Use of granulocyte type myeloid derived suppressor cell as diagnostic biomarker
A biomarker and cell-inhibiting technology, which is applied in the field of medical testing, can solve problems such as the absence of molecular biological indicators, achieve significant technological progress, avoid over-treatment, and improve survival rates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
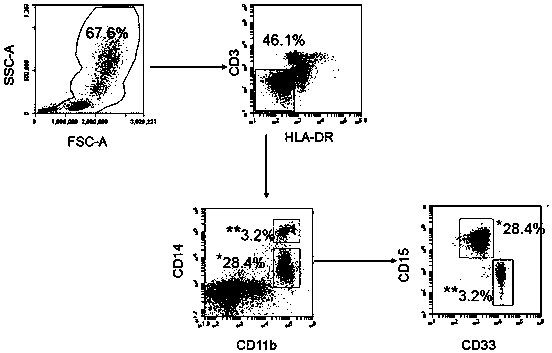
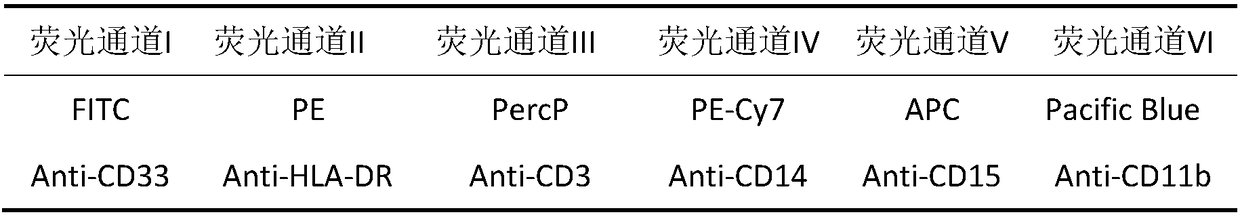
[0014] 1.1 Preparation of peripheral mononuclear cell suspension (Periphera lblood mononuclear cell, PBMC)
[0015] Isolation of human peripheral mononuclear cells (PMBCs) is a fundamental procedure in immunology research. Currently, the commonly used methods for separating PBMCs are Ficoll density gradient centrifugation and Percoll density gradient centrifugation. In this experiment, we used Ficoll density gradient centrifugation, which can separate PBMCs simply, quickly and efficiently. The principle of separation is that there is a density difference between PBMC and other components such as red blood cells, platelets, and plasma in the blood. When an isotonic mixed solution is used for density gradient centrifugation, it will re-aggregate and stratify into four layers. The uppermost layer is plasma and platelets, the middle layer is lymphocyte separation fluid, the lowermost layer is red blood cells and granulocytes, and there is a white, opaque cloudy layer on the middl...
Embodiment 2
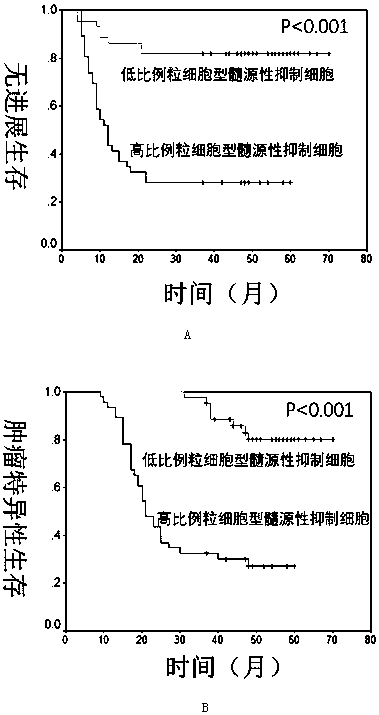
[0038] Example 2 A high proportion of G-MDSC is associated with NAC drug resistance and affects postoperative survival
[0039] Using SPSS, the effect of G-MDSCs on progression-free survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for bladder cancer was analyzed by Kaplan Meier univariate analysis. A high proportion of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells is associated with chemotherapy resistance, and a high proportion of patients has a progression-free survival time after surgery obviously decased( figure 2 A).
[0040] Using SPSS, the effect of G-MDSCs on tumor-specific survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for bladder cancer was analyzed by Kaplan Meier univariate analysis. A high proportion of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells is associated with chemotherapy resistance, and a high proportion of patients is tumor-specific after surgery. Significantly reduced survival time ( figure 2 B).
Embodiment 3
[0042] G-MDSC in the tumor microenvironment has a considerable relationship with neoadjuvant chemotherapy resistance. During the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer, the median value of the above G-MDSC ratio is used as the cutoff point (cutoff value). Values greater than the median were defined as high expression, and values below the median were defined as low expression. For the median value of G-MDSCs ratio of 20.2% (2.1–45.6%), 6 patients in the high G-MDSCs group had pathological remission after chemotherapy, while 26 patients in the low G-MDSCs group had pathological remission, and there was a significant difference between the two ( P<0.001). There were 12 cases of pathological remission in patients with high M-MDSCs and 20 cases in patients with low M-MDSCs. There was no significant difference between them (P=0.078). If the patient's G-MDSC ratio is less than 20%, neoadjuvant chemotherapy can be performed first, and then radical cystectomy, which will hel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com