Radar target recognition method based on micro-Doppler feature extraction and deep learning
A deep learning and radar target technology, applied in the field of radar target recognition, can solve the problems of inability to represent complex functions, limited processing capacity, low time-frequency resolution, etc., to suppress cross-term components, solve time-consuming and labor-intensive, and high recognition accuracy. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] The following will clearly and completely describe the technical solutions in the embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings in the embodiments of the present invention. Obviously, the described embodiments are only some, not all, embodiments of the present invention. Based on the embodiments of the present invention, all other embodiments obtained by persons of ordinary skill in the art without creative efforts fall within the protection scope of the present invention.
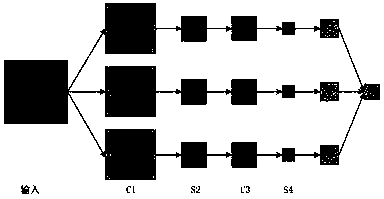
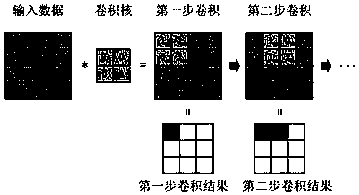
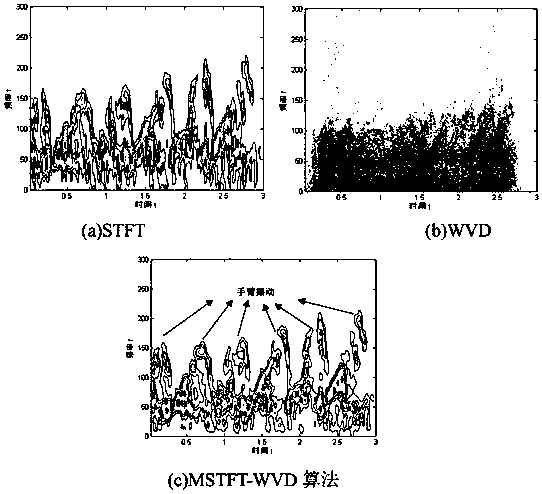
[0051] The present invention mainly takes different motion states of pedestrians as an example to identify, and the technology used can be easily transplanted to the identification of other types of radar targets. The whole process can be divided into two stages: radar target micro-Doppler feature extraction, target recognition based on micro-Doppler features and deep learning.
[0052] A radar target recognition method based on micro-Doppler feature extraction and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com