A panel of genes for molecular typing of non-hypermutated colorectal cancer and its application
A technology of hypermutated nodal and molecular typing, applied to the prediction of postoperative recurrence and metastasis of colorectal cancer, the genetic field of molecular typing of non-hypermutated colorectal cancer, can solve tumor recurrence or metastasis, patients Death and other issues, achieve good clinical guidance, strengthen monitoring, and avoid over-treatment effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Example 1 Preparation of Genomic DNA Samples and Determination of Tumor Somatic Mutation Sites
[0031] In order to detect the somatic mutation of colorectal cancer, the present invention completed the high-throughput sequencing of 338 colorectal cancer tissue samples in two stages, and completed the high-throughput sequencing of 80 cases of colorectal cancer in the first stage, of which 10 cases For whole genome sequencing, 70 cases for whole exome sequencing. Through the first stage of high-frequency gene analysis, further combining the high-frequency genes in the TCGA database and COSMIC database, and the NCCN guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of hereditary colorectal cancer, the present invention designed a gene group comprising 524 genes (Table 1), Capture probes targeting this gene group were customized for the second stage of sequencing. In the second phase, the targeted sequencing of 258 colorectal cancer tissue samples was completed using the capture ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Example 2 Establishment of a gene mutation prognosis prediction model for non-hypermutated colorectal cancer
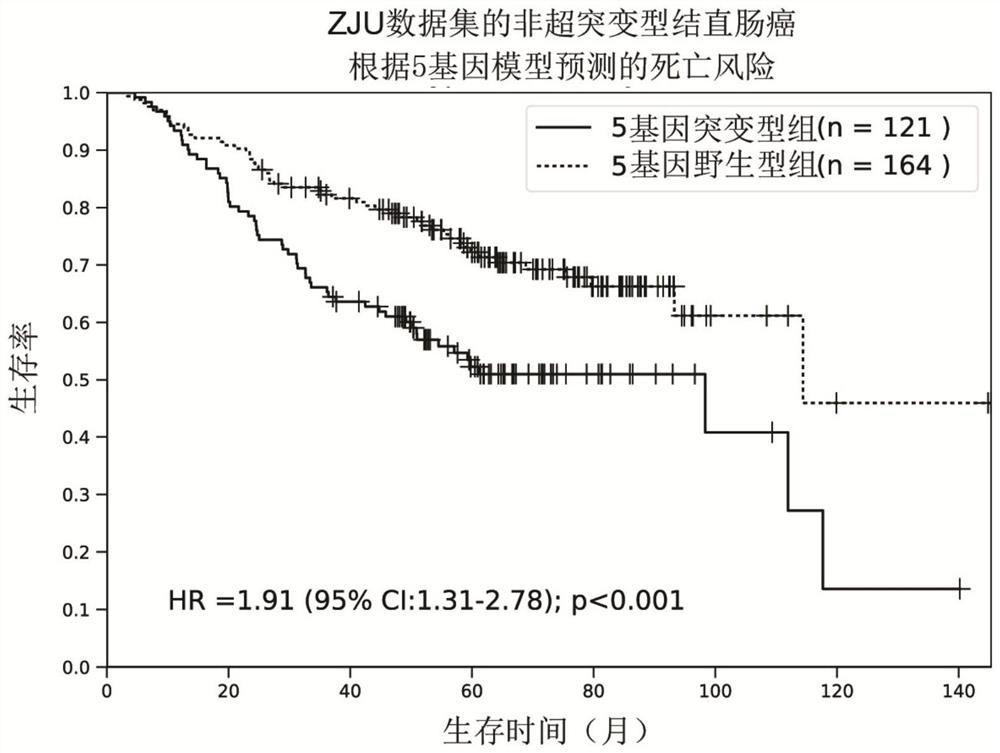
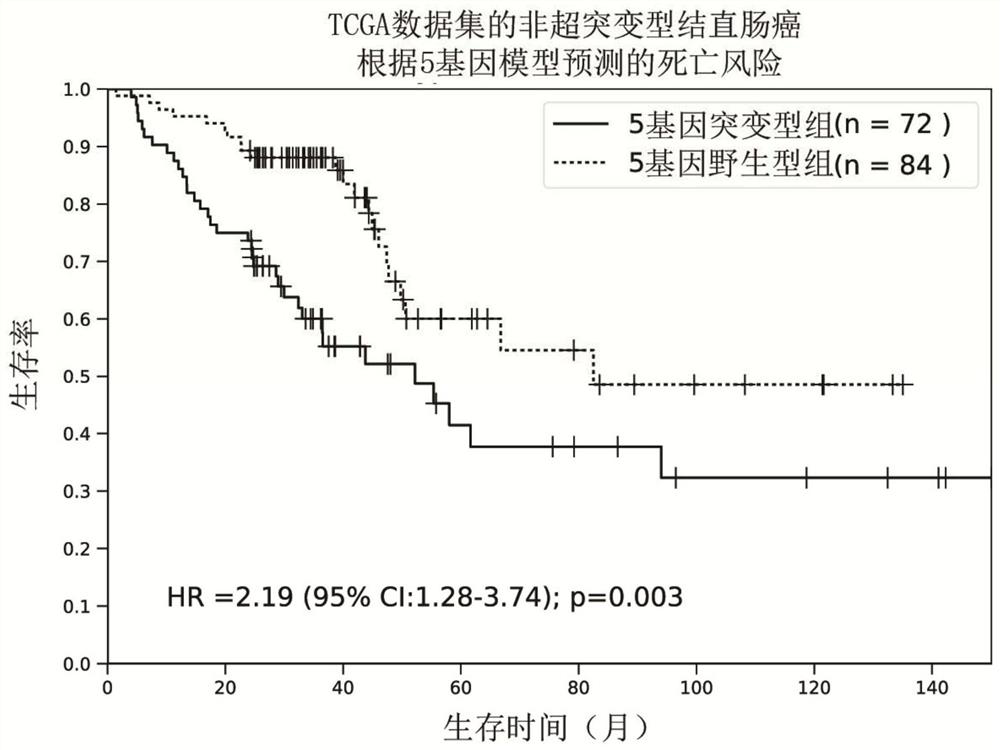
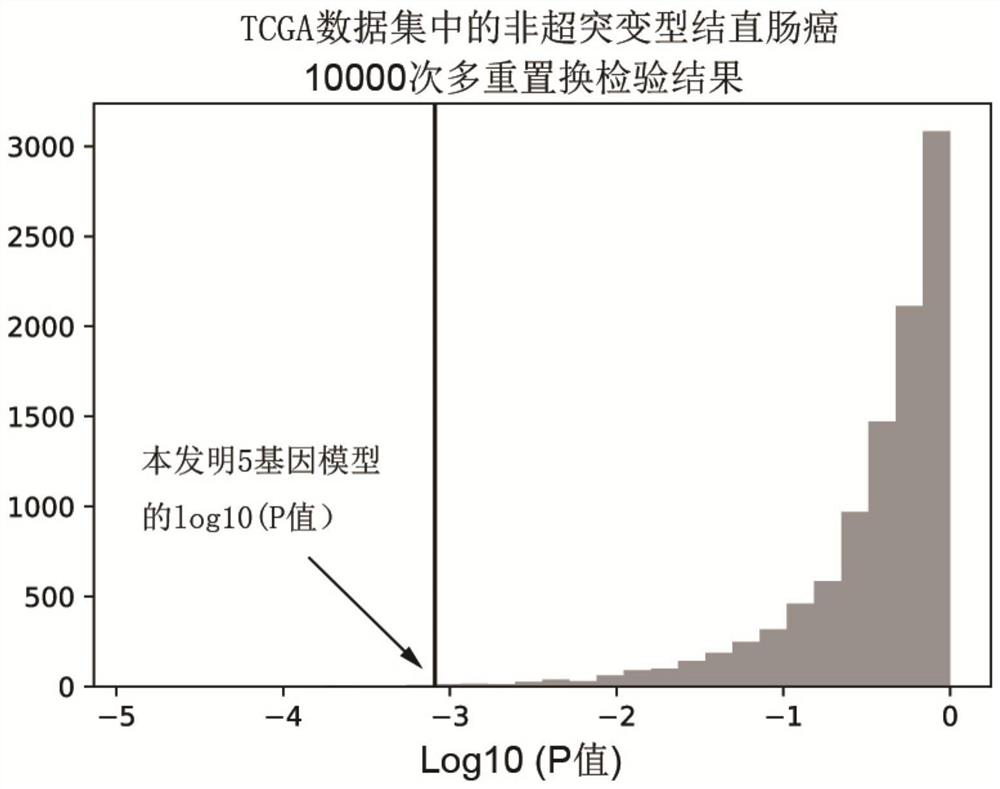
[0037] Since there are great differences in the pathogenesis, prognosis, and curative effect of hypermutated and non-hypermutated colorectal cancer, the present invention firstly divides colorectal cancer patients into two groups: hypermutated and non-hypermutated. Tumors with a mutation burden rate less than or equal to 10Mut / Mb were defined as non-hypermutated tumors. Of the 338 cases of colorectal cancer (ZJU data set) in Example 1, 293 cases were determined to be non-hypermutated. In addition, in order to verify the stability and universality of the model, the present invention downloaded a total of 382 cases of colorectal cancer data from TGCA as independent verification data (TCGA data set), and 319 cases were determined as non-hypermutated according to the same standard type colorectal cancer. Further, the present invention requires patient data with a...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3 Application of 5-gene prognostic prediction model to analyze postoperative recurrence and metastasis of nodal non-hypermutated rectal cancer
[0040] Since the main cause of death of tumor patients is recurrence and metastasis, and the main factor affecting prognosis is also recurrence and metastasis, so the present invention analyzes the correlation between the mutation status of 5 genes and recurrence and metastasis. In order to exclude the influence of residual tumor factors on the patient's prognosis, the present invention selects colorectal cancer patients whose tumors have been completely resected. According to the mutation characteristics of the 5 genes, patients are divided into mutant type and wild type, and survival analysis and comparison of disease-free survival time can prove that the recurrence risk of mutant type patients is significantly higher than that of wild type patients, with a hazard ratio of 2.01 (95% confidence interval =1.33‐3.04, P F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com