Reagent capable of detecting tumors and realizing auxiliary imaging and preparation method thereof
A tumor and imaging technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, to achieve the effect of increasing the penetration depth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0028] The preparation method of the reagent for detecting tumor and assisting imaging provided by the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0029] Dissolve 4-nitrophthalic anhydride, phthalimide, EDTA and 9-(o-carboxyphenyl)-6-hydroxy-3H-xanthene-3-one at a molar ratio of 5.8:4:0 .5:12 in ethylene glycol solution, followed by rotary evaporation to form crystals or films;
[0030] Then add 0.2 mg / ml of specific antibody PD-1 phosphate buffered saline solution, freeze the mixture, and then thaw it at 5.85°C;
[0031] Filter the solution after five times of freezing and thawing on a 200-nm filter membrane for ~50 times, and then purify it through an S-300 gel column to remove free 9-(o-carboxyphenyl)-6-hydroxy-3H- Ton-3-one and specific antibody PD-1.
[0032] The reagents, instruments or biological materials used in the reagents, instruments or biological materials used in the reagents, instruments or biological materials used in the tumor detection and imaging a...
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1: Preparation of reagents for detecting tumors and assisting imaging:
[0035] The reagents for detecting tumors and assisting imaging described in the present invention include a fluorescein-sensing agent characterized in that the fluorescein-sensing agent is composed of a specific fluorescein-sensing agent, a specific antibody PD-1 and 9-(o-carboxyphenyl) -6-hydroxy-3H-xanthene-3-one composition; the specific fluorescein sensor includes 4-nitrophthalic anhydride, phthalimide and EDTA; the outer layer of the specific fluorescein sensor A specific antibody PD-1 is set, and 9-(o-carboxyphenyl)-6-hydroxy-3H-xanthene-3-one is set in the inner layer of the specific fluorescein sensor.
[0036] The specific preparation method is based on a specific fluorescein sensor, and the specific antibody PD-1 is set in the outer shell, and the inner layer is used to set 9-(o-carboxyphenyl)-6-hydroxy-3H- Ton-3-one, etc., to form a fluorescein-sensing agent. Specifically inclu...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Specificity of the Nitric Oxide Response of Fluorescein Sensing Agents
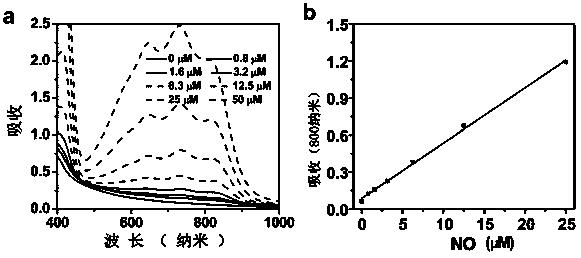
[0040] In order to study the specificity of the nitric oxide response of the fluorescein-sensing agent, in this example, the fluorescein-sensing agent and EDTA were incubated with different reactive oxygen species, including nitric oxide (NO), tert-butyl nitric oxide, hypochlorite (-OCl), hydroxyl radical (·OH), tert-butyl radical (·OtBu), nitric oxide radical (NO·), peroxide radical (O2-).
[0041] Absorption at 800 nm was measured after incubation with the above-mentioned fluorescein-sensing reagents with different reactive oxygen species for half an hour. It can be seen that the fluorescein sensor does not respond to almost all reactive oxygen species. The absorption of fluorescein-sensing agents at 800nm was significantly enhanced after incubation with nitric oxide, but the response to other types of reactive oxygen species was not very strong. Therefore, the fluorescein-sensing ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com