Wireless sensor network coverage optimization algorithm based on Dijkstra method
A wireless sensor and optimization algorithm technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of high complexity and low search ability of high-dimensional optimization space, and achieve the effects of saving energy consumption, shortening communication distance, and prolonging the life of the network
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
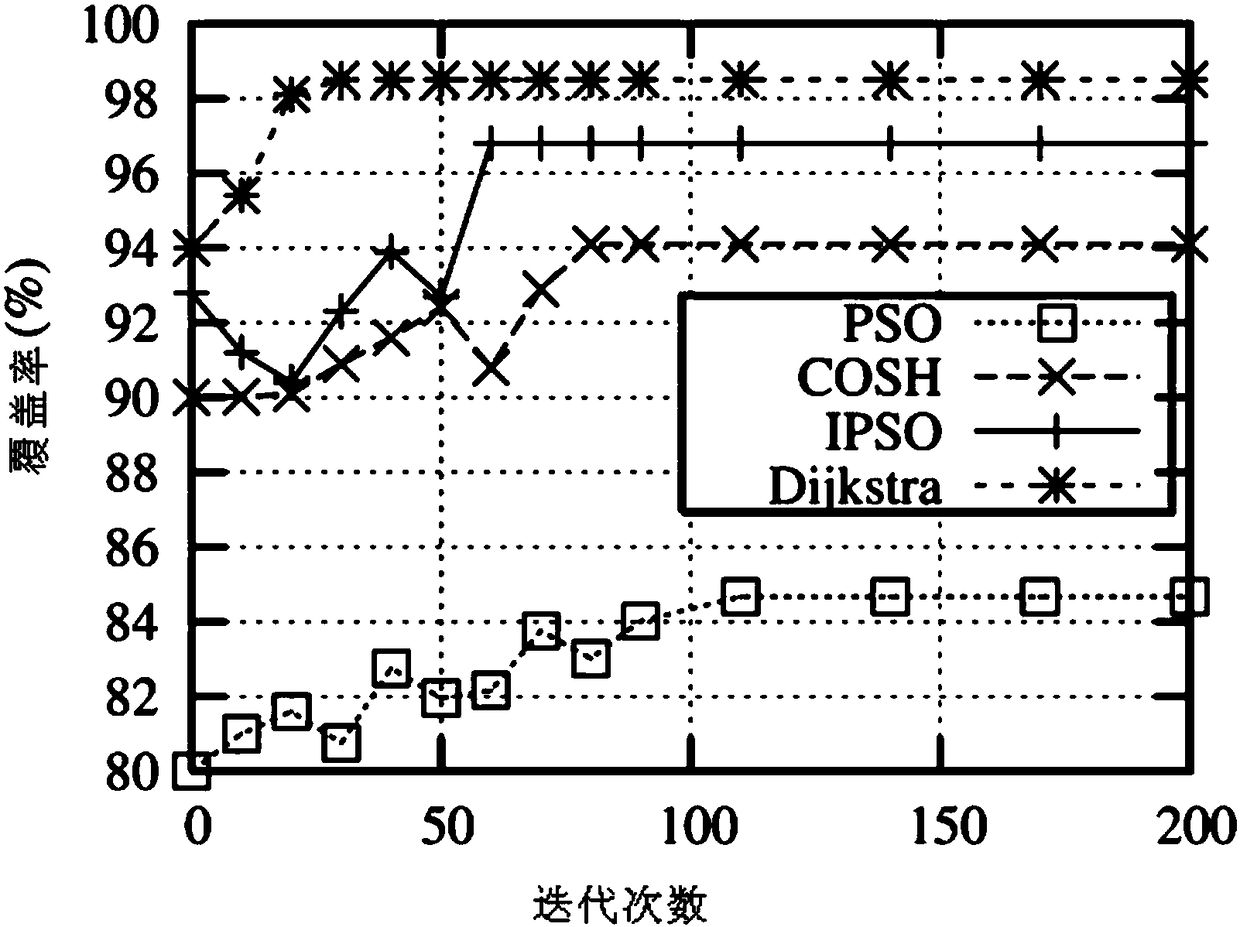
[0040] A wireless sensor network coverage optimization algorithm based on the Dijkstra method, which improves the energy transfer model by calculating the energy loss between nodes, and takes the energy constraints and channel selection of the sensor network as constraints. Using the Dijkstra algorithm (Dijkstra) in graph theory to transform the global optimum into the optimum between nodes, and transform the existing network layered architecture problem into sub-problems corresponding to each layer of the network layered architecture, Reflect the impact of energy and channel on the design of wireless sensor networks to achieve optimal coverage.
[0041] Assuming that n wireless sensor nodes are randomly generated in the target area, the set {1,2,...,n} formed is represented by graph G, and the edges formed by nodes and nodes (denoted as e ij ) with weight w ij ;
[0042] The optimization algorithm steps are as follows:
[0043] S1: Select the initial node First, determin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com