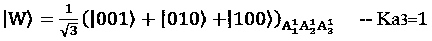Expandable multi-user-set quantum key sharing method
A technology of key sharing and quantum collection, which is applied in key distribution and can solve problems such as users not being online
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
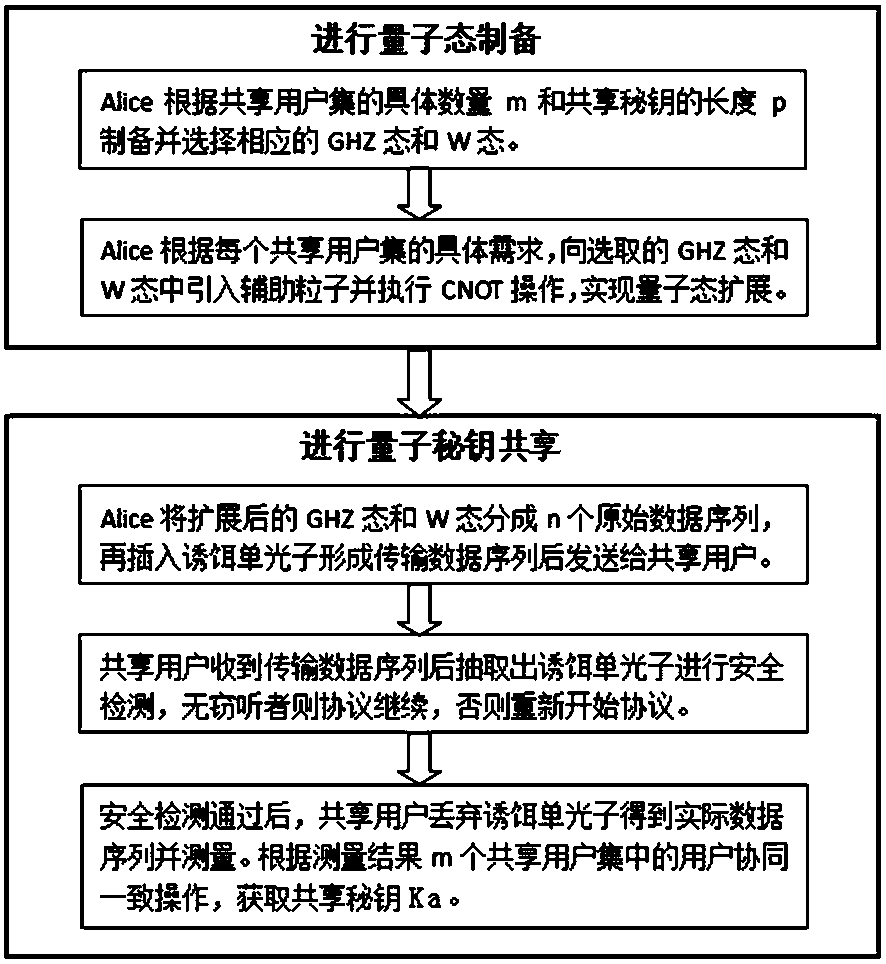
[0043] Embodiment one: see figure 1 As shown, a scalable multi-user set quantum key sharing method, Alice, the original holder of the secret key Ka, prepares the quantum state and expands it as required, and then encodes the secret key on the quantum state and sends it to the remote Users with a distance can obtain the shared secret key through joint measurement.
[0044] Step 1: Alice, the original holder of the secret key Ka, initially prepares a group of m particles of GHZ state and W state according to the specific number of shared users (assumed to be m). The initial GHZ state and W state are in the following form Shown:
[0045]
[0046]
[0047] Alice agrees with the user in advance that the m-particle GHZ state represents the binary number 0, and the m-particle W state represents the binary number 1. Alice can use the prepared GHZ state and W state to encode the secret key Ka she holds, and then share the secret key by sending the GHZ state or W state to the us...
Embodiment 2
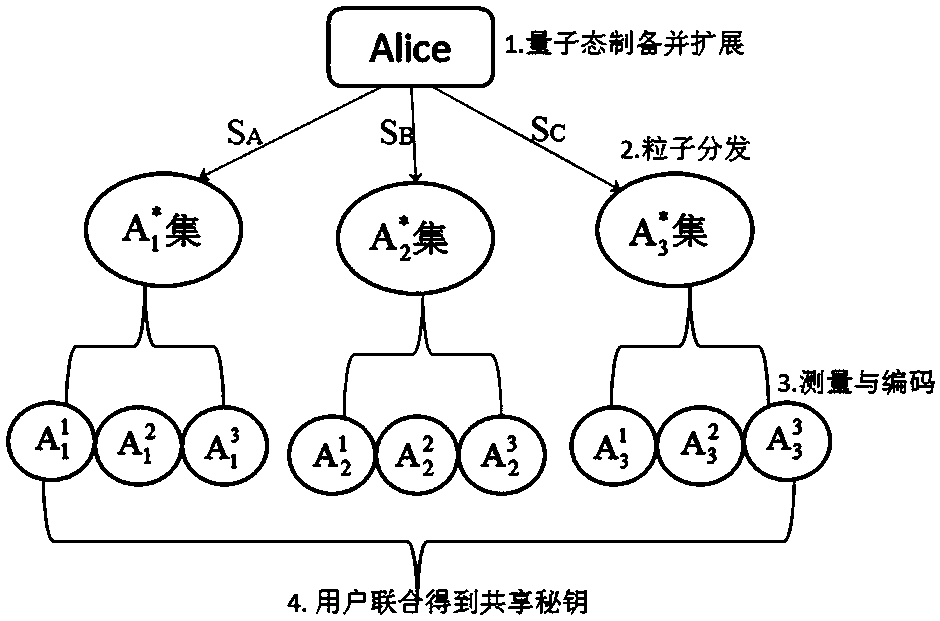
[0061] Embodiment 2: share the secret key with the channel after the three-particle GHZ state and the W state are expanded twice, and illustrate the process of the present invention (such as figure 2 shown):
[0062] Alice prepares a set of 3-particle GHZ states and W states in the form:
[0063] ,
[0064] Assuming that the shared secret key Ka=001 owned by Alice, according to the corresponding mapping relationship, the GHZ state represents the binary number 0, and the W state represents the binary number 1. Alice selects two GHZ states and one W state from the prepared quantum states as shared The channel of the secret key. As follows:
[0065]
[0066]
[0067]
[0068] At this time, each particle represents the particle held by the first user in an initial user set. In order to improve the stability of the system and increase the number of users in the user set, Alice expands the selected initial quantum state. Assuming that each user set needs 3 users, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com