Drug-resistance cell system for lung cancer and preparation method thereof
A technology for drug-resistant cells and lung cancer cells, which can be applied to tumors/cancer cells, biochemical equipment and methods, animal cells, etc., can solve problems such as drug resistance in patients with lung cancer, and achieve easy industrial preparation, volume increase, and invasion. Ability-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] After resuscitating the lung cancer cell line H1975 cells, use RPMI1640 culture medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, and incubate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator.
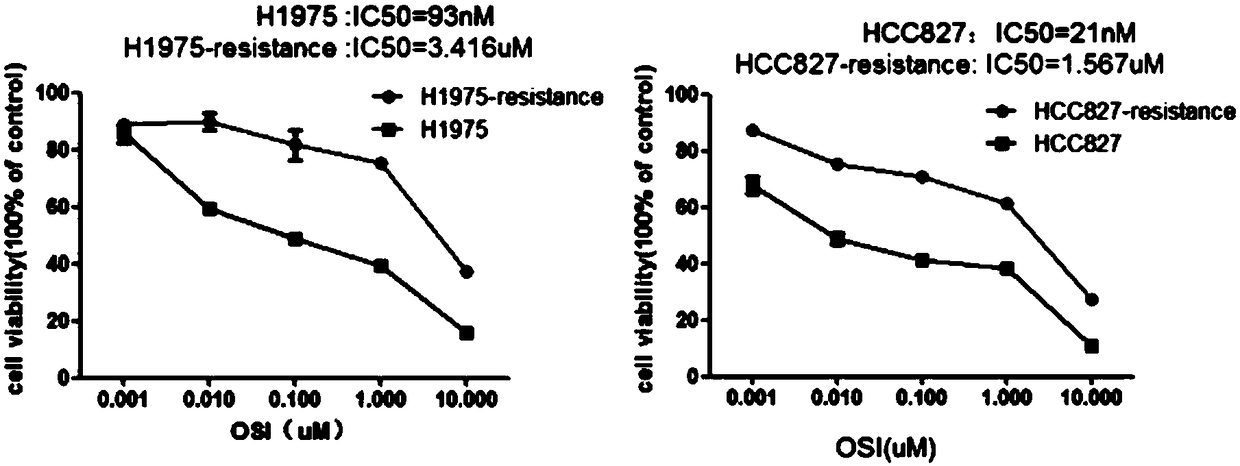
[0044] Take the H1975 cell line in the exponential growth phase 1×10 6 Cells / ml were seeded in a 6-well plate, and an appropriate amount of RPMI1640 medium containing osimertinib (AZD9291) was added, placed at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in a humidified incubator. The initial concentration of AZD9291 added was 93 nM.
[0045]Observe the condition of the cells after 72 hours of action, and when the cells return to normal growth, add the drug at the same concentration again until the cells survive and proliferate normally at this concentration, which is regarded as a culture cycle.
[0046] Continue to increase the drug concentration and carry out the next cycle. During the initial screening, increase the concentration difference by every 50nM. After 24 hours of treatment, replace the complete med...
Embodiment 2
[0051] After resuscitating the lung cancer cell line HCC827 cells, use RPMI1640 culture medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, and incubate at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator.
[0052] Take 1×10 HCC827 cell line in exponential growth phase 6 Cells / ml were seeded in a 6-well plate, and an appropriate amount of RPMI1640 medium containing osimertinib (AZD9291) was added, placed at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in a humidified incubator. The initial concentration of AZD9291 added was 21 nM.
[0053] Observe the condition of the cells after 72 hours of action, and when the cells return to normal growth, add the drug at the same concentration again until the cells survive and proliferate normally at this concentration, which is regarded as a culture cycle.
[0054] Continue to increase the drug concentration and carry out the next cycle. During the initial screening, increase the concentration difference by every 50nM. After 24 hours of treatment, replace the complete medium w...
experiment example 1
[0059] The functional experiment of the drug-resistant cell line that embodiment 1 and 2 make
[0060] (1) Changes in cell morphology
[0061] The drug-resistant cells after successful screening have morphological changes compared with non-resistant cells, such as cells becoming larger and spindle-shaped. Non-drug-resistant cells and drug-resistant cells were observed and photographed using an inverted microscope. Such as figure 1 shown. figure 1 Among them, A is H1975 normal cells; B is H1975 / RS; C is HCC827; D is HCC827 / RS.
[0062] figure 1 The results showed that the volume of the drug-resistant cell group was larger than that of the non-drug-resistant cell group, and the H1975 / RS cells showed an obvious spindle shape. The above results confirmed that the cell strains with characteristics of drug-resistant cells were successfully obtained.
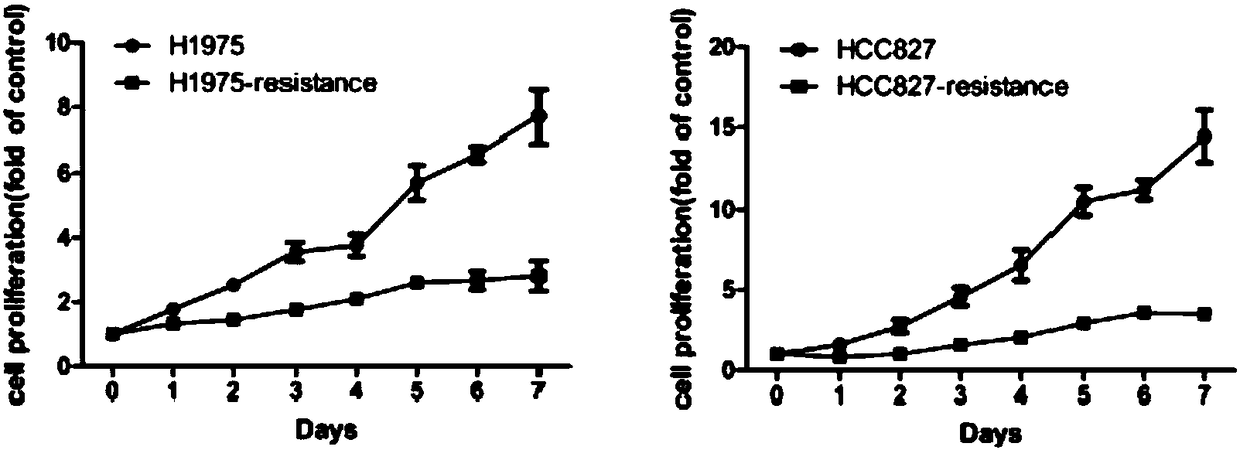
[0063] (2) Cell proliferation assay
[0064] Drug-resistant cells have the characteristics of long proliferation cycle and slo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com