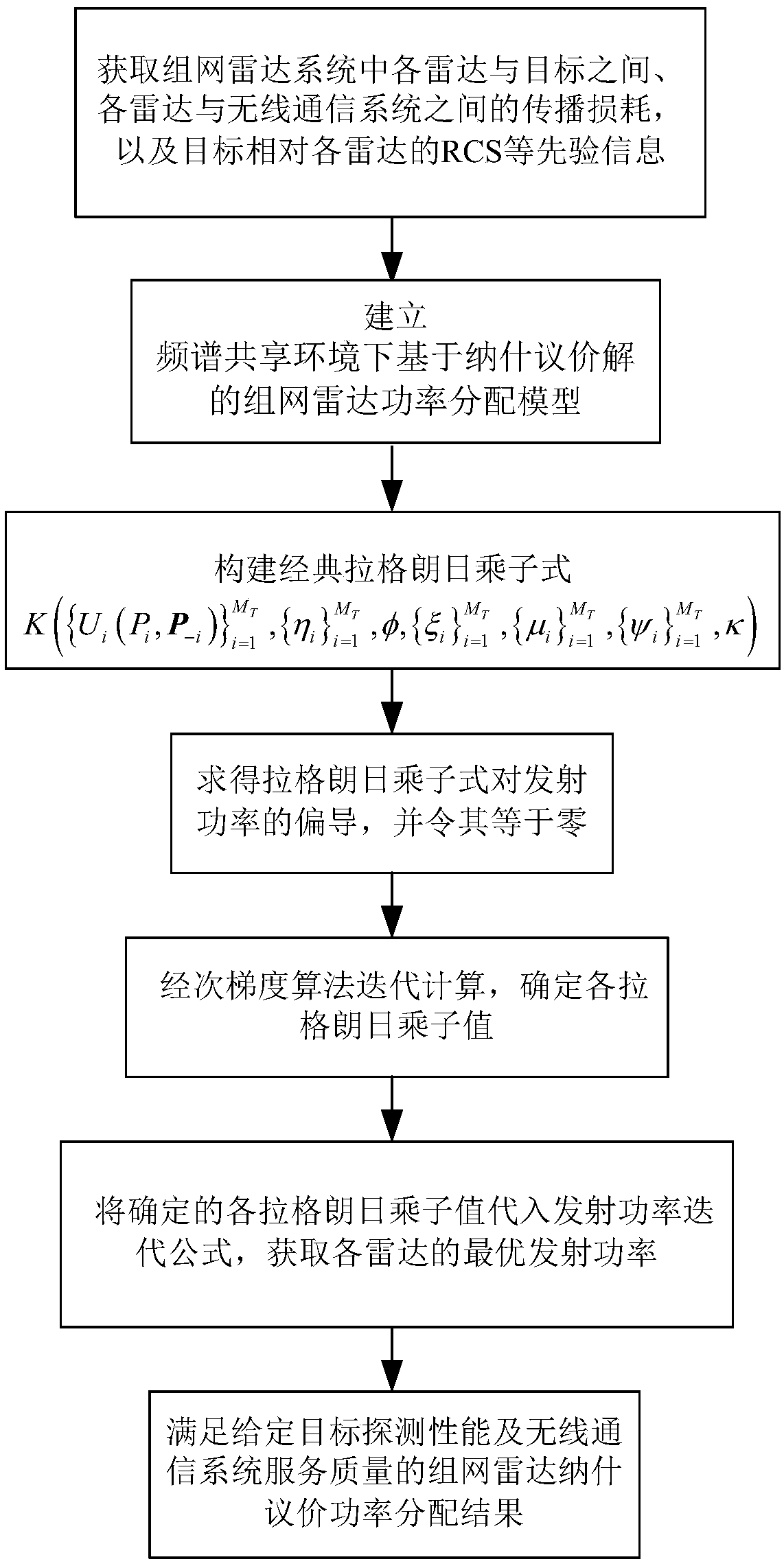
Nash-bargaining-solution-based networked radar power allocation method in spectrum coexistence environment
A networked radar and Nash bargaining technology, applied in power management, wireless communication, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of lack of networked radar, spectrum coexistence between networked radar and wireless communication system, interference of wireless communication services, etc. Achieve the effect of meeting the spectrum coexistence
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] The geometric position relationship between networked radar, wireless communication system and target is as follows: image 3 As shown, the RCS model is That is to say, the RCS of the target relative to each radar viewing angle is equal.
Embodiment 2
[0096] The geometric position relationship between networked radar, wireless communication system and target is as follows: image 3 As shown, the target RCS model is That is to say, the RCS of the target relative to each radar viewing angle is not equal.
Embodiment 3
[0098] The geometric position relationship between networked radar, wireless communication system and target is as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the RCS model is
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com