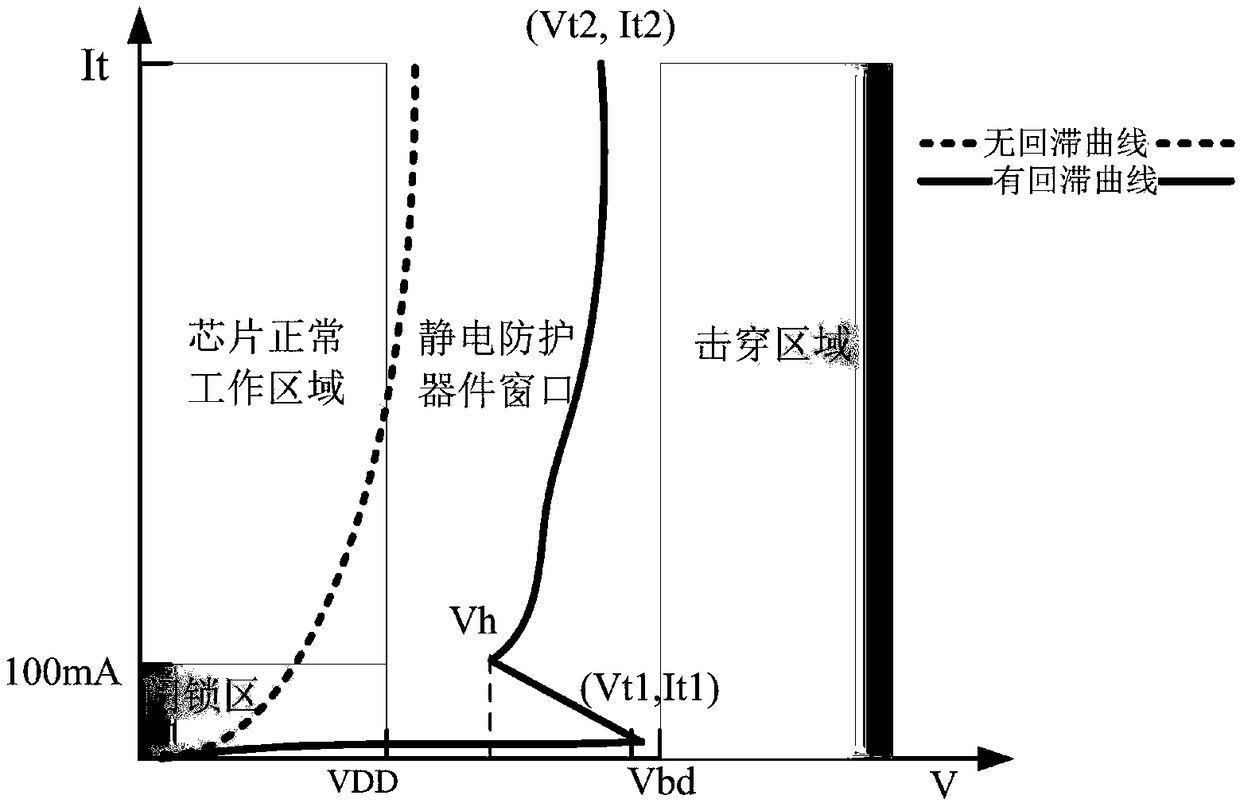
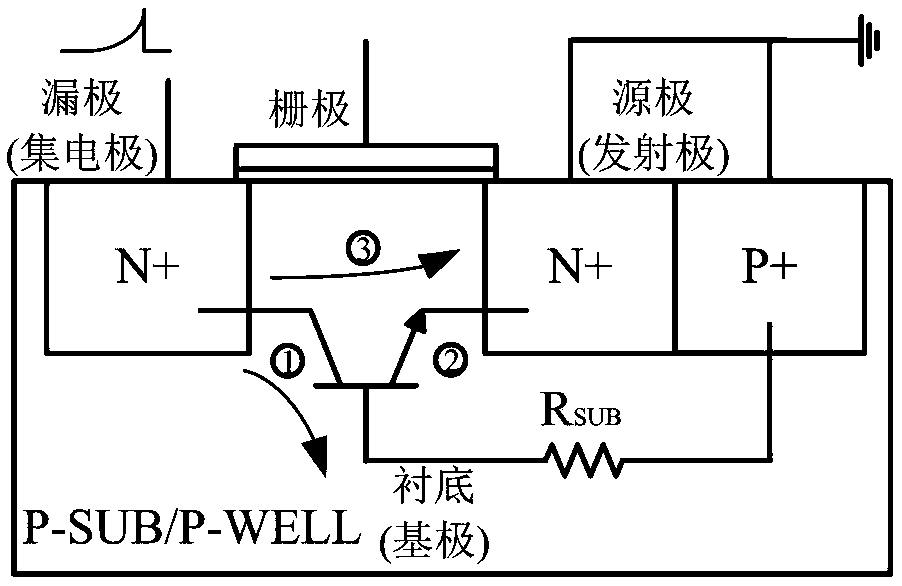
Electrostatic discharge self-protection circuit and self-protection method
An electrostatic discharge and self-protection technology, applied in circuits, electrical components, electronic switches, etc., to solve problems such as inflexible trigger point adjustment, uneven triggering, and large chip area costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
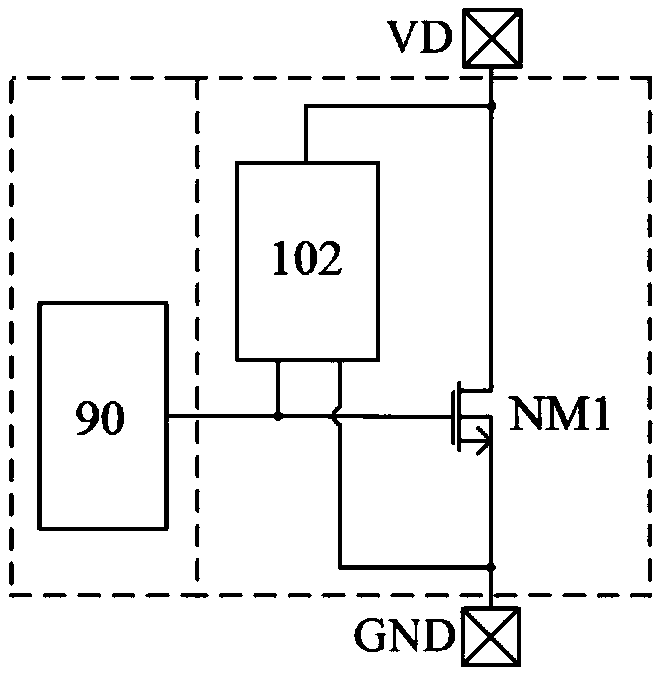
[0041] Figure 4 It is a schematic circuit diagram of an electrostatic discharge self-protection circuit 100 according to the first embodiment of the present invention, including an integrated power tube unit 101 and an auxiliary trigger circuit 102 .
[0042] The integrated power transistor unit 101 includes a power transistor NM1 , a drain pin VD and a ground pin GND. The power transistor NM1 is an N-channel MOS transistor and consists of several unit MOS transistors connected in parallel. The power tube NM1 is a power switch tube, which is the main MOS tube used in the power circuit of the power supply; and because the main function of the power tube in the power circuit is switching, it can also be referred to as a switch tube for short. The power switch tube, power tube or switch tube mentioned in this article all refer to this kind of MOS tube with the characteristics of large area, small conduction internal resistance and strong overcurrent capability. The drain of the...
no. 2 example
[0048] Figure 5 It is a schematic circuit diagram of an electrostatic discharge self-protection circuit 200 according to the second embodiment of the present invention, including an integrated power tube unit 101 and an auxiliary trigger circuit 202 . The difference from the first embodiment is that the auxiliary trigger circuit 202 of the second embodiment is composed of an NPN transistor B2 and a resistor R1. The collector of the NPN transistor B2 is connected to the drain of the power transistor NM1, the emitter of the transistor B2 is connected to the gate of the power transistor NM1, the base of the transistor B2 is connected to one end of the resistor R1, and the other end of the resistor R1 is connected to the power source of tube NM1.
[0049] Attached below Figure 5 Let me introduce, when a positive ESD event occurs at the VD terminal, the auxiliary trigger circuit 202 assists the power transistor to trigger and turn on the principle and working process of drain E...
no. 3 example
[0053] Image 6 It is a schematic circuit diagram of an electrostatic discharge self-protection circuit 300 according to the third embodiment of the present invention, including an integrated power tube unit 101 and an auxiliary trigger circuit 302 . For the electrostatic discharge self-protection circuits of the first and second embodiments, the power transistor NM1 is a high-voltage MOS transistor. As long as the appropriate NM2 and B2 devices are selected, the auxiliary trigger circuits provided by the auxiliary trigger circuits 102 and 202 can be applied to various switches The ESD protection trigger of the drain of the high-voltage switch tube is integrated in the power control chip, including the situation that the maximum drain voltage VDmax of the power tube NM1 is greater than, less than or equal to the chip power supply voltage VDD.
[0054] For the case where the power transistor NM1 is a low-voltage MOS transistor and its maximum drain voltage VDmax is lower than t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com