Functional biomaterial for inducing tissue regeneration after craniocerebral injury and application thereof
A technology for tissue regeneration and functional materials, applied in the fields of applications, biochemical equipment and methods, growth factors/growth regulators, etc., which can solve the problems of difficulty in maintaining VEGF, maintaining effective concentration, and rapid diffusion of soluble VEGF with a short half-life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0098] Embodiment 1, the preparation of collagen gel
[0099] 1. Take the isolated bovine tendon tissue from which fat and muscle have been removed.
[0100] 2. Take the tissue obtained in step 1 and follow the steps below:
[0101] (1) Soak in 1M NaCl aqueous solution for 24 hours, then wash with deionized water 5 times, 3 hours each time.
[0102] (2) Soak in PBS buffer solution containing 50U / ml DNaseI for 3 hours, then wash with deionized water 5 times, 3 hours each time.
[0103] (3) Soak in 1M KOH aqueous solution for 20 minutes, then wash with deionized water 10 times, 30 minutes each time.
[0104] (4) Dissolve in 0.5M acetic acid aqueous solution for 48 hours, centrifuge at 12000 g for 20 minutes to remove the precipitate, and take the supernatant.
[0105] (5) The supernatant was dialyzed with a dialysis bag, and the external liquid was deionized water, and dialyzed to neutrality to obtain a collagen gel.
[0106] Scanning electron micrographs of collagen gels as...
Embodiment 2
[0107] Embodiment 2, growth factor preparation
[0108] 1. The small fragment between the XbaI and XhoI restriction sites of the pET-28a(+) vector was replaced with the DNA molecule shown in the 1st-552th position of Sequence 1 in the sequence listing to obtain the recombinant plasmid pET28a-CBD-VEGF. The exogenously inserted DNA molecule is fused with part of the nucleotides on the carrier backbone to form a fusion gene shown in sequence 1 of the sequence listing, which encodes a fusion protein shown in sequence 2 of the sequence listing.
[0109] In sequence 2 of the sequence listing, amino acid residues 1-166 from the N-terminal are VEGF segments, amino acid residues 178-184 are CBD segments, and amino acid residues 187-192 are histidine tags.
[0110] In Sequence 1 of the sequence listing, nucleotides 1-498 from the 5' end are the coding gene of the VEGF segment, nucleotides 532-552 are the gene coding for the CBD segment, and nucleotides 559-576 are Acid is the coding se...
Embodiment 3
[0130] Embodiment 3, the preparation of collagen gel repair material
[0131] Prepare the following collagen gel repair materials:
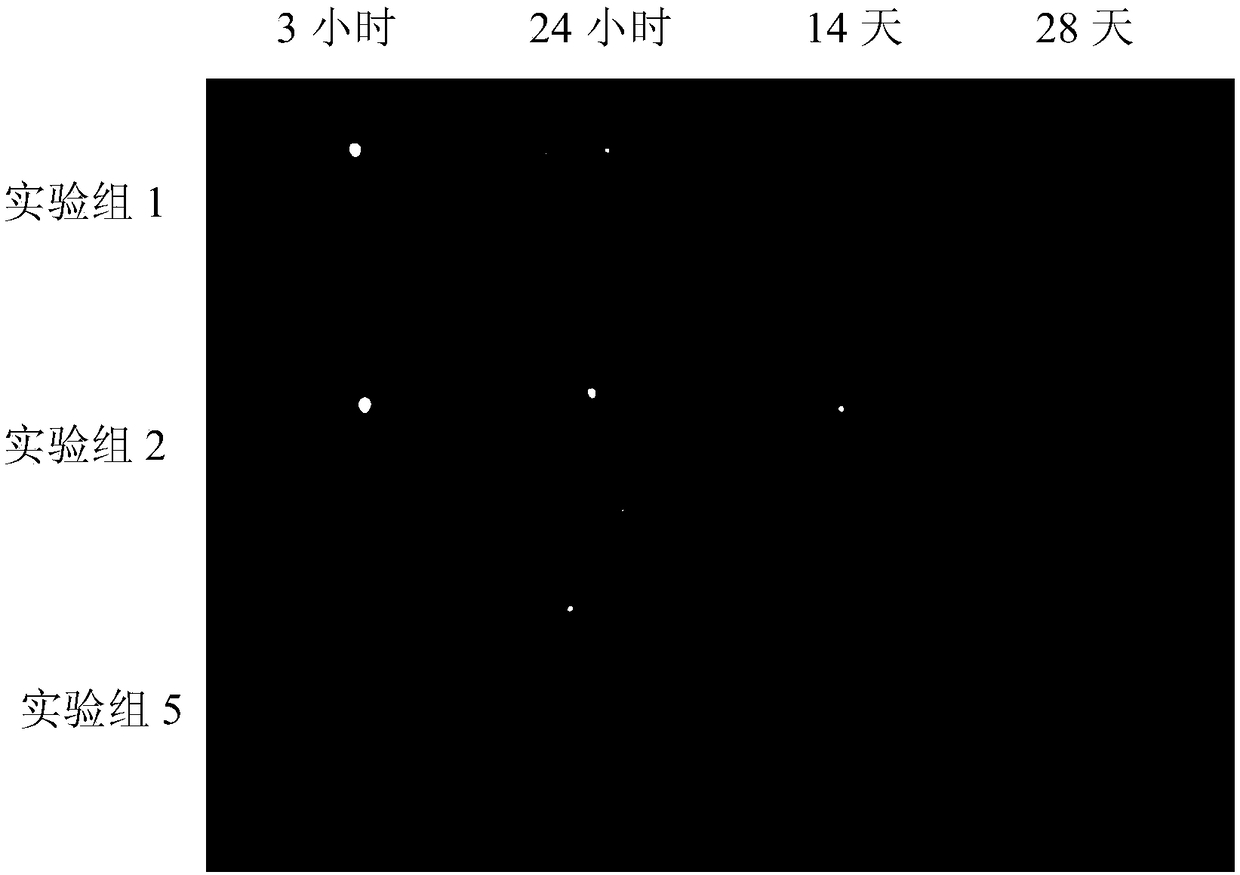
[0132] 1, 125 I-NAT-VEGF collagen gel repair material: 10 μL of Na prepared in Example 2 125 I-labeled NAT-VEGF protein solution (protein content: 0.5 nmol) was mixed with 190 μL of the collagen gel prepared in Example 1.
[0133] 2, 125 I-CBD-VEGF collagen gel repair material: 10 μL of Na prepared in Example 2 125 The I-labeled CBD-VEGF protein solution (protein content: 0.5 nmol) was mixed with 190 μL of the collagen gel prepared in Example 1.
[0134] 3. NAT-VEGF collagen gel repair material: 10 μL of the unlabeled NAT-VEGF protein solution (protein content: 0.5 nmol) prepared in Example 2 was mixed with 190 μL of the collagen gel prepared in Example 1.
[0135] 4. CBD-VEGF collagen gel repair material: Mix 10 μL of the unlabeled CBD-VEGF protein solution (protein content: 0.5 nmol) prepared in Example 2 with 190 μL of the collagen gel pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com