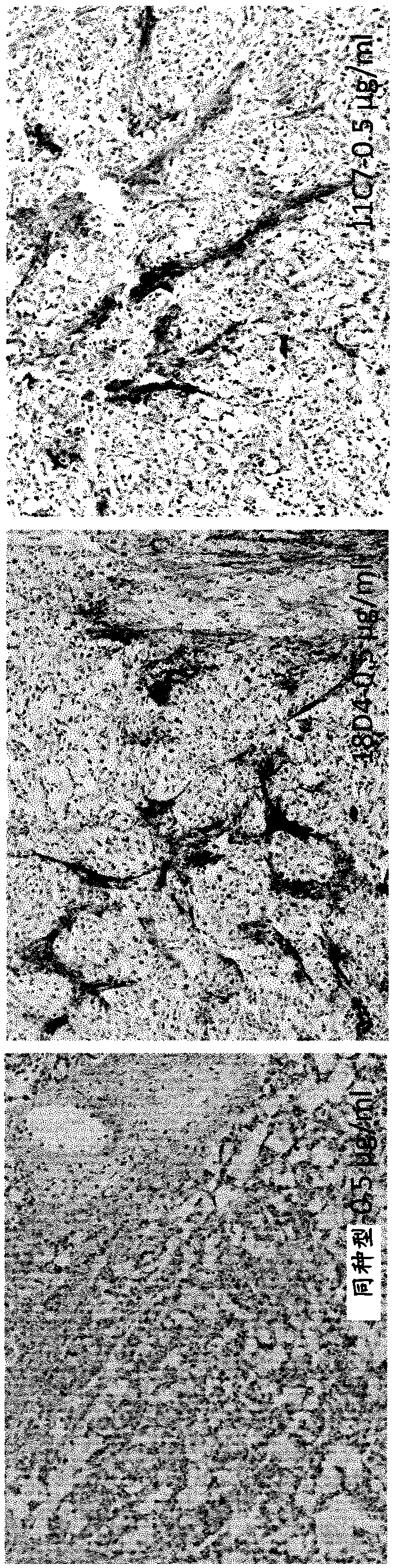Modified Anti-tenascin antibodies and methods of use
A tenascin and antibody technology, applied in the field of domain-specific anti-TnC antibody, vector and host cell, to generate the antibody, can solve the problem of adult tissue loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0436] TnC antigen sequence and antigen production
[0437] All constructs of Table 3 and Table 4 were fused to the C-terminus of GST and expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3). For site-specific biotinylation, an Avi tag was added to the C-terminus of the tenascin sequence and BirA biotin ligase (Avidity, Colorado, USA) was co-expressed on a separate plasmid. The growth medium was 2YT containing 100 μg / ml ampicillin and 20 μg / ml chloramphenicol. Add biotin to a final concentration of 50 μM. Protein expression was induced overnight at 22°C with 1 mM IPTG. Cells were harvested by centrifugation and lysed by sonication in the presence of B-PER reagent (pierce 78260) and 1 mg / ml lysozyme (Sigma L6876). The lysate was centrifuged and the clarified lysate was loaded onto a Glutathione Sepharose column (GE Healthcare; Product No. 17-0756-01). After washing, TnC molecules were cleaved from GST by thrombin (SigmaAldrich; Product No. 10602400001 ) overnight at 4°C. In 50mM Tris buffer pH ...
Embodiment 2
[0449] Selection of anti-TnC antibodies from a universal Fab library
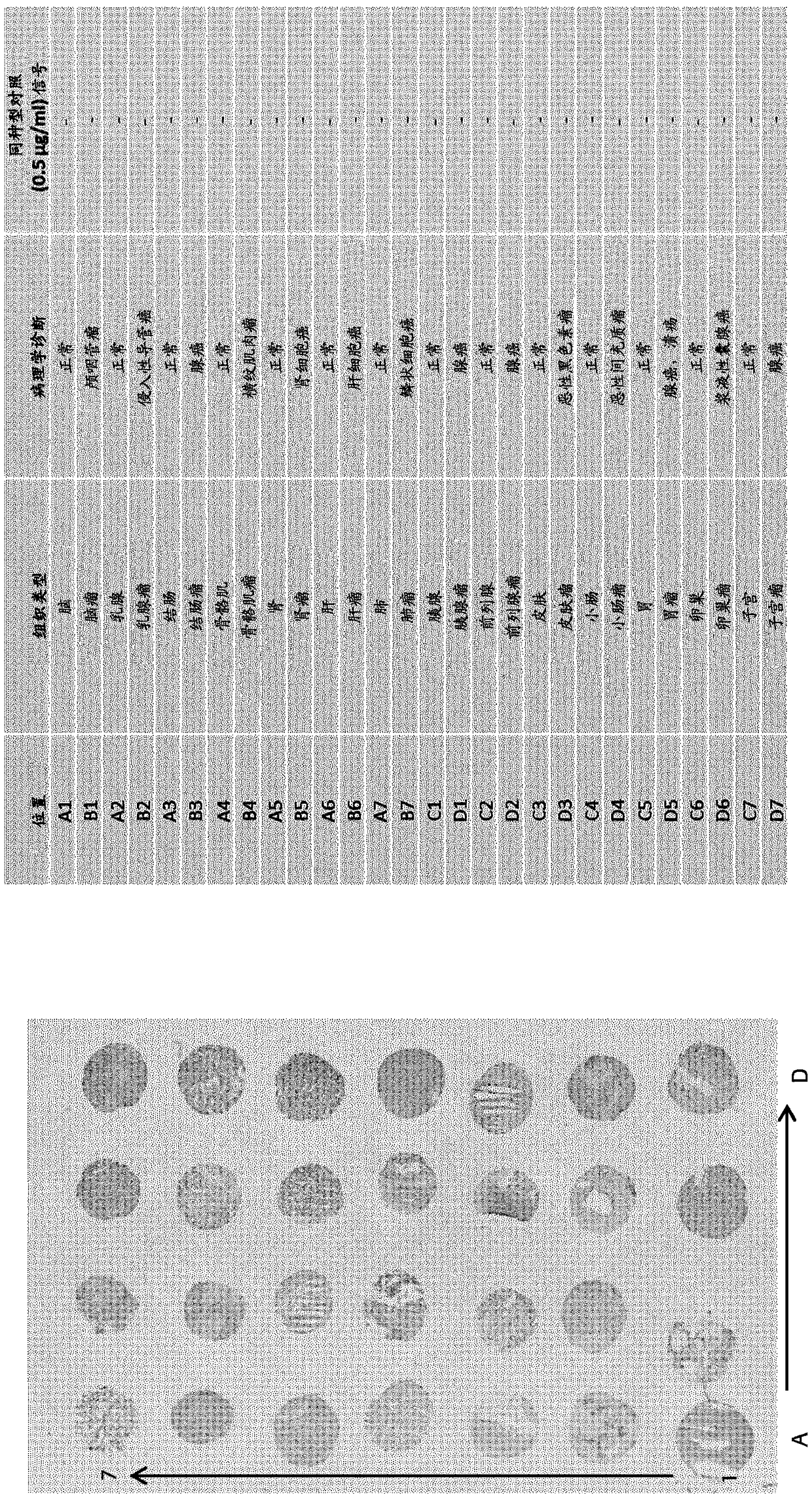
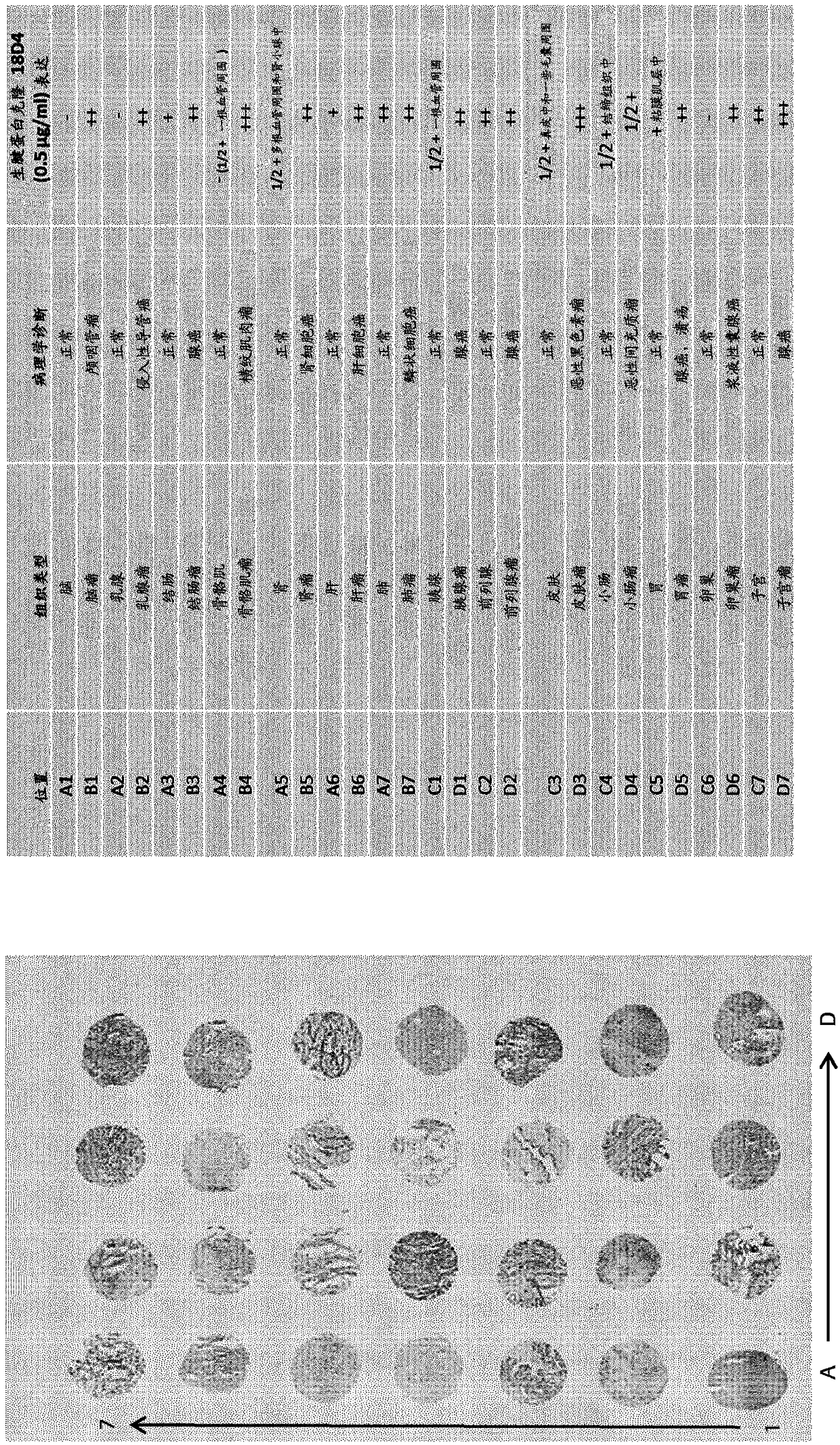
[0450] Anti-TnC antibodies were selected from two different universal phage display libraries: DP88-4 (clone 18D4) and lambda-DP47 (clone 11C7).
[0451] library construction
[0452] The DP88-4 library was created using the V domain pair Vk1_5 (κ light chain) and VH1_69 (heavy chain) based on human germline genes. Library generation was performed by assembling 3 PCR amplified fragments using splicing by overlap extension (SOE) PCR. Fragment 1 contains the 5' end of the antibody gene, including the randomized L3, Fragment 2 is the central constant fragment spanning L3 to H3, and Fragment 3 contains the randomized H3 and the 3' portion of the antibody gene. The following primer combinations were used to generate these library fragments for the DP88-4 library: Fragment 1 (forward primer LMB3 combined with reverse primer Vk1_5_L3r_S or Vk1_5_L3r_SY or Vk1_5_L3r_SPY), fragment 2 (forward primer RJH31 combine...
Embodiment 3
[0484] Cloning of variable antibody domains into expression vectors
[0485] The heavy and light chain variable region DNA sequences of selected anti-TnC binders were subcloned in-frame with either the constant heavy chain or the constant light chain of human IgGl (Tables 14 to 19). Antibodies were prepared either as wild-type human IgG1 backbone or as variants containing the Pro329Gly, Leu234Ala and Leu235Ala mutations introduced to abrogate Fcγ receptor combination.
[0486] The CDR sequences of the anti-TnC binders are shown in Table 16-19.
[0487] The base pair and amino acid sequences of anti-TnC IgG are shown in Table 20 and Table 21. The base pair and amino acid sequences of anti-TnCP319GLALAIgG are shown in Table 22 and Table 23. All antibody coding sequences were cloned into expression vectors with a chimeric MPSV promoter driving transcription of the insert and containing a synthetic polyA signal sequence located 3' to the CDS. In addition, the vector contains t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com