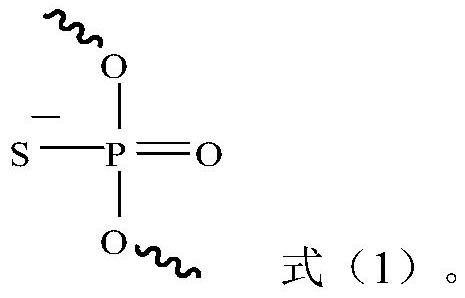
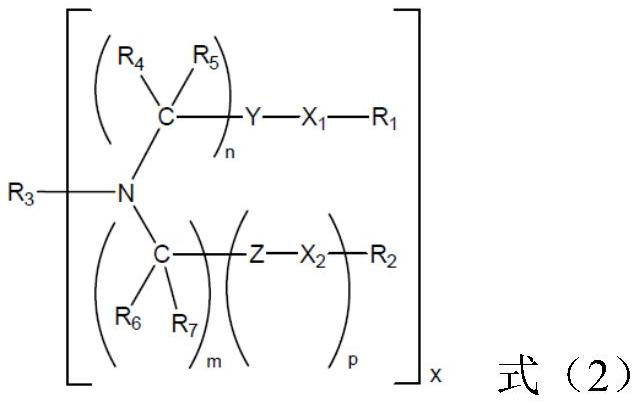
A kind of small interfering nucleic acid and pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
A composition and drug technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of being easily degraded by nucleases, poor stability of siRNA, differences between target nucleic acid species, etc., and achieve the effect of preventing and/or treating dyslipidemia and inhibiting content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
[0106] The sequence of siRNA is shown in Table 2, and the positive-sense strand nucleotide sequence numbered as siAP-1 is shown in SEQ ID NO.6, wherein the 1-19 nucleotide sequence is as shown in the human APOC3mRNA sequence (NM_000040.1) The target nucleic acid shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is identical; the antisense strand nucleotide sequence of the siRNA is shown in SEQ ID NO.7, wherein the 1-19 nucleotide sequence is the same as that of SEQ ID NO.1 in Table 1 The indicated target nucleic acids are complementary. The positive-sense strand nucleotide sequence numbered as siAP-2 is shown in SEQ ID NO.8, wherein the 1-19 nucleotide sequence is identical to the target nucleic acid shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in the APOC3 mRNA sequence; the siRNA The nucleotide sequence of the antisense strand is shown in SEQ ID NO.9, wherein the nucleotide sequence at positions 1-19 is complementary to the target nucleic acid shown in SEQ ID NO.2 in Table 1. The positive-sense strand nucleotide sequence numb...
Embodiment 1
[0114] This example is used to detect the inhibitory rate of the siRNA obtained in Preparation Example 1 on the expression level of APOC3 mRNA in vitro.
[0115] The human liver cancer cell line Huh7 was inoculated in 24-well plates with DMEM complete medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum at a seeding density of 4×10 5 Cells / well, 0.5mL culture medium per well, culture overnight at 37°C.
[0116] Aspirate the cell culture medium in the 24-well plate, and add 0.5 mL Opti-MEM serum-free medium to each well. Dilute 1.5 μL of the siRNA with a concentration of 20 μM in Preparation Example 1 with 50 μL of Opti-MEM serum-free medium; dilute 1 μL of Lipofectamine TM 2000 (Invitrogen Company) was diluted in 50 μL Opti-MEM serum-free medium, incubated at room temperature for 5 minutes after mixing; mixed diluted siRNA and diluted Lipofectamine TM 2000, mix gently, and let stand at room temperature for 20 minutes to allow complex formation. Add the above final mixed solution at 10...
preparation example 2
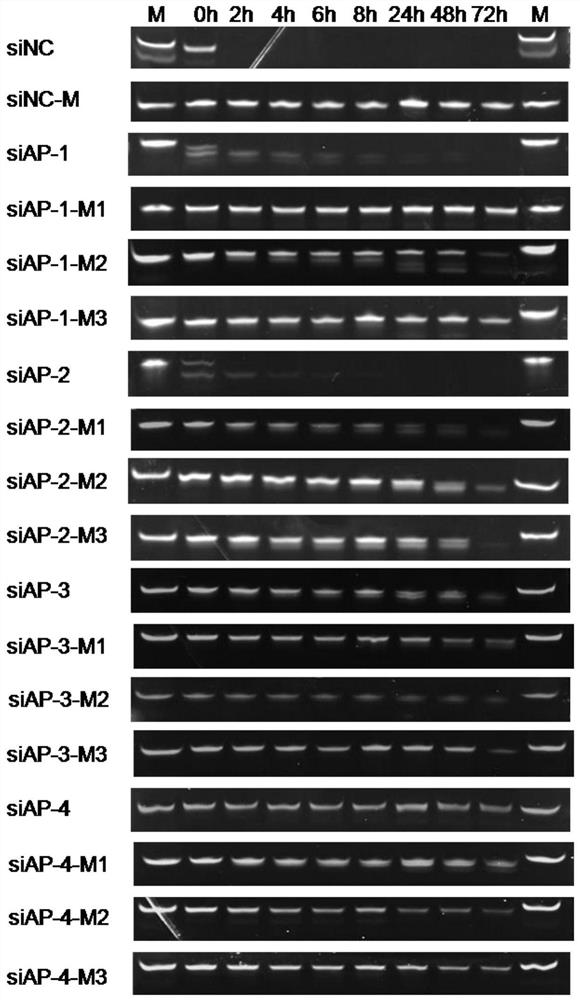
[0125] The siRNA obtained after the chemical modification of the sense and antisense strands of siRNA numbered siNC is shown in Table 5, and the number is siNC-M; the three groups of siRNAs obtained after the chemical modification of the sense and antisense strands of siRNAs numbered siAP-1 As shown in Table 5, they are respectively numbered siAP-1-M1, siAP-1-M2, and siAP-1-M3. The three groups of siRNA obtained after chemically modifying the siRNA sense strand and antisense strand numbered siAP-2 are shown in Table 5 and numbered siAP-2-M1, siAP-2-M2, and siAP-2-M3 respectively. The three groups of siRNA obtained after chemically modifying the siRNA sense strand and antisense strand numbered siAP-3 are shown in Table 5, and are numbered siAP-3-M1, siAP-3-M2, and siAP-3-M3 respectively. The three groups of siRNA obtained after chemical modification of the siRNA sense strand and antisense strand numbered siAP-4 are shown in Table 5 and numbered siAP-4-M1, siAP-4-M2, and siAP-4-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com