Use of microRNA in exosomes for diagnosis of cerebral arterial thrombosis
A technology of ischemic stroke and exosomes, which is applied in the field of medical diagnosis, can solve the problems of insufficient patients, early and reliable assessment of the cause of stroke, and accurate measurement of personalized treatment plans, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
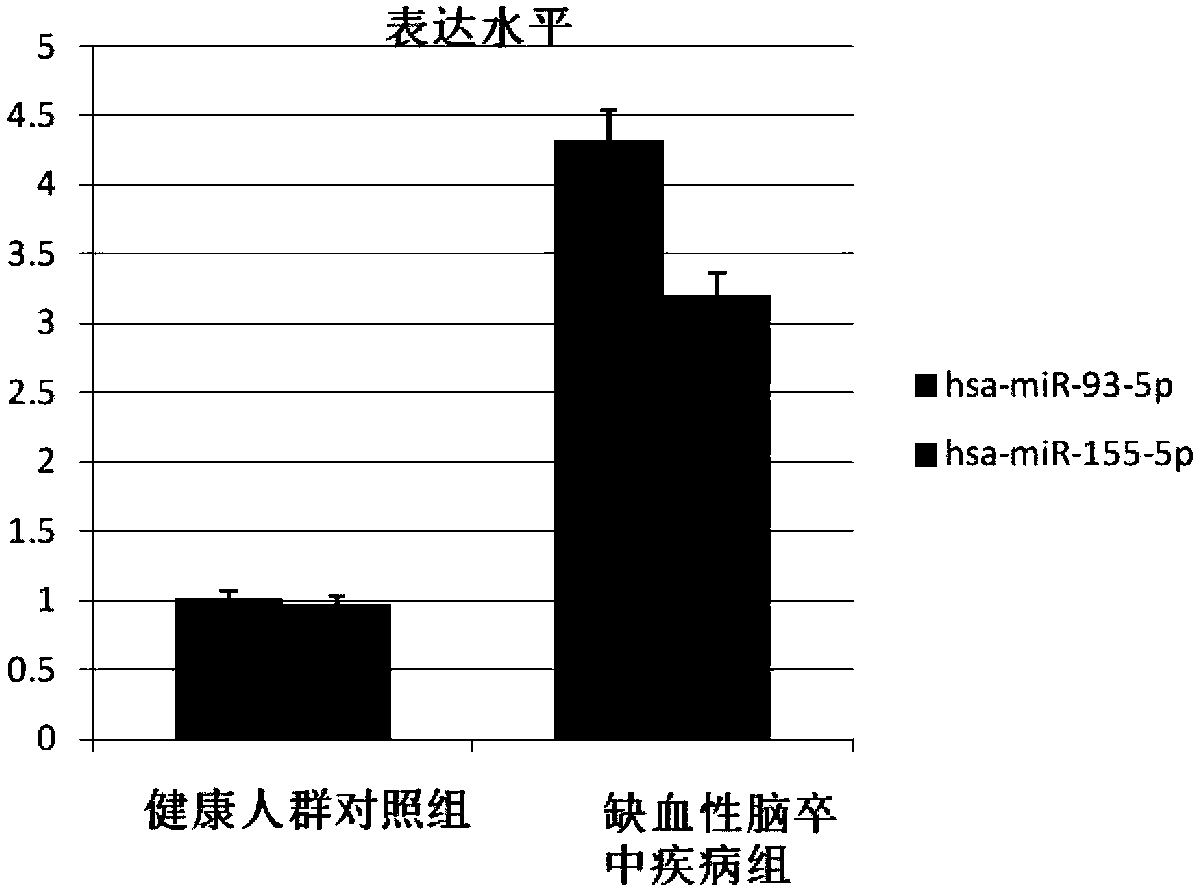
[0070] Example 1 Research Objects and Serum Collection
[0071] From January 2017 to May 2017, 40 patients with acute stroke in the Department of Neurology, Shenzhen Second People's Hospital were selected as the research group (20 males and 20 males). Among them, there were 20 cases of cardiogenic stroke and 20 cases of non-cardiogenic stroke. Aged 39 to 73 years old, with an average of (56.4±13.3) years old. All of them were confirmed by cranial CT or MRI examination and met the diagnostic criteria of stroke revised by the 4th National Cerebrovascular Disease Academic Conference. The onset time was 48-72 hours, and the median (interquartile range) of NIHSS score was 8 (8-12). In addition to malignant tumors, heart failure, blood, endocrine, metabolic or digestive system diseases, malnutrition, severe lung infection, liver and kidney insufficiency, and other diseases of the nervous system. In the same period, 30 healthy volunteers diagnosed by the physical examination cente...
Embodiment 2
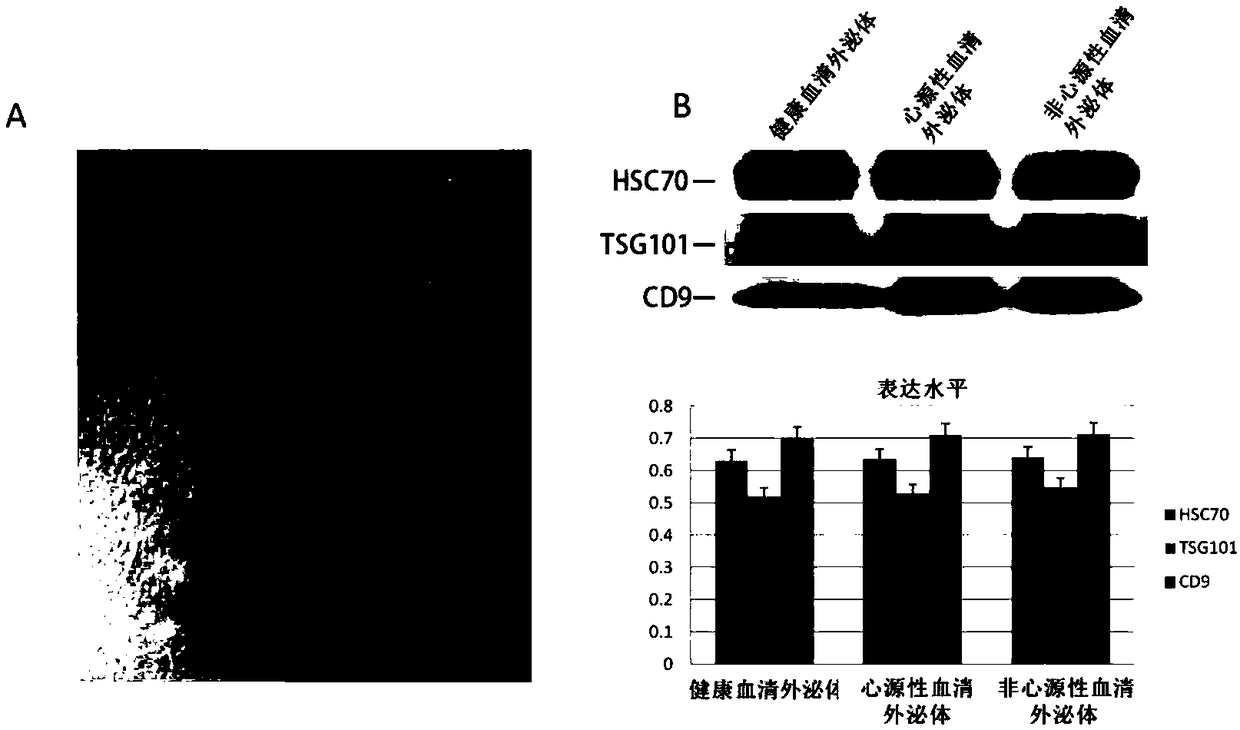
[0074] Example 2 Isolation of Serum Exosomes
[0075] (1) Exosomes in serum were isolated using the Exoquick kit from SBI (System Biosciences Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA). The serum stored at -80°C was thawed on ice and centrifuged at 3000g for 15min. Transfer the supernatant to a new EP tube, add an appropriate amount of ExoQuick solution and mix gently by inversion, react at 4°C for 30 minutes (preferably add 63 μL exoquick reagent to 250 μL serum), and centrifuge at 1500 g for 30 minutes (the exosomes sink under the tube); Aspirate the supernatant, and centrifuge at 1500g for 5 minutes to aspirate all the supernatant (do not shake the centrifuge tube); dissolve all the precipitates with 250 μL PBS, and store at -80°C for later use.
[0076] (2) Analysis of particle size and concentration of exosomes: Nanoparticle-tracking analysis (NTA) was used to analyze the number and size distribution of particles. The above pellet was resuspended with 30 μL particle-free PBS, and th...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3 Extraction of exosome RNA and determination of microRNA by real-time quantitative PCR
[0081] The total RNA of serum exosomes was extracted using mirVana (Ambion, TX, USA) kit. Bioanalyzer2100 (Agilent, CA) detected the quality and concentration of the extracted RNA. The exosomal miRNA in each group was detected by CFX96 PCR instrument (Biorad), and the detection was repeated 3 times for each sample.
[0082] (1) Obtain cDNA by reverse transcription:
[0083] 1) Extract the RNA in the exosomes of the above samples as a template, add template (50-150ng), RT primer (15-20pmol) and RNA free H to the RNase-free PCR tube 2 O to a total volume of 12 μl.
[0084] 2) Mix the above solution and incubate at 65°C for 5 minutes to open the RNA secondary structure, and then place it on ice immediately to prevent RNA renaturation from restoring the secondary structure.
[0085] 3) reverse transcription:
[0086] During the reverse transcription process, the specific r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com