A flexible passive foot system based on bionics
A bionic, flexible foot technology, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of unnatural gait, unstable support, and large impact of the robot, and achieve the effects of easy research and promotion, easy installation and disassembly, and low robot load.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
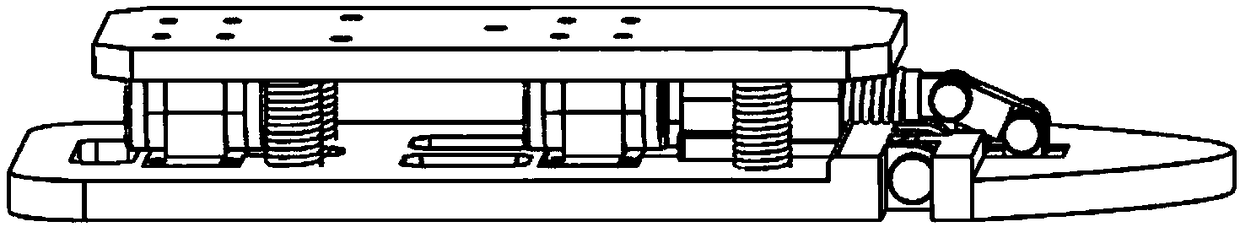
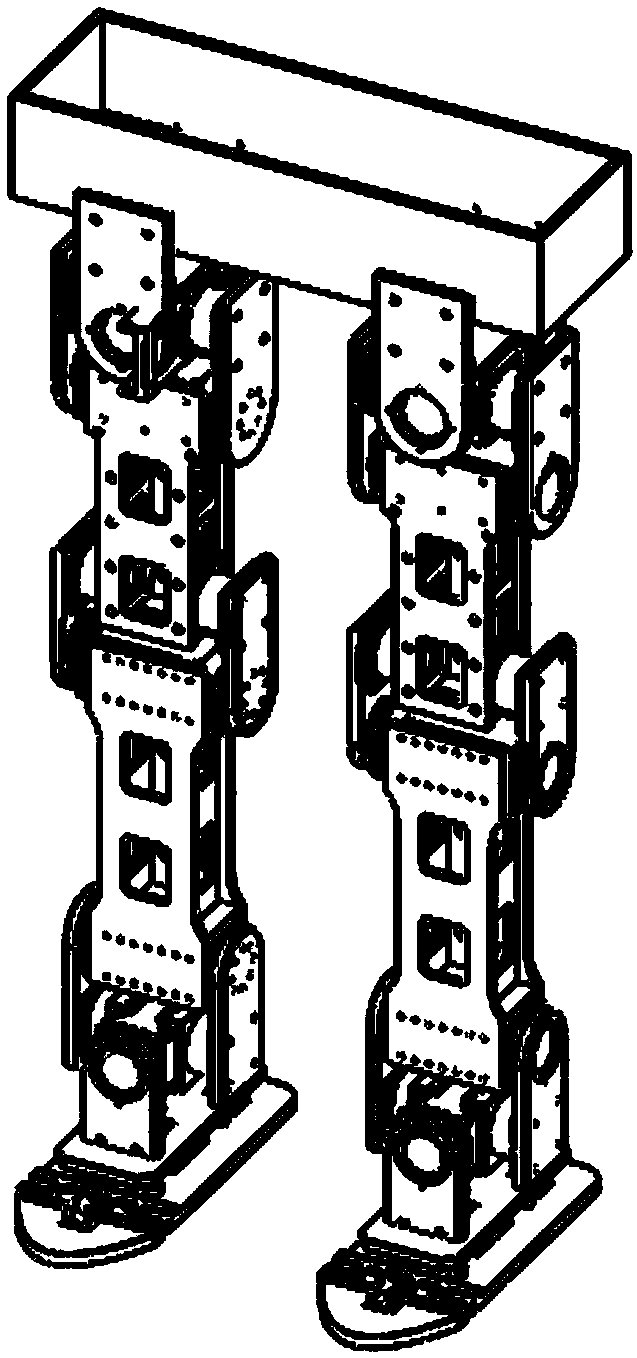
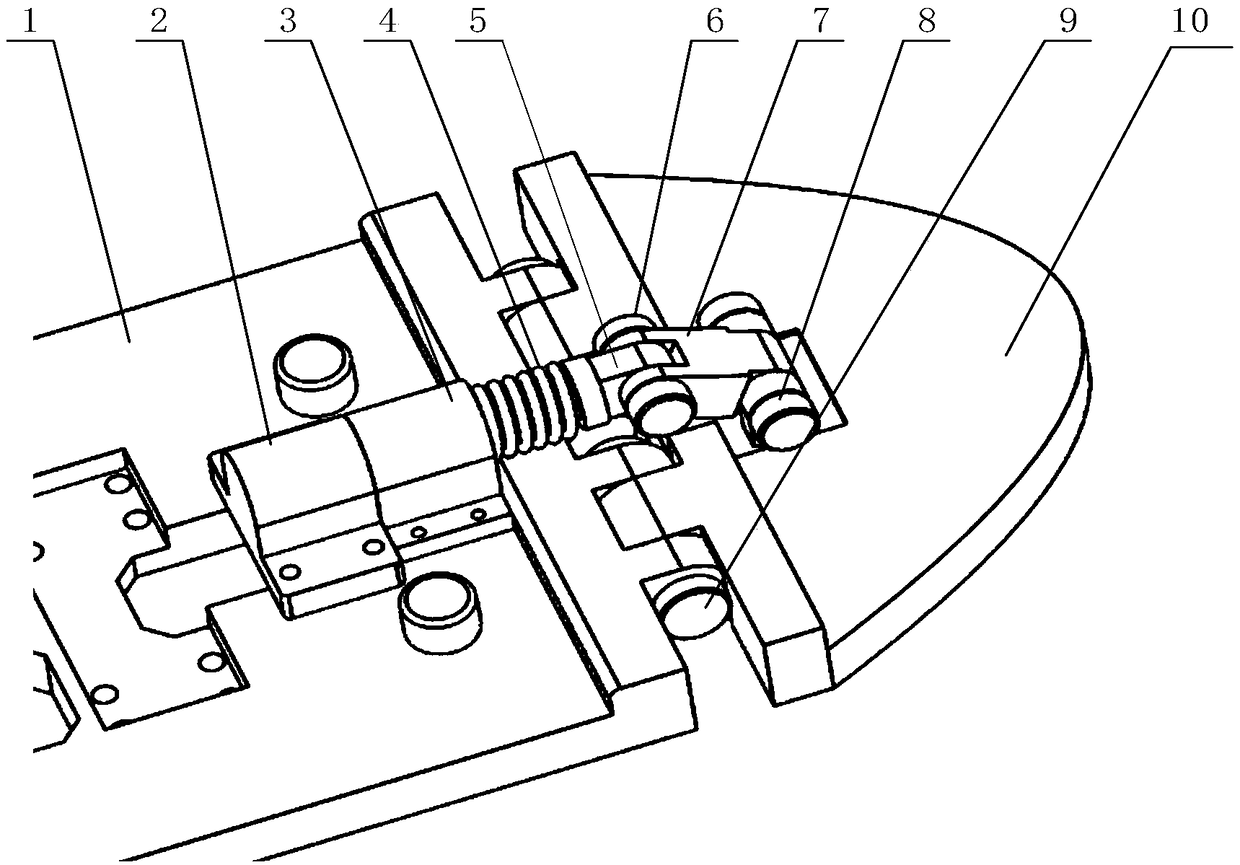
[0027] The details of the present invention can be understood more clearly below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and the description of specific embodiments of the present invention. However, the specific embodiments of the present invention described here are only for the purpose of explaining the present invention, and should not be construed as limiting the present invention in any way. Under the teaching of the present invention, the skilled person can conceive any possible modification based on the present invention, and these should be regarded as belonging to the scope of the present invention. In the figure, humanoid passive flexible toe joint Ⅰ, lateral cushioning and shock-absorbing layer Ⅱ, sole 1, spring top seat 2, spring sleeve 3, toe compression spring 4, slider 5, flexible mechanism pin 6 , toe connecting rod 7, flexible mechanism pin two 8, toe joint pin 9, toe 10, pin between feet 11, support seat 12 on the foot, support seat 13 under the foot, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com