Pig genome molecular marker excavation method based on combination of LINE1 transposon and microsatellite primer
A LINE1 and molecular marker technology, applied in the fields of molecular biology and bioinformatics, can solve the problems of slow template response, cumbersome, difficult gene fine positioning, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
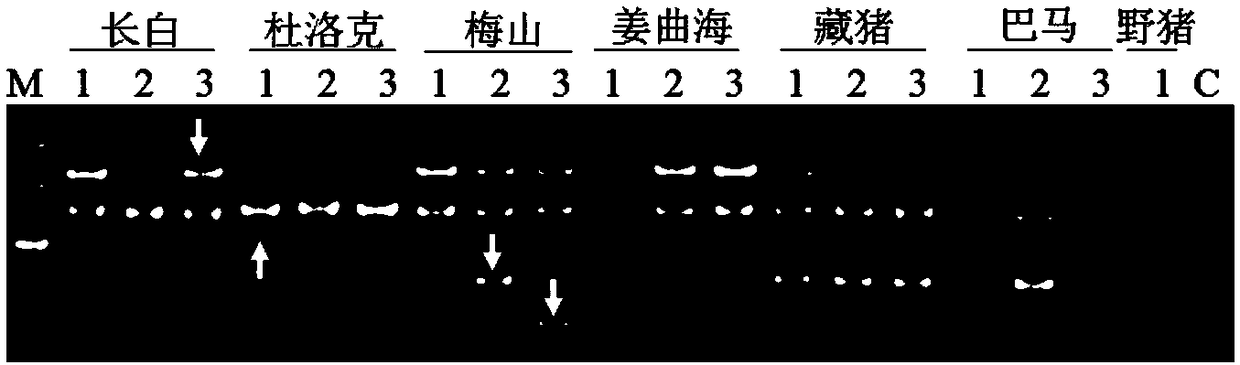
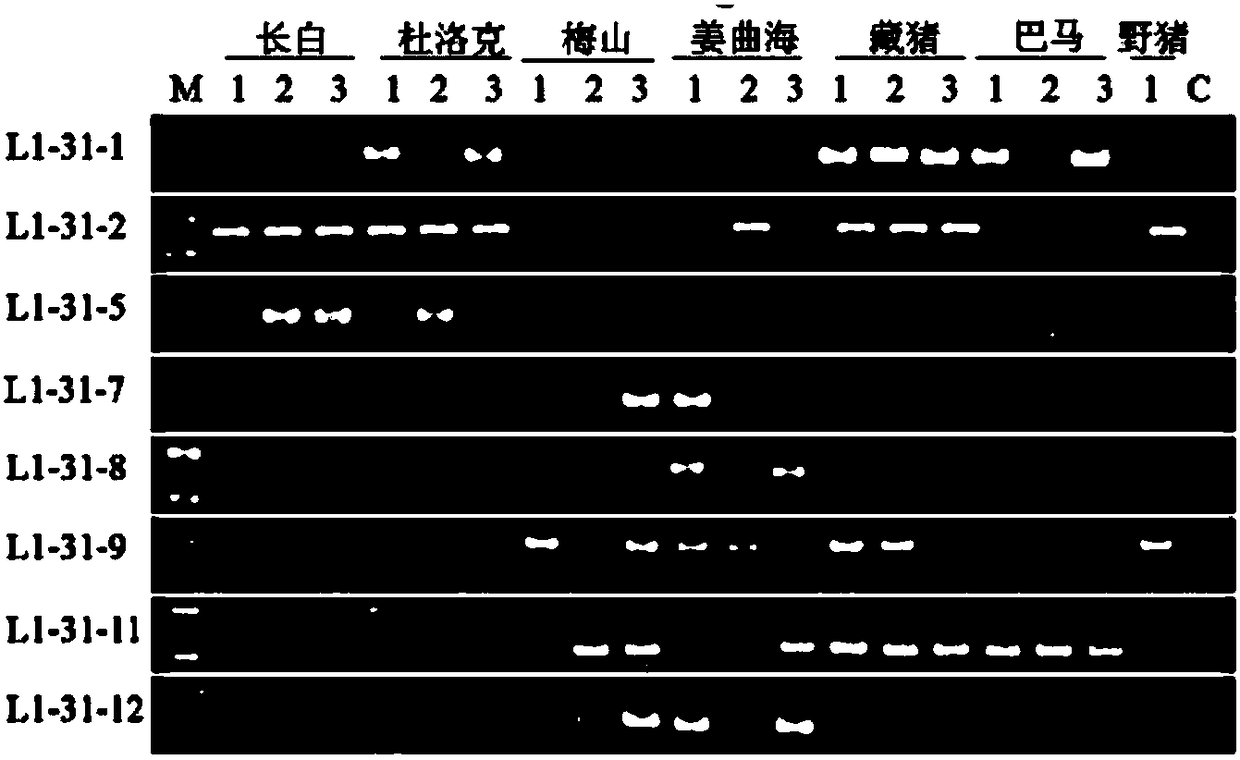
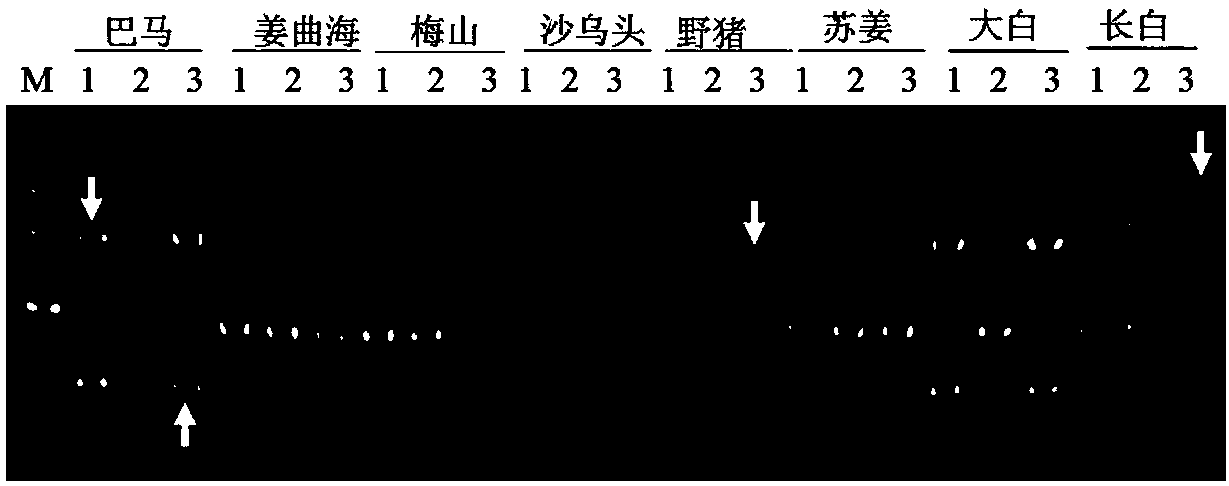
[0094] Example 1 Design of 14 flanking specific primers based on 14 unique sequences. The primers are located at the genomic flanking sequence of the LINE1 insertion site, combined with Primer L1-3'UTR. Example 2 Design of 3 flanking specific primers based on 3 unique sequences. The primers are located at the genomic flanking sequence of the LINE1 insertion site, combined with Primer L1-5'UTR.
[0095] 5. Detection of molecular markers in different species
[0096] 1. Genome preparation:
[0097] (1) Example 1 selects 7 breeds (Landrace pig, Large White pig, Duroc pig, Meishan pig, Jiangquhai pig, Bamaxiang pig, Tibetan pig), several samples of each breed except one sample of Tibetan pig. Example 2 selects 8 varieties (Bamaxiang pig, Jiangquhai, Meishan, Shawutou, wild boar, Sujiang, Dabai, Changbai), and each individual has three samples. Ear tissues were collected, and the respective genomes were extracted with TIANamp Genomic DNAKit. The main steps are as follows:
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com