A Stochastic Optimal Scheduling Method for Hydropower Station Reservoirs
A technology of stochastic optimization and scheduling method, applied in data processing applications, forecasting, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as infeasibility and difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0144] 1) Example 1 - no forecast SDP model
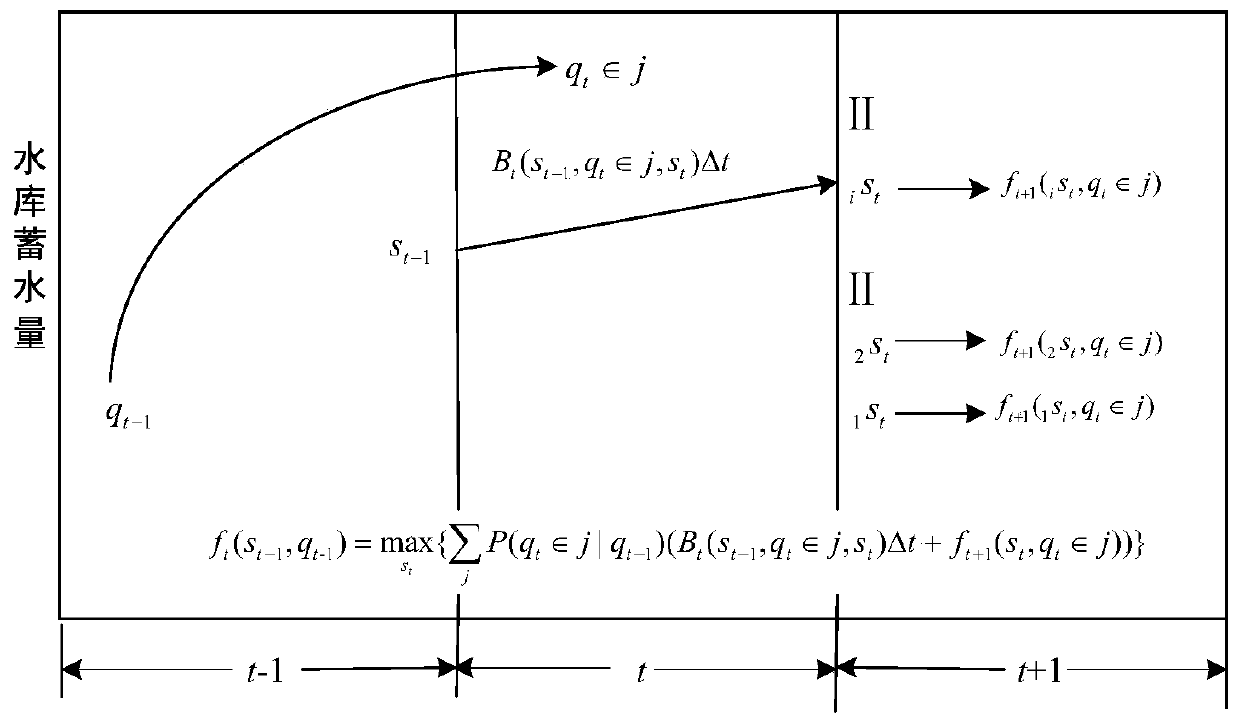
[0145] The No Forecasting SDP (No Forecasting SDP, NF-SDP) model does not consider the runoff forecast information of the current period, but only considers the random transfer law of the runoff itself. The runoff in period t changes from the runoff state q in the previous period t-1 Determined, the reservoir scheduling decision is determined by the measured runoff q t-1 and initial storage capacity s t-1 decided together. The recurrence equation of the NF-SDP model is:
[0146]
[0147] Among them, j is the measured runoff grade index; P(q t ∈j|q t-1 ) is the runoff prior state transition probability in period t; B t (s t-1 ,q t ∈j,s t ) is the storage capacity at the beginning and end of period t, respectively s t-1 , s t , runoff q t Immediate benefit when ∈j; f t (s t-1 ,q t-1 ) for a given initial state s t-1 ,q t-1 In the case of , the maximum expected benefit from period t to T. The recursive process of ...
Embodiment 2
[0149] 2) Embodiment 2-BSDP model
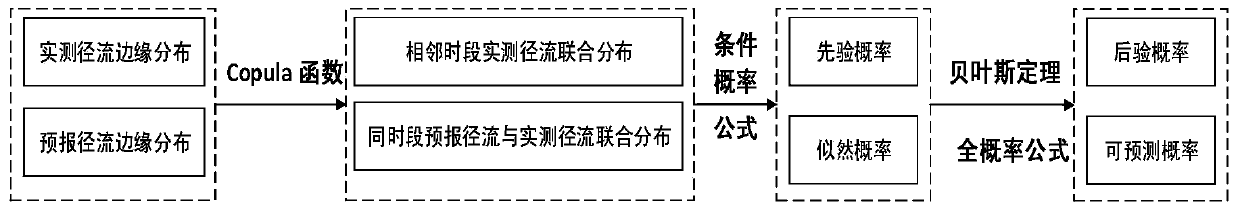
[0150] In addition to considering the random transfer law of runoff itself, BSDP also uses Bayesian theorem to take runoff forecast uncertainty into the recurrence equation in the form of likelihood probability. The runoff in period t changes from the runoff state q in the previous period t-1 and the runoff forecast q of this period f t jointly determined, the reservoir scheduling decision is determined by the measured runoff q t-1 , forecast runoff q f t and initial storage capacity s t-1 Decide. At this time, the recurrence equation of the BSDP model is:
[0151]
[0152] Among them, j and k are the level indicators of measured runoff and forecasted runoff respectively; q f t and q f t+1 are the runoff forecast values of period t and period t+1, respectively; P(q t ∈j|q t-1 ,q f t ) is the posterior state transition probability of runoff in period t; P(q f t+1 ∈k|q t ∈j) is the predictability probability of runoff in...
Embodiment 3
[0154] 3) Embodiment 3-perfect forecast SDP model
[0155] The Perfect Forecasting SDP (Perfect Forecasting SDP, PF-SDP) model assumes that there is accurate runoff forecast information in the current period. The predicted value of runoff in period t is equal to the measured value, that is, q f t =q t . The reservoir scheduling decision in period t is determined by the measured runoff q t and initial storage capacity s t-1 decided together. The recurrence equation of the PF-SDP model is:
[0156]
[0157] Among them, j is the measured runoff grade index; P(q t+1 ∈j|q t ) is the prior state transition probability of runoff in period t+1; B t (s t-1 ,q t ,s t ) is the storage capacity at the beginning and end of period t, respectively s t-1 and s t , the runoff is q t The immediate benefit of the time; f t (s t-1 ,q t ) for a given initial state s t-1 ,q tIn the case of , the maximum expected benefit from period t to T. The recursive process of PF-SDP mod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com