A low-temperature curing agent for cement-based grouting materials for deep-water underwater concrete structures
A technology for concrete structures and grouting materials, applied in the field of low-temperature curing agents, can solve the problems of accelerating the strength development of grouting materials, difficult to ensure fluidity, long conveying pipelines, etc., so as to improve grouting, improve crack plugging efficiency, and improve the effect. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
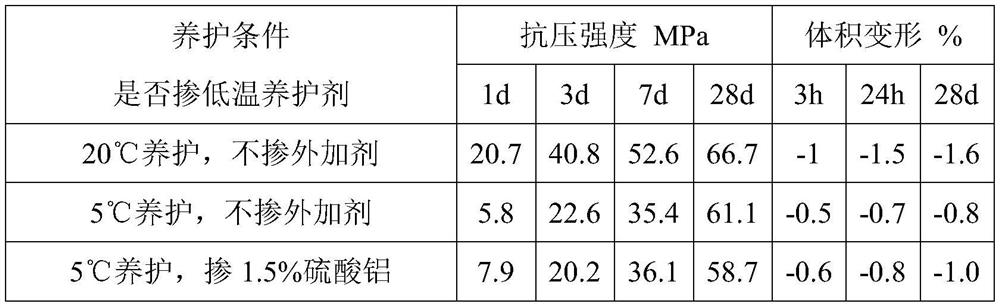
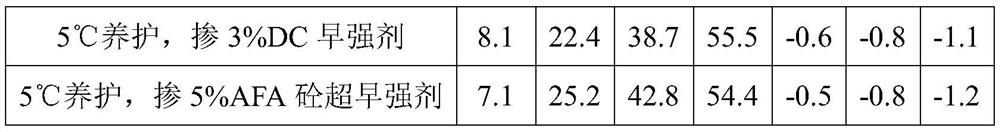
[0021] In this embodiment, commonly used early strength agents in the market are aluminum sulfate, DC early strength agent of Beijing Dechang Weiye Construction Engineering Technology Co., Ltd., and calcium formate of Suzhou Longlong Chemical Technology Co., Ltd., all of which are mixed by external mixing method. First, mix the early strength agent into the cementitious material and dry mix it evenly, then add water and sand and mix it into shape. The water-cement ratio of the prepared slurry is 0.45. Immediately after molding, put the mold into a low-temperature curing box at 5±1°C and a standard curing box at 20±1°C for curing until the specified age, and then take it out to test the compressive strength. Under this example, the strength test results are shown in Table 1 below. When several early strength agents were added, the early strength increased significantly compared with the slurry without additives at a low temperature of 5°C, but there was still a large gap with t...
Embodiment 2
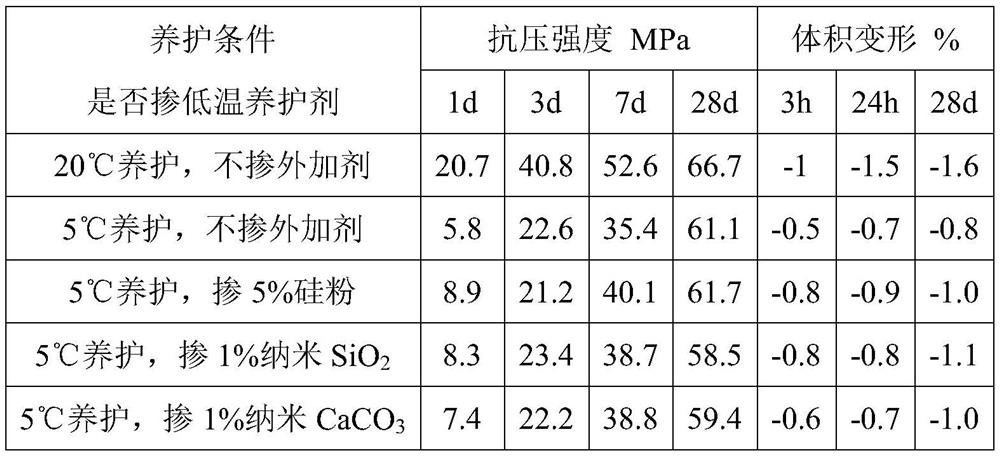
[0026] This embodiment uses crystal nucleus materials alone, including silicon powder, nano-SiO 2 , Nano CaCO 3 etc., using the external mixing method to mix, first mix the crystal nucleus material into the cementitious material and dry mix it evenly, then add water and mix it into shape. The water-cement ratio of the prepared slurry is 0.45. Immediately after molding, put the mold into a low-temperature curing box at 5±1°C and a standard curing box at 20±1°C for curing until the specified age, and then take it out to test the compressive strength. Under this example, the strength test results are shown in Table 2 below. After being mixed with crystal nucleus materials, the strength of 1-3 days is also significantly improved, and the improvement range is slightly lower than that of ordinary early strength agents, and it cannot be compared with that under the standard curing condition of 20°C; crystal nucleus materials will also increase volume shrinkage .
[0027] Table 2 E...
Embodiment 3
[0030] In this embodiment, the expansion agent is selected from gypsum and calcium oxide expansion agents, and the dosage is 10% of the total amount of the cementitious material. Water is stirred into shape. The water-cement ratio of the prepared slurry is 0.45. Immediately after molding, put the mold into a low-temperature curing box at 5±1°C and a standard curing box at 20±1°C for curing until the specified age, and then take it out to test the compressive strength. Under this example, the strength test results are shown in Table 3 below. The expansion agent material has no obvious effect on the early strength. The expansion agent material can reduce part of the volume shrinkage, but the overall performance is still shrinkage deformation, because the time for the expansion agent to work cannot match the shrinkage of the slurry.
[0031] Table 3 Embodiment 3 Effect
[0032]
[0033]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com