Method and kit for in vitro detecting responsiveness of epithelial tumor cells to therapeutic agent
A technology for in vitro detection of tumor cells, applied in cell culture active agents, tumor/cancer cells, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as inability to quickly and effectively obtain accurate results of in vitro drug screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0091] Isolation of CTOS and conditional reprogramming in single-cell cultures
[0092] After obtaining informed consent from the patients, tumor samples and normal samples from patients undergoing colorectal cancer surgery were obtained from Beijing Cancer Hospital.
[0093] First, non-tumor tissue and necrotic tissue are carefully stripped from the tumor sample. Cut the tumor tissue and normal tissue into small pieces with a diameter of less than 1 mm with scissors. Transfer the chopped tumor tissue and normal tissue to a 100 ml sterile conical glass bottle with a magnetic stirring bar. Add 0.25U / ml Liberase DH digestive enzyme (a certain proportion of collagenase I and collagenase, with neutral non-clostripain) to the shredded tissue ) and incubate at 37°C for 1-2 hours with gentle magnetic stirring.
[0094] The partially digested tumor cell clusters were first filtered through a 100-μm filter, and the filtrate was then filtered through a 40-μm filter. Tumor cell cl...
Embodiment 2
[0099] in vitro susceptibility testing
[0100] Following initial inoculation, drug testing was performed using dissociated tumor epithelial cells in a defined selective growth medium supplemented with nicotinamide and Y27632 (Rho-related helical coil containing protein kinase (ROCK-1) inhibitor) hESC SFM (defined, serum-free and feeder-free medium (SFM).
[0101] For ex vivo drug testing, inoculated tumor cells were exposed to the drug or drug combination for 72 hours. Drugs were prepared in DMSO and the final concentration of DMSO in the medium was 0.1%. Drugs and drug combinations were tested at ten-point serial dilutions (see Image 6 and related drawings). After drug exposure, tumor epithelial cells were labeled with 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (Edu) to assess tumor cell proliferation rate. The labeling process lasted 24 hours with drug exposure. In the control group, epithelial cells did not receive drug exposure to media changes, but were similarly labeled with ...
Embodiment 3
[0105] Image Acquisition and Analysis
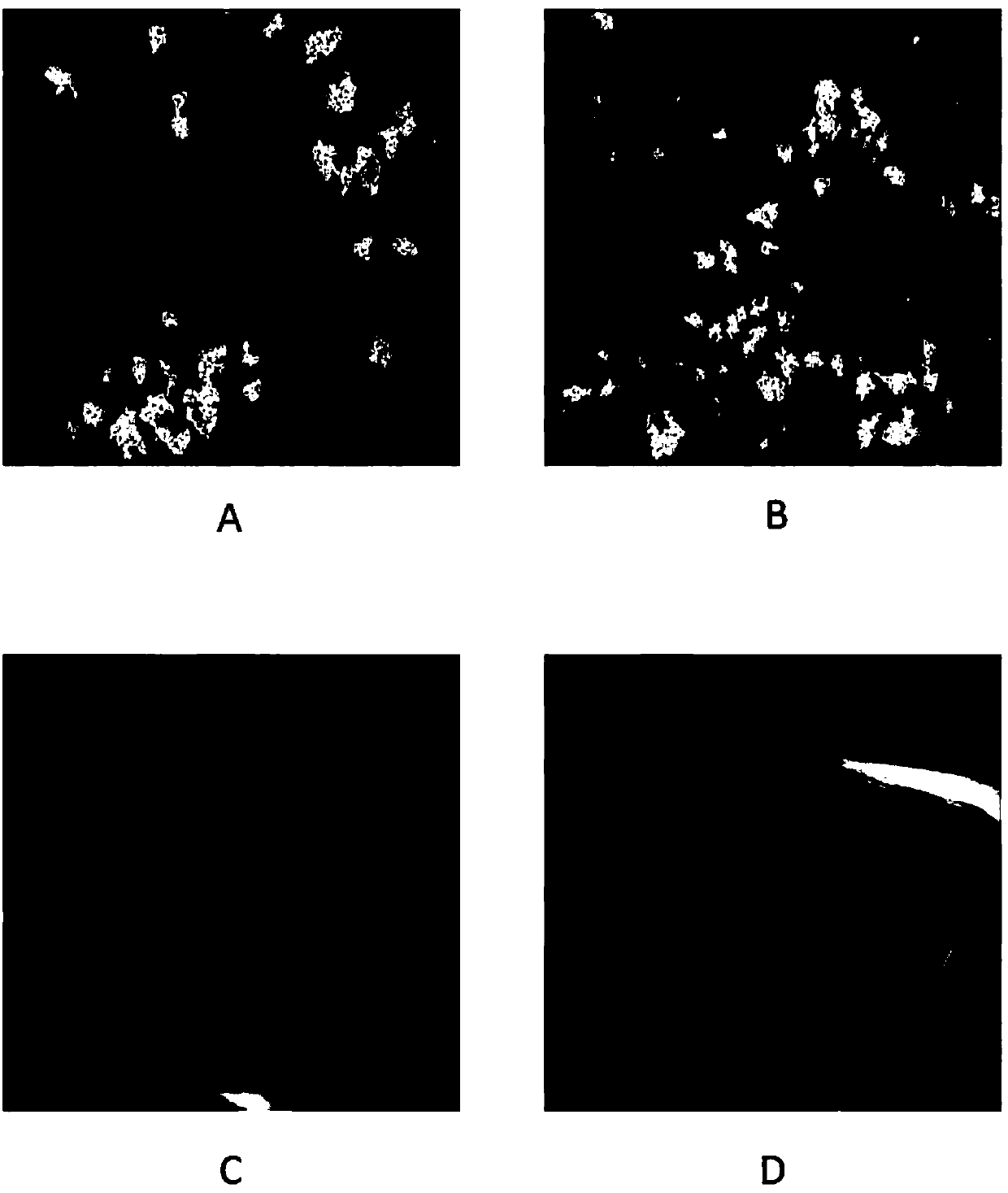
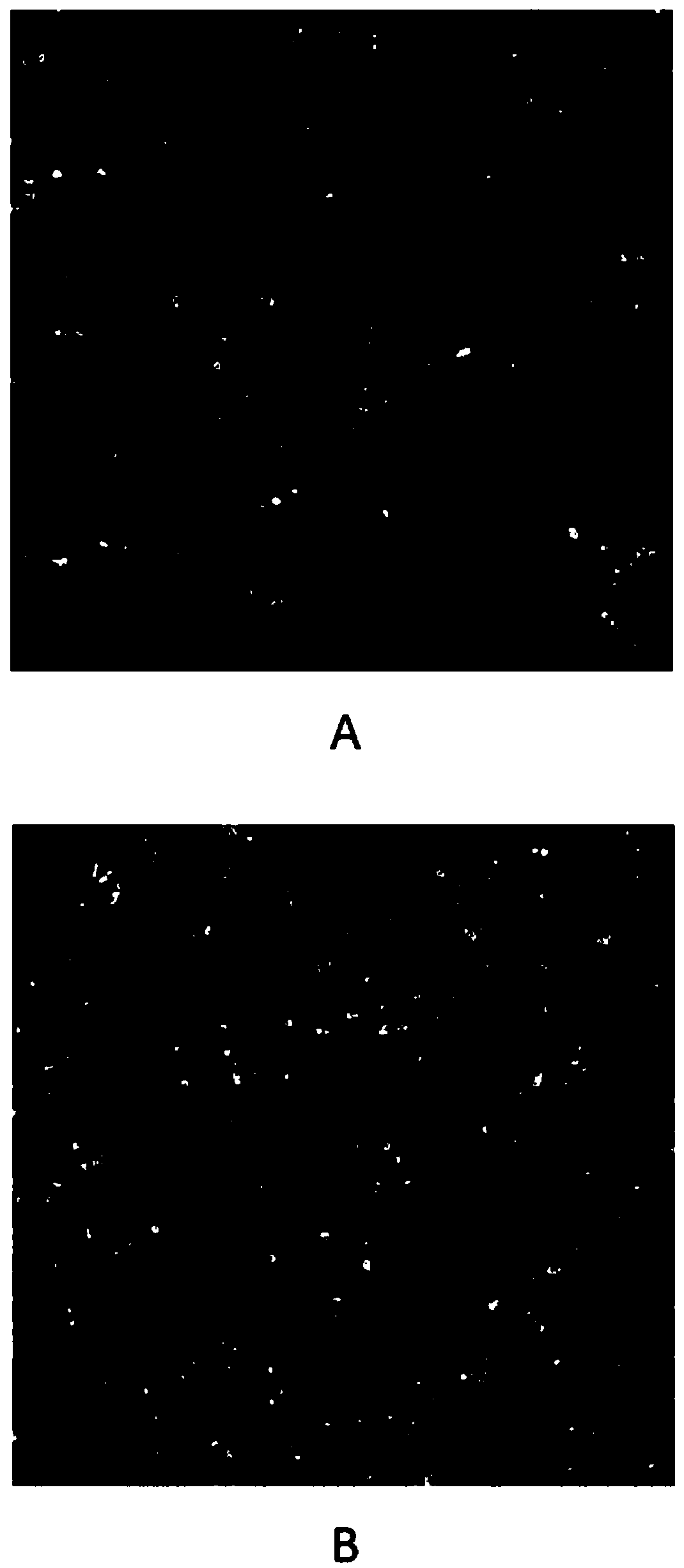
[0106] Stained tumor cells were imaged by a high-content screening (HCS) platform (Thermo Scientific Cellomics ArrayScan XTi HCSreader). Select a 10X objective lens to collect images, select 25 fields of view for each detection hole, and analyze a total of more than 3000 cells. The three fluorescent signals from the images were acquired from an HCS reader. The blue fluorescent signal records the signal of nuclei stained with Hoechst 33342; the green fluorescent signal detects Edu incorporated in newly synthesized DNA; the red fluorescent signal detects the EpCAM-positive epithelial cell population. Calculate the percentage of Edu-positive subpopulation cells in the total epithelial cells.
[0107] Such as Figures 7A-7B As shown in , for eight different patients, dose-response data were generated for Edu incorporation percentages for drugs and drug combinations, as well as quantitative drug susceptibility scores ( Figure 7B ). Da...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com