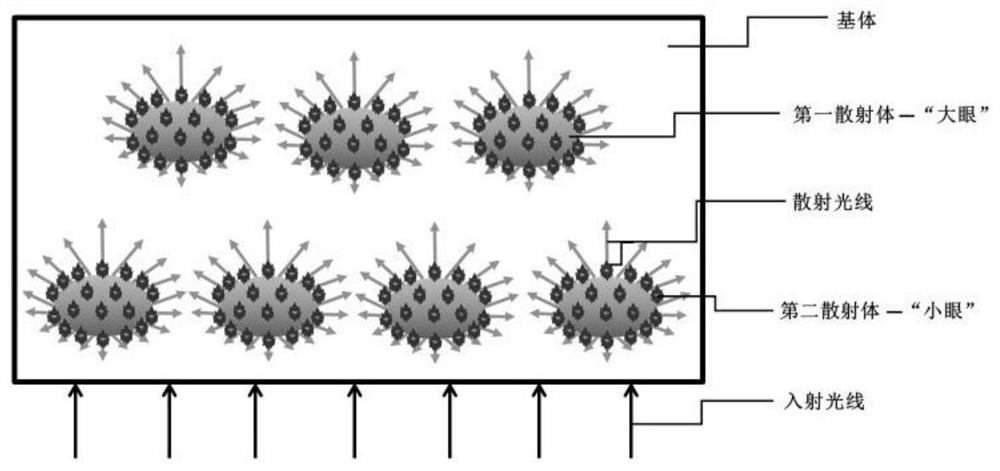
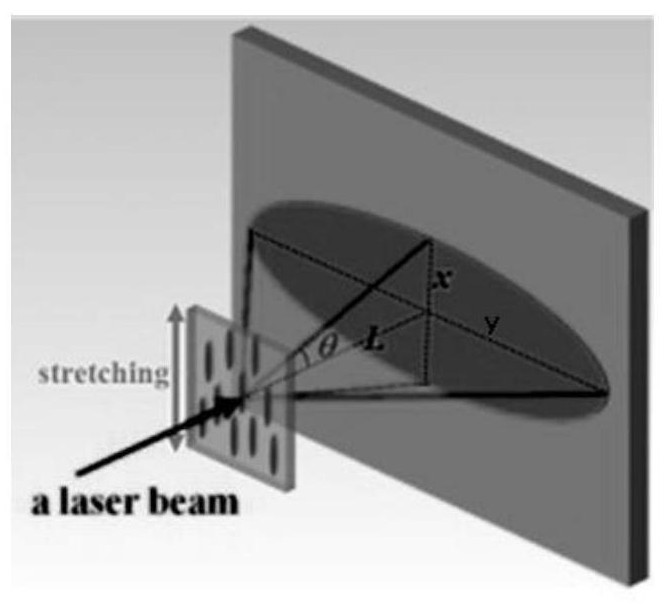
A method for increasing the scattering angle of the short-axis scattering direction of anisotropic light-scattering materials
An anisotropic and directional scattering technology, applied in the field of polymer-based composite material preparation technology, can solve the problems of small scattering angle and shrinking scattering angle, and achieve the effect of large scattering angle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] 70 parts by mass of polycarbonate (PC), 30 parts by mass of acrylonitrile copolymer (SAN) and 1.7%, 3.3%, 5.0%, 6.7% of the total weight of SAN, respectively, polymethylsilsesquioxane with a diameter of 10um Polycarbonate beads (OSB3) were melted and blended by a torque rheometer, and granulated to obtain polycarbonate composite particles. The composite particles were molded at 240°C into 100.0mm (length) × 30.0mm (width) × 1mm ( thick) samples. Then the sample was fixed in a high-temperature universal tensile testing machine and thermally stretched at 190°C with a stretch ratio of 2. The scattering angles in the short-axis scattering direction (x direction) are 18.7º, 20.1º, 20.8º, 22.0º, respectively, and the scattering angles in the long-axis scattering direction (y direction) are 30.2º, 30.9º, 31.0º, 32.3º, respectively. .
Embodiment 2
[0039] 30 parts by mass of acrylonitrile copolymer (SAN) were mixed with 1.7%, 3.3%, 5.0%, and 6.7% of the total weight of SAN with nano-calcium carbonate (nano-CaCO3) after surface treatment with a silane coupling agent. 3 ) was extruded at 200°C with a micro-blending extrusion rheometer, pelletized, and the pelletized SAN / nano-CaCO 3 The blend and 70 parts by mass of polycarbonate (PC) were melt-blended in a torque rheometer and granulated at a temperature of 240°C to obtain polycarbonate composite particles. The composite particles were heated at 240°C Molded into a sample of 100.0mm (length) × 30.0mm (width) × 1mm (thickness). Then the sample was fixed in a high-temperature universal tensile testing machine and thermally stretched at 190°C with a stretch ratio of 2. The scattering angles in the short-axis scattering direction (x direction) were measured to be 33.2º, 35.9º, 39.9º, 41.1º, and the scattering angles in the long-axis scattering direction (y direction) were 55....
Embodiment 3
[0041]70 parts by mass of polycarbonate (PC), 30 parts by mass of acrylonitrile copolymer (SAN) and 3.3% of the total weight of SAN polymethylsilsesquioxane beads (OSB1) with a diameter of 2um were subjected to torque flow Polycarbonate composite particles were obtained by melt blending and granulation, and the composite particles were molded at 240°C into a sample of 100.0 mm (length) × 30.0 mm (width) × 1 mm (thickness). Then the samples were fixed in a high-temperature universal tensile testing machine and thermally stretched at 190°C, and the stretching ratios were 2 and 2.5, respectively. It is measured that the scattering angles in the short-axis scattering direction (x direction) are 27.4º and 23.8º, and the scattering angles in the long-axis scattering direction (y direction) are 33.4º and 31.0º.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heat deflection temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com