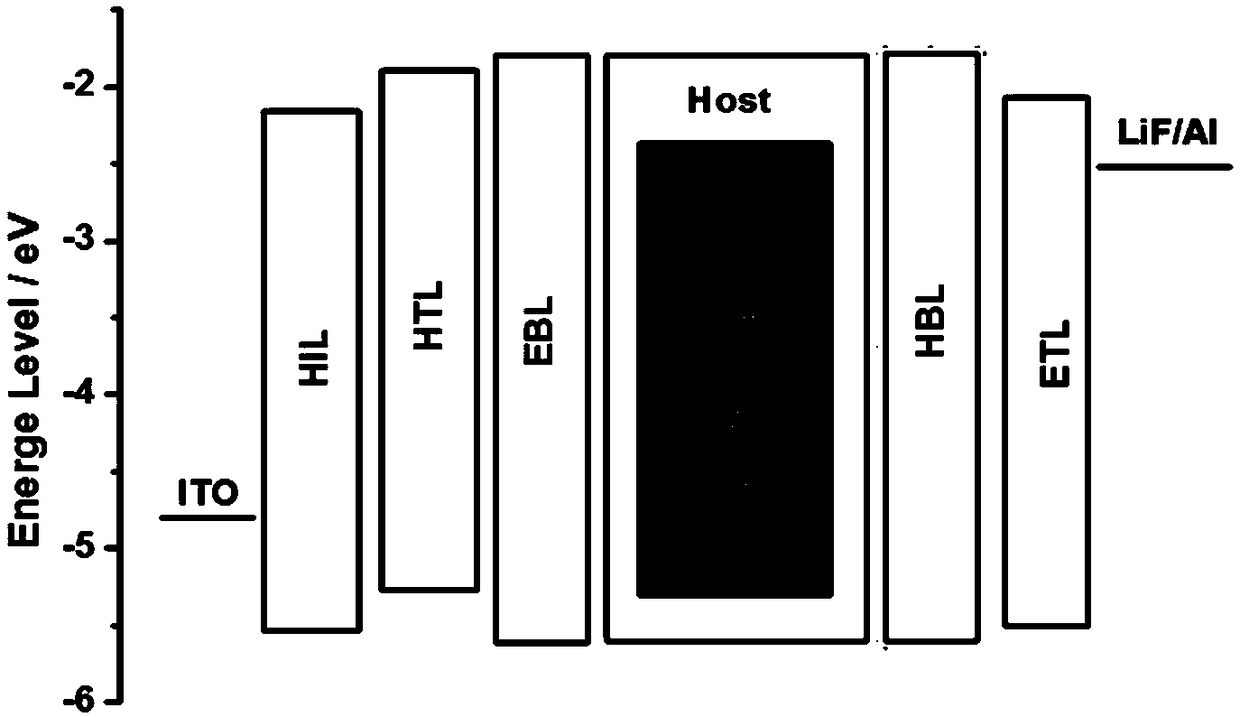
[0057] Embodiments 1-7 respectively provide an organic electroluminescent device, such as figure 2 As shown, the device structure sequentially includes ITO anode, hole injection layer (HIL), hole transport layer (HTL), electron blocking layer (EBL), light emitting layer (EML), hole blocking layer (HBL), electron transport layer layer (ETL), electron injection layer (EIL) and cathode.
[0058] Wherein, the material of the hole injection layer is HATCN, and generally the total thickness is 5-30nm, which is 10nm in this embodiment. The material of the hole transport layer is a common material for HTL in OLEDs, which is NPB in this embodiment, and generally has a total thickness of 5-500 nm, and is 40 nm in this embodiment. The thickness of the electron blocking layer is generally 1-500nm, which is 5nm in this embodiment. The host material (Host) of the light-emitting layer is consistent with the materials of the electron blocking layer and the hole blocking layer, the guest ma...
Embodiment 8-10
[0077] Embodiments 8-10 respectively provide an organic electroluminescent device, such as image 3 As shown, the device structure sequentially includes ITO anode, hole injection layer (HIL), hole transport layer (HTL), electron blocking layer (EBL), light emitting layer (EML), hole blocking layer (HBL), electron transport layer layer (ETL), electron injection layer (EIL) and cathode. Among them, the host material (Host) of the light-emitting layer, the material of the hole blocking layer and the material of the electron blocking layer are all the same, and the TADF material is used as the sensitizer of the light-emitting layer, and the traditional fluorescent dye is used as the guest material of the light-emitting layer (ie Fluorescent dyes). The materials and thicknesses used for other functional layers are consistent with those in Examples 1-7. The thickness of the light-emitting layer is 30 nm, the thickness of the hole blocking layer is 5 nm, and the thickness of the ele...
Embodiment 1
[0090] Embodiments 11-14 respectively provide an organic electroluminescent device, the structure of which is consistent with that of Embodiments 1-7. For details, please refer to figure 2 . The material and thickness used for each functional layer of the OLED device in Examples 11-14 are basically the same as those in Example 1, the only difference lies in the thickness of the electron blocking layer and the hole blocking layer.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com