Application of aminopeptidase reducing function
A technology of aminopeptidase and aminopeptidase coding, applied in the application field of enhancing the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics, can solve problems such as food pollution, fluid flow resistance, material surface corrosion, etc., to promote disintegration and weaken drug resistance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0031] According to another preferred embodiment of the present invention, said reducing the function of aminopeptidase includes reducing the extracellular secretion of aminopeptidase.
[0032] In addition to reducing the expression of aminopeptidase so as to reduce its extracellular secretion in the above way, the following methods can also be used, for example, to reduce or inhibit the function of aminopeptidase-dependent extracellular secretion signal peptide, so that aminopeptidase Losing the guidance of the extracellular secretion signal peptide or reducing the guidance function of the extracellular secretion signal, so that the amount of aminopeptidase outside the cell is greatly reduced, and the biofilm loses its dependence on its formation to hinder the formation of the biofilm or disintegrate the biofilm .
[0033] Wherein, the method for reducing or inhibiting the function of the aminopeptidase-dependent extracellular secretion signal peptide may include knockout, in...
Embodiment 1
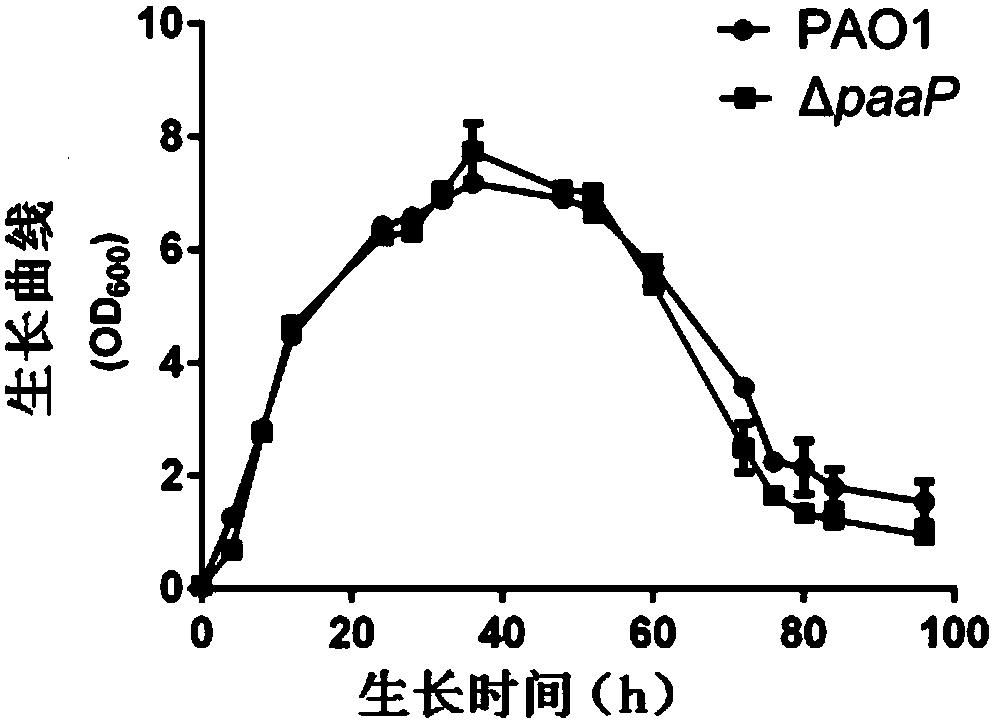
[0060] This example is used to illustrate the effect of PaAP deletion on the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
[0061] 1. Inoculate Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and PaAP deletion mutant ΔpaaP on LB solid medium plate, and culture overnight at 37°C.
[0062] 2. Pick out the single clones of PAO1 and ΔpaaP from the plate that completed step 1, inoculate them into LB liquid medium, and cultivate overnight at 37°C and 200rpm with shaking.
[0063] 3. After completing step 2, inoculate 1ml of the bacterial solution into 100ml of Jensen’s medium, culture at 37°C with shaking at 200rpm, and use a spectrophotometer to detect the absorbance of the bacterial solution at 600nm at different times. see results figure 1 .
[0064] Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the OD of PAO1 and ΔpaaP at different times 600 There was no significant difference, indicating that the deletion of PaAP had no significant effect on the growth of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Embodiment 2
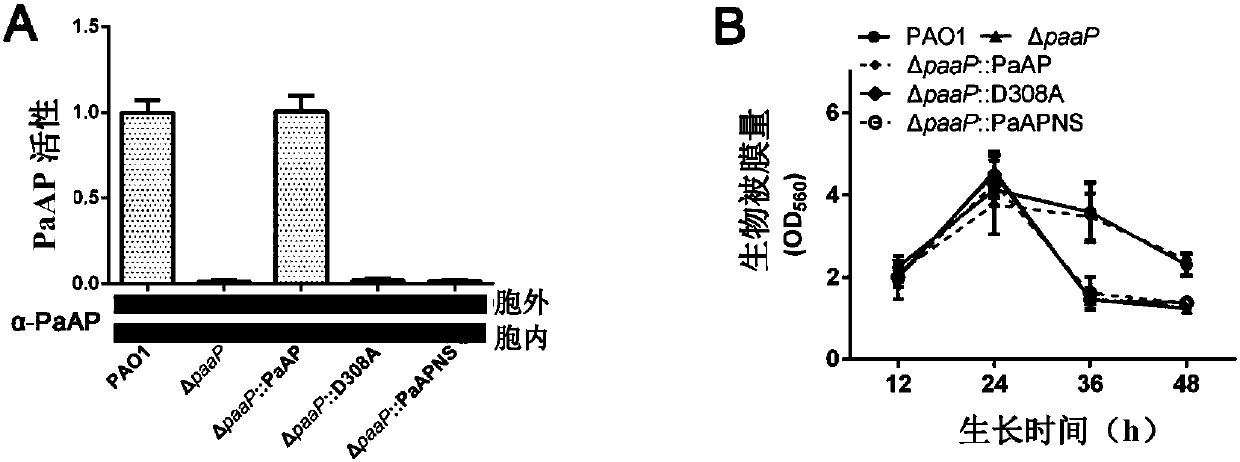
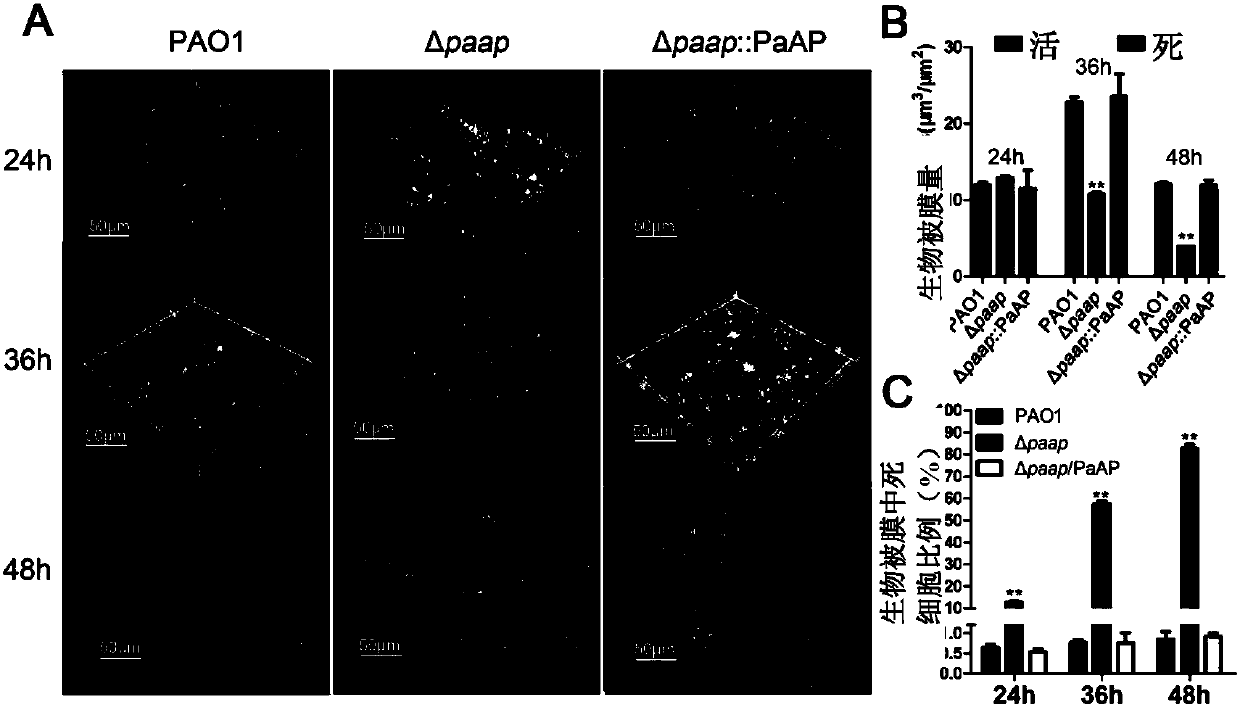
[0066] This example is used to illustrate the effect of PaAP deletion on biofilm disintegration
[0067] 1. Inoculate Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, PaAP deletion mutant ΔpaaP, PaAP complementation strain ΔpaaP::PaAP, PaAP point mutant ΔpaaP::D308A, and signal peptide-deleted PaAP mutant ΔpaaP::PaAPNS on LB solid culture Incubate overnight at 37°C on base plates.
[0068] 2. Same as 2 of Implementation Case 1.
[0069] 3. Inoculate 1 μl of the overnight bacterial solution into 100 μl of Jensen’s medium, add it to a 96-well PVC plate (Falcon3911), and culture at 30°C for 12h, 24h, 36h and 48h.
[0070] 4. The biomass of bacteria adsorbed on the 96-well plate was detected by the crystal violet method. (1) Suck away the free and loosely adsorbed bacteria with a row gun, and gently wash 3 times with normal saline. (2) Add 120 μL of 0.1% crystal violet to stain the firmly adsorbed bacterial cells in the small holes, and let stand at 30° C. for 10 minutes. (3) Take out the PVC boa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com