Anti-collapsible injectable magnesium phosphate-based bone cement
A magnesium phosphate-based bone, anti-collapse technology, applied in the field of medical biomaterials, can solve the problems of good anti-collapse, unfavorable bone cement repair, long setting time, etc., achieves appropriate setting time, avoids drop in injectability, and improves anti-scour. performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Magnesium oxide is calcined at 1600°C for 2h, the heating rate is 3°C / min, and the particle size is 0.4-3μm. The particle sizes of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and calcium dihydrogen phosphate are 1-20 μm and 0.5-30 μm, respectively. Weigh 1.5g of magnesium oxide, 3g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 1g of calcium dihydrogen phosphate powder, then add 0.1g of citric acid and 0.02g of xanthan gum and mix well. The liquid phase is 5% volume concentration of glycerol aqueous solution, mixed at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 2.2 g / mL, and stirred for 5 minutes until viscous.
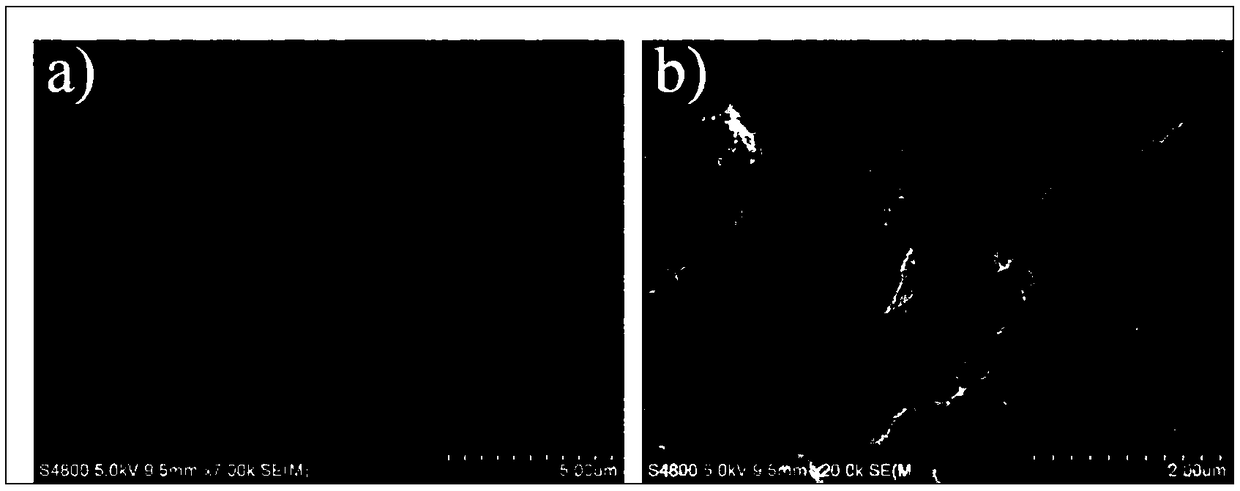
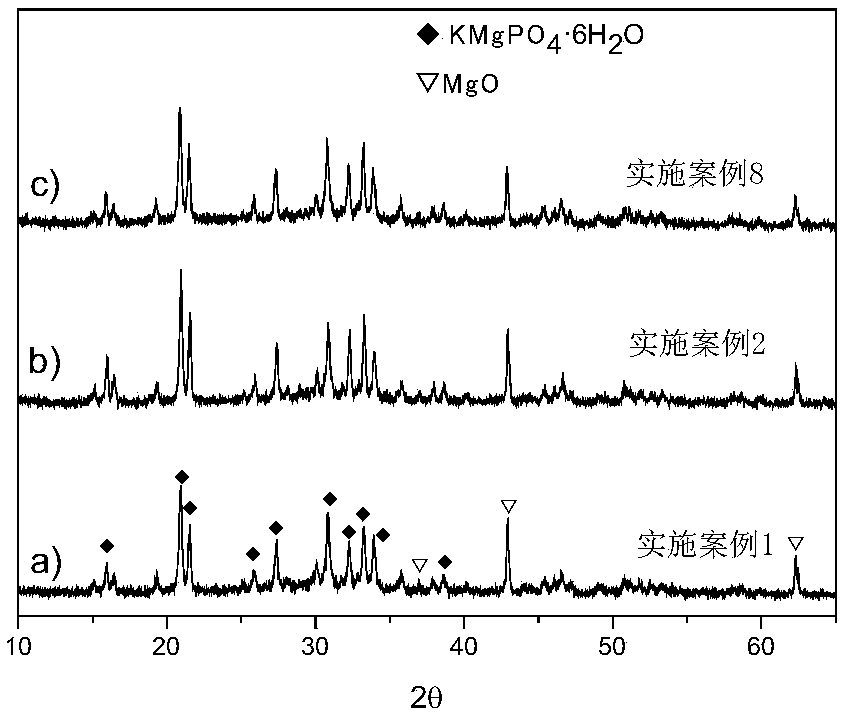
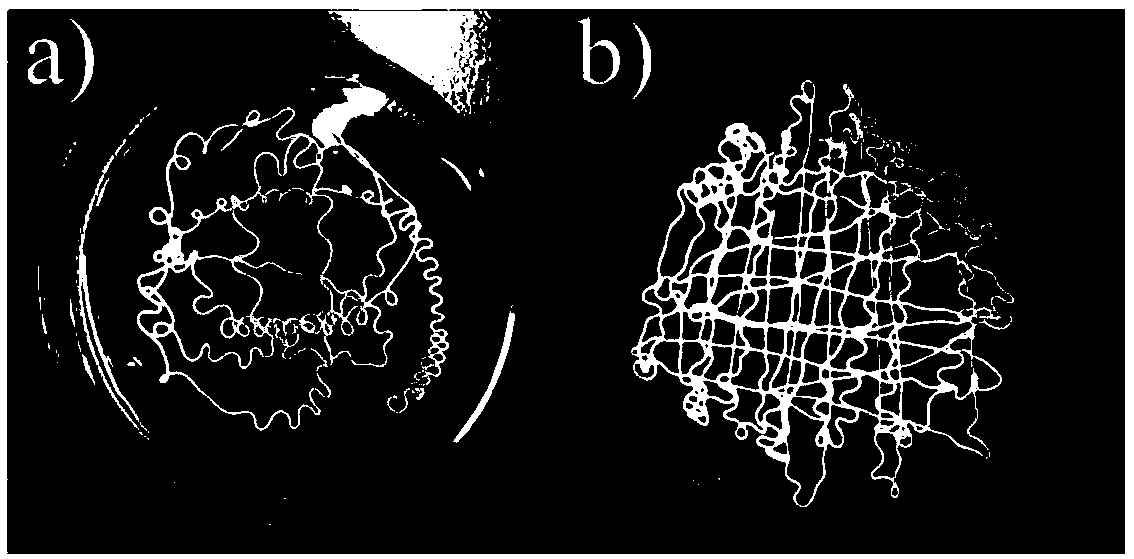
[0045] The setting time of the bone cement is 15.5min, the compressive strength is 53.2MPa, and the injectability is 98%. Its anti-collapse performance is as figure 2 As shown in a), there is almost no powder spillage with the naked eye. The phase after curing for 2 days is as follows figure 1 As shown in a), it is mainly potassium magnesium phosphate hexahydrate and unreacted magnesium oxide. ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Magnesium oxide is calcined at 1600°C for 2h, the heating rate is 3°C / min, and the particle size is 0.4-3μm. The particle sizes of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and calcium dihydrogen phosphate are 1-20 μm and 0.5-30 μm, respectively. Weigh 1.5g magnesium oxide, 3g potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 1g calcium dihydrogen phosphate powder, add 0.05g citric acid, 0.01g xanthan gum and mix well. The liquid phase is a 5% volume concentration aqueous glycerin solution. Mix at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 2.2 g / mL, and stir for 5 minutes until viscous.
[0048] The setting time of the bone cement is 13.5min, the compressive strength is 48.1MPa, and the injectability is 96%. Its anti-collapse performance, such as figure 2 As shown in b), there is almost no powder spillage with the naked eye. The phase after curing for 2 days is as follows figure 1 As shown in b), it is mainly potassium magnesium phosphate hexahydrate and unreacted magnesium oxide.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Magnesium oxide is calcined at 1600°C for 2h, the heating rate is 3°C / min, and the particle size is 0.4-3μm. The particle sizes of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and calcium dihydrogen phosphate are 1-20 μm and 0.5-30 μm, respectively. Weigh 1.5g magnesium oxide, 3g potassium dihydrogen phosphate and 1g calcium dihydrogen phosphate powder, add 0.23g citric acid, 0.05g xanthan gum and mix well. The liquid phase is a 5% volume concentration aqueous glycerin solution. Mix at a solid-to-liquid ratio of 2.2 g / mL, and stir for 5 minutes until viscous.
[0051] The setting time of the bone cement is 19 minutes, the compressive strength is 42MPa, the injectability is 96%, the anti-collapse performance is good, and there is little powder overflowing by naked eyes.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com